Managing Regulatory Compliance inside the Context of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity for personal and organizational data is essential in the emerging digital era. In response to this requirement, network penetration testing services in Indian governments and regulatory companies around the globe have enacted strict data protection laws to protect humans’ right to privacy and maintain groups accountable for information breaches and unsuitable records processing. We’ll talk about the value of regulatory compliance in Cyber Security Companies and offer recommendations on coping with the complex international statistics safety laws in this blog article.
Cybersecurity in the Regulatory Compliance Landscape
Numerous policies govern the managing, processing, and garage of facts throughout diverse industries and jurisdictions. Some of the most first-rate guidelines encompass:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enforced using the European Union, GDPR units stringent necessities for organizations managing the personal facts of EU citizens, which includes consent mechanisms, facts breach notification duties, and fines for non-compliance.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): California’s landmark privacy regulation offers customers greater manipulation over their data, requiring businesses to disclose information series practices, honor purchaser requests to decide out of data sharing, and put in force affordable security measures.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA regulates the handling of protected health records (PHI) using healthcare companies, insurers, and their commercial enterprise friends, mandating safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS establishes safety standards for companies that manage price card facts, aiming to prevent credit score card fraud and beautify price card facts protection.
The Importance of Compliance
Compliance with data safety guidelines in cybersecurity services is vital for several reasons:
- Legal Obligations: Non-compliance with regulatory necessities can bring about extreme consequences, along with fines, criminal action, and reputational harm. By adhering to policies, businesses mitigate the risk of regulatory enforcement actions and associated consequences.
- Protecting Customer Trust: Demonstrating compliance with records protection rules instills trust and confidence among customers, assuring them that their non-public records is dealt with responsibly and securely.
- Global Market Access: Compliance with policies inclusive of GDPR allows groups to conduct business the world over by ensuring adherence to records protection standards required for move-border facts transfers.
- Risk Mitigation: Compliance frameworks offer a structured method to assessing and mitigating cybersecurity dangers, supporting organizations to perceived vulnerabilities and putting in force powerful safety controls to guard in opposition to records breaches and cyber threats.
Managing Compliance Challenges
Achieving and maintaining regulatory compliance of RedTeam assessment services in UAE can be challenging because of the following factors:
- Complexity and Scope: Regulatory necessities are often complex and subject to interpretation, making compliance efforts in-depth and time-consuming.
- Evolution of Regulations: Data safety guidelines evolve over the years in response to rising threats and technological improvements, requiring organizations to stay informed and adapt their compliance strategies for that reason.
- Cross-Border Considerations: Organizations operating globally need to navigate the complexities of compliance with a couple of regulatory frameworks, each with its own set of requirements and standards.
- Resource Constraints: Small and mid-sized organizations might also lack the assets and information essential to put in force comprehensive compliance applications, posing challenges in assembly regulatory duties successfully.
Conclusion
Managing regulatory compliance inside the RedTeam assessment services in UAE requires a proactive and strategic technique. Organizations must stay abreast of evolving regulatory necessities, investigate their cybersecurity posture against compliance requirements, and put in force robust safety controls to guard statistics and mitigate risks. By prioritizing compliance, organizations can build consideration with customers, mitigate felony and economic liabilities, and demonstrate a commitment to defensive individuals’ privacy rights in a more and more digitized international. With careful plans and investment in Application Security Assessment Kerala, corporations can navigate the regulatory landscape with self-assurance and ensure the integrity and security of their facts belongings.
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting structures, networks, and information from digital assaults. With the increasing reliance on generation in almost every aspect of our lives, cybersecurity has grown to be crucial to safeguarding touchy facts and keeping the integrity of virtual infrastructure. From economic transactions to private communications, cybersecurity guarantees that statistics stay confidential, available, and unaltered.
In this digital age, cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and class, presenting great challenges for safety professionals. Traditional cybersecurity methods, even as effective to a certain extent, warfare to keep pace with the sheer extent and complexity of current threats. This is wherein Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a sport-changer.
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence approaches via machines, primarily laptop systems. It encompasses numerous subfields, which include device gaining knowledge of, natural language processing, and PC vision. In cybersecurity, AI is leveraged to analyze many records, hit upon patterns, and make informed selections autonomously.
The role of AI in cybersecurity is multifaceted and critical:
Advanced Threat Detection:AI-powered structures excel in figuring out subtle styles and anomalies within considerable datasets, allowing early detection of potential threats. By constantly mastering new records and evolving attack strategies, AI can hit upon previously unknown threats more correctly than conventional strategies.
Proactive Threat Mitigation: AI enables companies to proactively mitigate threats by identifying vulnerabilities earlier than they may be exploited. Through automatic vulnerability exams and predictive analytics, AI facilitates prioritizing security measures and allocating assets efficaciously.
Enhanced Incident Response: In the occasion of a safety incident, AI assists protection experts by offering actual-time insights, contextual facts, and actionable guidelines. This enables quicker and greater effective incident reactions, minimizing the impact of cyberattacks.
Automated Security Operations: AI-powered equipment automates ordinary safety tasks, along with network monitoring, chance looking, and malware analysis, bringing human assets to the attention of greater strategic cybersecurity initiatives. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces the danger of human error.
Adaptive Defense Mechanisms: AI permits adaptive protection mechanisms that can dynamically regulate security controls based on evolving threats and attack styles. By continuously gaining knowledge from new facts and adapting in real-time, AI enhances the resilience of cybersecurity defenses.
In summary, AI plays a critical position in improving cybersecurity talents by augmenting human know-how, automating customary duties, and enabling proactive danger detection and mitigation. As cyber threats continue to conform, the combination of AI with cybersecurity strategies becomes increasingly more fundamental, ensuring companies can efficiently guard in opposition to rising threats and protect vital assets.
Safeguarding Healthcare Navigating Cybersecurity Challenges in the Medical Industry
Introduction
Welcome to our blog devoted to exploring the critical intersection of cybersecurity and the medical industry. In today’s digital age, the importance of securing sensitive medical data and critical infrastructure can not be overstated. This blog aims to dig in into the complications, challenges, and solutions surrounding cybersecurity in the medical field.
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
As healthcare becomes increasingly digitized, the industry’s vulnerability to cyber threats rises proportionally. This digital transformation, while beneficial, also presents significant challenges in securing patient data and medical systems from vicious actors.
Challenges Faced by the Medical Industry
The medical industry faces multitudinous challenges in maintaining robust cybersecurity measures. Legacy systems, human error, and the increasing connectivity of medical devices each contribute to the complexity of the cybersecurity geography.
Strategies for Enhancing Cybersecurity in Healthcare
To address these challenges, healthcare organizations can implement the following strategies
1. Risk Assessment and Management – Regular assessments help identify vulnerabilities and prioritize security measures.
2. Data Encryption – Implement encryption protocols to protect sensitive data.
3. Access Control – Limit access to PHI to minimize the risk of unauthorized breaches.
4. Security Training and Awareness – Educate employees about cybersecurity stylish practices.
5. Collaboration and Information Sharing – Share threat intelligence and collaborate with other organizations to enhance defense.
The Road Ahead
As cyber threats evolve, the healthcare industry must remain visionary in securing patient privacy and medical systems. By adopting amulti-layered approach to cybersecurity and fostering a culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can mitigate risks and ensure patient safety
Conclusion
In this blog, we have explored the challenges and results surrounding cybersecurity in the medical industry. By staying informed and visionary, healthcare organizations can navigate these challenges and continue to provide safe and effective care to patients worldwide. Stay tuned for further insights and updates on this critical content.
Why Penetration Testing Matters:
- Penetration testing serves as a vital security check for digital systems, assessing the strength of computer networks, websites, and applications by seeking out vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit. Regular testing enables organizations to proactively identify and remedy security weaknesses before they become targets for cybercriminals. This proactive approach not only helps businesses stay ahead of evolving threats but also ensures that their systems are fortified against potential attacks, offering reassurance and peace of mind.
Types of Penetration Testing
- Different types of penetration testing target various aspects of IT infrastructure, including networks, web applications, social engineering, physical barriers, and more. Organizations can comprehensively assess their security posture and address vulnerabilities across multiple fronts by employing a combination of these testing methodologies.
Reactions After Penetration Testing:
- After a successful penetration test, organizations should promptly address identified vulnerabilities, develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, and ensure ongoing monitoring and testing to maintain robust security measures. By integrating penetration test findings into their incident response and risk management processes, organizations can effectively mitigate cyber threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Conclusion:
Penetration testing is essential for businesses of all sizes to mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively. By implementing penetration testing practices and leveraging insights gained from these tests, organizations can safeguard their systems and operations against evolving cyber threats, ensuring a secure business environment.
Identifying Critical Threats Through Penetration Testing
Automated Pentesting and red teaming are crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats. Ransomware attacks are getting faster, and companies face risks like phishing and DDoS attacks. To defend against these threats, organizations need to test their security defenses like real attackers would.
Traditionally, red teamers and Pentesters used manual methods to find weaknesses in systems. But now, automation tools like BreachLock use AI to do these tests faster and more often. This helps companies stay ahead of attackers without breaking the bank.
- Vulnerabilities in Password Security: Weak passwords are easy targets for cybercriminals to breach systems. Penetration testing identifies weak passwords and evaluates password policies and enforcement mechanisms. Organizations can strengthen their authentication processes by assessing password complexity, expiration, and reuse policies and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
- Risks Associated with Unpatched Software and Systems: Outdated software exposes systems to exploitation. Penetration testing detects vulnerabilities stemming from unpatched software and assesses patch management practices. Additionally, it evaluates the effectiveness of patch deployment processes to ensure timely updates and minimize the window of vulnerability.
- Addressing Misconfigured Security Controls: Misconfigurations in security controls, such as firewalls and routers, provide avenues for cyber attacks. Penetration testing identifies these weaknesses and assesses configuration management practices. By implementing robust configuration baselines and regular audits, organizations can enhance their security posture and prevent unauthorized access.
- Combatting Social Engineering Attacks: Psychological manipulation tactics, like phishing, exploit user identities to access sensitive information. Penetration testing evaluates susceptibility to social engineering attacks and assesses employee awareness and training programs. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, organizations can educate employees and bolster their resilience against social engineering tactics
Detecting Flaws in Application Development: Flaws in application development, including logic flaws and authentication vulnerabilities, expose systems to unauthorized access. Penetration testing assesses application security controls and evaluates secure coding practices. By identifying vulnerabilities in custom and third-party applications, organizations can remediate issues and enhance their overall security posture.
Why Penetration Testing Matters:
- Penetration testing serves as a vital security check for digital systems, assessing the strength of computer networks, websites, and applications by seeking out vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit. Regular testing enables organizations to proactively identify and remedy security weaknesses before they become targets for cybercriminals. This proactive approach not only helps businesses stay ahead of evolving threats but also ensures that their systems are fortified against potential attacks, offering reassurance and peace of mind.
Types of Penetration Testing
- Different types of penetration testing target various aspects of IT infrastructure, including networks, web applications, social engineering, physical barriers, and more. Organizations can comprehensively assess their security posture and address vulnerabilities across multiple fronts by employing a combination of these testing methodologies.
Reactions After Penetration Testing:
- After a successful penetration test, organizations should promptly address identified vulnerabilities, develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, and ensure ongoing monitoring and testing to maintain robust security measures. By integrating penetration test findings into their incident response and risk management processes, organizations can effectively mitigate cyber threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Conclusion:
Penetration testing is essential for businesses of all sizes to mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively. By implementing penetration testing practices and leveraging insights gained from these tests, organizations can safeguard their systems and operations against evolving cyber threats, ensuring a secure business environment.
Automated Pentesting and Red Teaming: An Effective Method for Enhanced Cybersecurity
Automated Pentesting and red teaming are crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats. Ransomware attacks are getting faster, and companies face risks like phishing and DDoS attacks. To defend against these threats, organizations need to test their security defenses like real attackers would.
Traditionally, red teamers and Pentesters used manual methods to find weaknesses in systems. But now, automation tools like BreachLock use AI to do these tests faster and more often. This helps companies stay ahead of attackers without breaking the bank.
Automated testing is essential for a few reasons:
- It helps companies find vulnerabilities in their systems before attackers do: Automated Pentesting tools simulate real-world attacks, helping businesses identify weak points in their defenses. By uncovering these vulnerabilities early, organizations can fix them before cybercriminals exploit them, reducing the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
- Frequent testing is crucial to keep up with new threats: The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with attackers developing new tactics and techniques. Automated Pentesting allows organizations to test their defenses regularly, ensuring they are prepared to defend against the latest threats. This proactive approach helps businesses stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and minimize the risk of successful attacks.
- It saves money compared to manual testing: Manual Pentesting and red teaming require significant time and resources, making them costly for many organizations. Automated tools streamline the testing process, reducing the need for human intervention and lowering overall costs. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can conduct more tests within their budget constraints, improving their security posture without overspending.
- It’s accessible to all sizes of businesses, not just big ones with huge budgets: In the past, red teaming and pentesting were primarily used by large organizations with dedicated cybersecurity teams and substantial budgets. However, automated Pentesting tools have democratized these practices, making them accessible to businesses of all sizes. Small and medium-sized enterprises can now leverage automated tools like BreachLock to assess their security defenses and protect against cyber threats without breaking the bank.
Automated Pentesting also brings other benefits:
- It gives a complete view of security risks: Automated Pentesting examines all aspects of an organization’s security, identifying vulnerabilities and evaluating security controls. This comprehensive assessment helps prioritize efforts to strengthen defenses and improve overall security.
- It helps manage risks from third-party vendors: By assessing vendors’ security postures, automated Pentesting ensures they meet necessary standards and compliance requirements. This reduces the risk of supply chain attacks and protects sensitive data.
- It makes meeting compliance requirements easier: Automated Pentesting enables regular security assessments to validate compliance with regulations like PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 2, and ISO 27001. This helps avoid fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage while enhancing trust with stakeholders.
Overall, automated Pentesting and red teaming are essential for all businesses to stay safe from cyber threats. By using AI-powered tools like BreachLock, companies can improve their security without breaking the bank.
Understanding Write Blockers Securing Digital Evidence
Introduction
In the world of digital forensics and data preservation, there exists a vital tool that plays a pivotal part in ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital evidence: the write blocker. Write blockers are essential devices used to prevent any data alteration on a storage device while it’s being examined or imaged. In this blog post, we will claw into the world of write blockers, exploring what they are, why they’re essential, and how they contribute to the field of digital forensics.
What Are Write Blockers?
A write blocker, also known as a write- protect device or forensic bridge, is a hardware or software tool designed to prevent any write( or modification) commands from being sent to a storage device similar to a hard drive, solid- state drive, or USB drive. Its primary purpose is to protect the original data on the storage device during forensic analysis.
Write blockers come in colourful forms, including:
Hardware Write Blockers: These are standalone devices that physically connect to the suspect storage device, intercepting and blocking any write commands. Hardware write blockers are largely dependable and trusted in digital forensics.
Software Write Blockers: Software- based write blockers are applications or drivers that run on the forensic analyst’s computer. They produce a virtual barrier between the storage device and the operating system, preventing write operations.
Why Are Write Blockers Essential?
Data Integrity: The foremost reason for using write blockers is to maintain the integrity of digital evidence. By preventing any write commands from reaching the storage device, write blockers ensure that the original data remains untouched during the examination process.
Legal Admissibility: Write blockers are pivotal for ensuring that the data acquired during a forensic investigation is permissible in court. Without write blockers, the defense could argue that the evidence may have been tampered with, making it inadmissible.
Chain of Custody: Write blockers help maintain a clear chain of custody for digital evidence. When evidence is properly handled using these tools, it becomes easier to prove that it has not been tampered with or altered during the investigation.
Compliance: In numerous cases, law enforcement agencies and organizations dealing with sensitive data are required to adhere to strict compliance standards. Write blockers help them meet these standards by ensuring data integrity and security.
How Write Blockers Work
Write blockers operate by intercepting write commands that the computer or operating system sends to the storage device. They work at the hardware or software position to prevent any data from being written to the device. Then is a introductory overview of how hardware write blockers function
Connection: The forensic analyst connects the suspect storage device to the write blocker using applicable cables and connectors.
Command Interception: When the computer or operating system attempts to write data to the storage device, the write blocker intercepts these commands.
Blocking Writes: The write blocker effectively blocks any write or modify commands while allowing read commands to pass through. As a result, the data on the storage device remains unchanged.
Data Acquisition: The forensic analyst can also use forensic software to produce a forensically sound image or copy of the data on the storage device. This image can be analyzed without threat to the original data.
Conclusion
Write blockers are necessary tools in the field of digital forensics. They serve as the first line of defense in preserving the integrity and authenticity of digital evidence. By preventing any alterations to the data, write blockers ensure that the evidence collected during an investigation stands up to legal scrutiny and maintains a solid chain of custody. In a world where digital evidence plays an increasingly significant role, write blockers are essential for safeguarding the truth and upholding the principles of justice.
Remarkable Advantages of Penetration Testing
Safeguarding Your Business: Unveiling the Remarkable Advantages of Penetration Testing
Introduction
In today’s ever-expanding threat landscape, robust cybersecurity measures have become a crucial necessity for businesses. The increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks demands proactive approaches to protect sensitive data, intellectual property, and customer trust. One of the most effective ways to identify vulnerabilities and fortify defenses is through penetration testing.
Understanding Penetration Testing
Definition and Concept
Penetration testing, often referred to as pen testing, is a systematic approach to assessing the security of an organization’s digital infrastructure. It involves simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in security controls and expose potential vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. This proactive methodology aims to prevent potential breaches and minimize the impact of successful attacks.
Types of Penetration Testing
- Focuses on assessing the security of an organization’s network infrastructure, including routers, switches, firewalls, and servers.
- Aims to identify vulnerabilities that could provide unauthorized access to critical systems or sensitive data.
2- Web Application Penetration Testing
- Concentrates on evaluating the security of web-based applications, including APIs, websites, and web services.
- Identifies vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure session management that could be exploited by attackers.
3- Wireless Network Penetration Testing
- Involves assessing the security of wireless networks, including Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, and other wireless protocols.
- Helps in identifying vulnerabilities that could lead to unauthorized access or eavesdropping.
4- Social Engineering Penetration Testing
- Focuses on exploiting human vulnerabilities by attempting to deceive employees through various techniques like phishing, pretexting, or social manipulation.
- Evaluates the effectiveness of security awareness training and identifies areas for improvement.
Benefits of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing offers several advantages for organizations:
- Identifying vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them
- Allows organizations to detect and patch vulnerabilities proactively, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Provides an opportunity to strengthen security controls, processes, and configurations.
- Assessing the effectiveness of security controls
- Enables organizations to evaluate the adequacy and efficiency of their existing security measures.
- Pinpoints areas where improvements or updates are necessary, such as firewall rules, intrusion detection systems, or access controls.
- Regulatory compliance
- Helps organizations comply with industry-specific regulations and standards, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Demonstrates the organization’s commitment to data protection and security best practices.
Preparing for a Successful Penetration Test
Establishing Objectives
Before conducting a penetration test, it is crucial to establish clear objectives:
- Defining the scope and goals of the test ensures that the testing aligns with organizational requirements.
- Determining the desired level of intrusion helps testers understand the extent to which they can exploit vulnerabilities without causing significant harm or disruptions.
Assembling the Right Team
Assembling a competent and diverse team is vital to the success of a penetration test:
- Identifying crucial team members with a wide range of expertise, including network security, web application development, and social engineering, ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Building a team with diverse skillsets provides different perspectives and enables more thorough testing in varying scenarios.
Comprehensively Scope and Coverage
Determining the scope and coverage of the penetration test involves the following considerations:
- Targeting specific systems or conducting an organization-wide test allows for a tailored approach to address specific security concerns adequately.
- Including physical security assessments ensures a holistic evaluation of an organization’s vulnerabilities, including access control systems, surveillance equipment, and physical barriers.

The Penetration Testing Process
The process of penetration testing typically involves the following phases:
Gathering Information
- Open-source intelligence gathering helps acquire publicly available information that potential attackers might exploit.
- Network scanning and identification of potential vulnerabilities involve actively searching for open ports, misconfigurations, or outdated software versions.
Vulnerability Identification and Analysis
- Active and passive vulnerability scanning includes the use of automated tools to detect vulnerabilities within an organization’s systems.
- Vulnerabilities identified are subsequently analyzed for potential exploits and to determine the potential impact of successful attacks.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities and Gaining Access
- Using a combination of manual and automated techniques, penetration testers attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities.
- By gaining access to systems or sensitive information, testers can demonstrate the potential consequences of successful attacks.
Evaluating Impact and Recommending Countermeasures
- Assessing the potential impact of successful exploits provides organizations with insights into the ramifications of successful attacks.
- Suggesting appropriate remedial actions helps organizations develop effective strategies to mitigate vulnerabilities and strengthen overall security.
Benefits of Regular Penetration Testing
Regular penetration testing offers various benefits for organizations:
- Continuous defense improvement
- Identifying emerging vulnerabilities helps organizations stay ahead of constantly evolving threat landscapes.
- Keeping pace with evolving attack techniques ensures that security measures remain up to date and effective.
- Confidence in security posture
- Demonstrating commitment to security to stakeholders, including partners, customers, and regulatory bodies.
- Enhancing customer trust and loyalty by proactively addressing security concerns and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Identifying weaknesses in incident response
- Assessing the effectiveness of incident response procedures helps organizations refine and streamline their processes.
- Strengthening incident containment and mitigation strategies minimizes the impact of successful attacks.
Creating an Organizational Culture Focused on Security
Integrating security into the organizational culture requires:
- Raising awareness among employees through training programs and regular security updates.
- Encouraging proactive security practices, such as strong password management, two-factor authentication, and regular system updates.
Conclusion
Penetration testing emerges as a vital strategy to protect businesses and their assets in today’s dynamic threat landscape. By conducting regular tests, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, optimize security controls, and foster a culture that prioritizes robust cybersecurity measures. Embracing penetration testing is a proactive step towards fortifying defenses and instilling confidence in stakeholders.
How To Secure IoT devices: A Comprehensive Guide
How To Secure IoT Devices : A Comprehensive Guide to Defend Against Cyberattacks
Introduction
The exponential growth of IoT devices has revolutionized the way we live and interact with technology. From smart homes and wearable devices to industrial systems and healthcare equipment, IoT devices have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, this rapid expansion has also brought about an increased vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Understanding IoT Devices
IoT, or the Internet of Things, refers to the network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity that enables them to collect and exchange data. These devices range from simple household appliances like smart thermostats and voice assistants to complex industrial machinery and autonomous vehicles.
IoT devices have applications in many fields, including healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing.. They enable remote monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making, leading to improved efficiencies and enhanced services. However, their interconnected nature also makes them susceptible to cybersecurity threats.
Importance of Securing IoT Devices
Cybercriminals target IoT devices for various reasons, including unauthorized access to sensitive data, conducting DDoS attacks, ransomware extortion, and even using compromised devices as gateways to infiltrate other systems. The vast amounts of valuable and personal information stored within these devices make them attractive targets for hackers.
Potential consequences of compromised IoT devices
The consequences of a successful IoT cyberattack can be severe. For individuals, it can lead to privacy breaches, financial losses, and even physical harm if critical systems like medical devices are compromised. In the case of organizations, attacks on IoT devices can result in substantial data breaches, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.

Identifying Vulnerabilities
1- Weak passwords and default settings
One common vulnerability lies in weak or default passwords and settings. Many users neglect to change default credentials, making it easier for hackers to gain unauthorized access. Strong, unique passwords, and the alteration of default settings are essential in mitigating this risk.
2- Lack of firmware updates and patches
IoT manufacturers regularly release firmware updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities. However, users often fail to install these updates, leaving their devices exposed to known security flaws. Regularly checking for and applying these updates is crucial for maintaining a secure IoT device environment.
3- Insufficient encryption protocols
Inadequate encryption protocols leave data transmitted between IoT devices and networks vulnerable to interception and decryption by attackers. Utilizing robust encryption algorithms and protocols is vital to safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring secure communication.
4- Inadequate network segmentation
Failing to segment IoT devices from other networked systems can lead to increased exposure to attacks. Separating IoT networks from critical infrastructure and implementing access controls can limit the potential impact of a compromised device and prevent lateral movement within the network.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices
1- Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment
Before implementing security measures, it is essential to conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation strategies. This assessment should consider the type of devices, their applications, and the potential impact of a cyberattack on the device, network, and user.
2- Implementing strong access controls and user authentication
Enforcing strong access controls and user authentication mechanisms adds an extra layer of security to IoT devices. Multi-factor authentication, biometric identification, and role-based access control help ensure that only authorized individuals can interact with the devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
3- Ensuring regular firmware updates and security patches
Staying up-to-date with the latest firmware updates and security patches is critical for combating evolving threats. Regularly checking for updates and ensuring their timely installation keeps IoT devices protected from known vulnerabilities and exploits.
4- Utilizing encryption and secure communication protocols
Encrypting data transmitted between IoT devices and networks makes it harder for attackers to intercept or manipulate the information. Employing robust encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), and using secure communication protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) safeguards data integrity and confidentiality.

Network Security Measures
1- Securing Wi-Fi networks
Securing the Wi-Fi network is crucial as many IoT devices rely on wireless connectivity. Enabling strong encryption, changing default SSID and password, and disabling remote management are some basic steps to enhance Wi-Fi network security.
2- Implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems
Deploying firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) protects IoT devices from unauthorized access and network-based attacks. Firewalls filter incoming and outgoing traffic, while IDS monitors network activity and alerts administrators of potential threats.
3- Creating separate IoT networks
Segmenting IoT devices into dedicated networks provides isolation from other devices and systems. Creating VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) or deploying separate SSIDs for IoT devices can prevent attackers from pivoting to more critical network resources.
Physical Security Measures
1- Limiting physical access to devices
Physical security measures must be in place to prevent unauthorized physical access to IoT devices. These include securing devices in locked cabinets, restricting physical access to critical infrastructure, and implementing surveillance systems to deter unwanted tampering.
2- Changing default credentials and enforcing strong passwords
Changing default credentials and enforcing strong passwords mitigates the risk of unauthorized access to IoT devices. Users should customize default usernames and passwords and adopt complex, unique credentials to enhance security.
Incident Response and Recovery
1- Developing an incident response plan
Preparing an incident response plan helps organizations respond effectively to IoT device security incidents. This plan should outline the steps to be taken when a cyberattack is detected, including containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis.
2- Regularly backing up IoT device configurations and data
Regularly backing up the configurations and data of IoT devices is crucial for efficient recovery in the event of a cyberattack. Reliable backups enable organizations to restore devices to a known secure state and minimize downtime and data loss.

Privacy and Data Protection
1- Understanding data collected by IoT devices
IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, often including personal and sensitive information. Understanding the nature of data collected, how it is used, and where it is stored is crucial for ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and protecting user information.
2- Complying with data protection regulations
Organizations must adhere to data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Implementing appropriate privacy policies, obtaining user consent, and securing data transmission and storage are essential aspects of compliance.
Educating Users and Raising Awareness
1- Promoting IoT security awareness
Increasing awareness about IoT security is vital for empowering users to take proactive measures. Educating users about the risks, best practices, and the importance of regular updates and strong passwords helps create a security-first mindset within the IoT community.
2- Educating users on potential risks and precautions
Users need to be informed about the potential risks associated with IoT devices and the precautions they can take to mitigate those risks. Providing user-friendly guides and conducting awareness campaigns can equip individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions regarding their device security.
Conclusion
As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, establishing unified security frameworks becomes imperative. These frameworks should provide standardized security measures, encryption protocols, and device management practices to ensure consistent and robust security across diverse IoT applications.
Safeguarding IoT devices from cyberattacks is of utmost importance in today’s interconnected world. Implementing strong access controls, regular firmware updates, encryption protocols, and physical security measures are crucial steps in defending against threats. By understanding the risks and following best practices, both individuals and organizations can contribute to the overall security of the IoT ecosystem.
8 Things to Avoid in Azure Active Directory: A Guide to Secure Your Infrastructure
Introduction:
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) offers a centralized solution for managing digital identities and simplifying IT infrastructure. However, it’s important to note that the default configuration of Azure AD includes basic features and security settings. This leaves organizations vulnerable to potential data leaks, unauthorized access, and targeted cyberattacks.
One example of such vulnerability is the default setting for Azure storage accounts, which allows access from anywhere, including the internet. This can introduce significant security risks if not properly addressed.
A critical aspect of securing Azure AD is protecting against attacks on Azure AD Connect. Cybercriminals can exploit this service, which synchronizes Azure AD with Windows AD servers, to decrypt user passwords and compromise administrator accounts. Once inside the system, attackers have the potential to access and encrypt an organization’s most sensitive data, leading to severe consequences.
Neglecting to enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) creates an opportunity for attackers to easily connect a malicious device to an organization using compromised account credentials. Implementing MFA for all users joining the Active Directory with a device is a commonly overlooked security measure.
In addition to increased security risks, a poorly configured Azure AD can also result in process bottlenecks and poor system performance. It is crucial to ensure proper configuration to maintain smooth operations and optimize efficiency.
Production Tenants Used for Tests:
Using production tenants for testing purposes is a common mistake. We recommend creating separate tenants dedicated to testing new apps and settings. By minimizing the exposure of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in these testing environments, you can mitigate potential risks.
Overpopulated Global Admins:
Assigning the Global Admin role to user accounts grants unlimited control over your Azure AD tenant and, in some cases, your on-premises AD forest. To reduce risks, consider using less privileged roles for delegation of permissions. For example, the Security Reader or Global Reader role can be sufficient for security auditors.
Not Enforcing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Failure to enforce MFA for all users joining the Active Directory with a device can lead to security breaches. Temporary MFA exclusions should not become permanent, and trusted IP address ranges should be carefully configured. Leveraging Azure AD’s Security Defaults or configuring Global Administrators for continuous MFA usage can significantly enhance security.
Overprivileged Applications:
Applications registered in Azure AD often have stronger privileges than necessary. Regularly audit registered applications and service principals to prevent privilege escalation and potential misuse by malicious actors.
Fire-and-Forget Approach to Configuration:
Azure AD is continuously evolving, introducing new security features. Ensure that these features are enabled and properly configured, treating Azure AD deployment as an ongoing process rather than a one-time operation.
Insecure Azure AD Connect Servers:
Azure AD Connect servers, responsible for synchronizing Azure AD with on-premises AD, can be targeted by hackers. Consider them as Tier 0 resources and limit administrative rights to only Domain Admins.
Lack of Monitoring:
Default user activity logs in Azure AD are stored for only 30 days. Implement custom retention policies, leverage Azure Log Analytics, Unified Audit Log, or third-party SIEM solutions to monitor user activity and detect anomalies effectively.
Default Settings:
Default settings in Azure AD may not provide the highest level of security. Review and adjust settings such as third-party application registration, passwordless authentication methods, and ADFS endpoints to align with your organizational security policies.

Conclusion:
Securing Azure Active Directory is essential to protect your infrastructure from data breaches and cyberattacks. By avoiding these eight common misconfigurations, you can significantly enhance the security posture of your Azure AD environment. Regularly assess and monitor your configuration, stay up-to-date with Azure AD’s evolving features, and adopt a proactive approach to maintain a robust security framework. Safeguard your organization’s digital identities with a well-configured Azure Active Directory.
Defending Against Infection Monkey Ransomware
Defending Against Infection Monkey Ransomware: A Cybersecurity Survival Guide
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must be proactive in safeguarding their sensitive data and infrastructure. One such threat that has become particularly prevalent is Infection Monkey Ransomware. This malicious software can infiltrate a network, encrypt vital data, and hold it hostage until a ransom is paid. To help you stay one step ahead of this menacing threat, we have compiled a comprehensive cybersecurity survival guide. By implementing these strategies, you can fortify your defenses and ensure your organization remains secure.
Understanding Infection Monkey Ransomware
Infection Monkey Ransomware, also known as Ryuk ransomware, is a sophisticated type of malware designed to exploit vulnerabilities in network security. It typically enters a system through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or compromised websites. Once inside, it employs a combination of encryption algorithms to encrypt critical files, rendering them inaccessible to users. The attackers will then demand a ransom in exchange for the decryption key, holding the victim’s data hostage.
Recognizing the Signs
To effectively defend against Infection Monkey Ransomware, it is crucial to be able to recognize the signs of a potential infection. Some indicators include:
– Unusual network behaviour, such as increased traffic or slowed performance
– Unexpected system restarts or shutdowns
– File extensions changed to unknown or encrypted formats
– Ransom notes appearing on the affected devices
Spotting these signs early on can help you take immediate action and mitigate the potential damage.
Strengthening Network Security
Preventing Infection Monkey Ransomware from infiltrating your network requires robust security measures. Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Regularly update software and operating systems to patch any known vulnerabilities.
- Utilize strong and unique passwords for all accounts, regularly changing them.
- Utilize multi-factor verification at whatever point conceivable to include an additional layer of security.
- Employ a reliable firewall and intrusion detection system to monitor network traffic and identify any suspicious activities.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address any weaknesses in your system.
- Educate employees about safe browsing practices, recognizing phishing attempts, and the importance of not clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown attachments.
Backing Up Your Data
As a proactive measure against Infection Monkey Ransomware, regularly backing up your data is essential. By maintaining secure and up-to-date backups, you can significantly reduce the impact of a potential attack. Here are some best practices for data backup:
Store backups offline or in a separate network segment to ensure they are not vulnerable to ransomware attacks.
Regularly test backups to verify their integrity and restoration capabilities.
- Implement a robust backup rotation policy, ensuring multiple versions of critical files are available.
- Consider utilizing cloud-based backup solutions for added redundancy and availability.
Incident Response Planning
Preparing for a potential Infection Monkey Ransomware attack is critical to minimizing its impact. Develop an incident response plan that includes the following:
Establish clear communication channels and points of contact during a security incident.
Define roles and responsibilities for each team member involved in the response process.
Conduct regular tabletop exercises to simulate various attack scenarios and test the effectiveness of your response plan.
- Identify trusted cybersecurity incident response partners and establish relationships in advance.
Conclusion: Staying One Step Ahead of Infection Monkey Ransomware
In the face of evolving cyber threats like Infection Monkey Ransomware, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity and stay one step ahead. By understanding the nature of this ransomware, recognizing the signs of infection, strengthening network security, regularly backing up data, and implementing a robust incident response plan, you can effectively defend against this malicious threat. Remember, staying proactive is key to ensuring your organization’s data and infrastructure remain secure in an increasingly interconnected digital world.
The Art of EDR Bypassing: Secrets to Success with Hooking and Unhooking
Introduction
In the world of cybersecurity, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) technology is used to detect and respond to cybersecurity incidents. EDR is a critical element in any organization’s cybersecurity posture as it can help detect and prevent malicious activity from occurring. However, for security researchers and hackers, EDR can pose a significant challenge. The purpose of this article is to explore the techniques, tools, and best practices for bypassing EDR using hooking and unhooking methods.
Understanding Hooking and Unhooking
Definition of Hooking and Unhooking
Hooking is a technique used to modify the behaviour of an operating system or an application by intercepting function calls or messages passed between software components. Unhooking is the process of removing the hooks inserted into the operating system or the application to restore their original behaviour.
Types of Hooks
There are two types of hooks: static and dynamic. Static hooks are defined at compile time and are part of the code itself. Dynamic hooks are inserted into the code at runtime and can be added or removed dynamically.
Difference between Static and Dynamic Hooking
Static hooking requires access to the source code, and changes made to the code need to be recompiled. Dynamic hooking, on the other hand, can be performed without access to the source code, and the hooks can be added or removed at runtime.
Hook Detection Techniques
Hook detection techniques involve monitoring the system for suspicious behavior. It can be difficult to detect hooks as they can be inserted at various points in the system without being noticed. Common techniques for detecting hooks include memory analysis and reverse engineering.
Challenges in EDR Bypassing
EDR is designed to detect malicious behaviour, including hooking. Therefore, the primary challenge in EDR bypassing is to avoid detection. EDR has sophisticated detection mechanisms that can detect the presence of hooks in the system.
Techniques for detecting hooks
Techniques for detecting hooks can include memory analysis and reverse engineering.
Why hook detection is challenging for EDR
EDR has a variety of built-in techniques to detect the presence of hooks in the system.

Anti-Hooking Techniques
Importance of anti-hooking measures
Anti-hooking measures are designed to protect applications from being modified by hooks and to prevent attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in the system.
Techniques for avoiding hooks
Techniques for avoiding hooks can include the use of code obfuscation and the implementation of anti-hooking measures.
Limitations of anti-hooking measures
While anti-hooking measures can be effective, they have limitations. Attackers can modify the system in a way that can bypass these measures, and attackers can use evasion techniques to avoid detection
Evasion Techniques
Types of Evasion Techniques
Evasion techniques involve modifying or disguising the malicious code so that it avoids detection by EDR. Common techniques for evasion include using code masking techniques, exploiting vulnerabilities in the system, and using rootkits.
Using code masking techniques to bypass hooks
Code masking techniques involve modifying the code to hide the malicious activity. Techniques for code masking can include polymorphism and metamorphism.
Importance of code obfuscation
Code obfuscation is a technique used to make the code less readable and understandable to humans but still maintain its functionality. Code obfuscation can make it more difficult for the code to be detected by EDR.
Bypassing EDR in Practice
Planning for EDR Bypassing
Effective EDR bypassing requires careful planning. It is essential to understand the system being targeted, the detection mechanisms in place, and the techniques that will be used to bypass those mechanisms.
Practical steps in bypassing EDR
Practical steps in bypassing EDR can include identifying the vulnerabilities in the system, selecting the appropriate tools, and testing the bypass techniques.
Challenges to overcome during EDR Bypassing
Challenges that must be overcome during EDR bypassing include modifying the code without being detected, evading detection by the EDR system, and covering tracks after the attack is complete.
Case Studies
Real-life examples of successful EDR Bypassing
Real-life case studies can help illustrate the effectiveness of the techniques and tools used in EDR bypassing.
Overview of EDR Bypass tools used
Tools commonly used in EDR bypassing can include Metasploit, Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, and various other open-source tools.
Lessons learned from case studies
Lessons learned from case studies can help security researchers and hackers improve their techniques for EDR bypassing.
Post Exploitation
Importance of post-exploitation actions
Post-exploitation actions involve covering tracks and maintaining access to the system. These actions are critical for maintaining long-term access to the system.
Techniques for covering tracks after bypassing EDR
Techniques for covering tracks can include deleting logs, clearing event logs, and modifying timestamps.
Limitations of post-exploitation actions
While post-exploitation actions can be effective, there are limitations. Detecting the attack is still possible, and forensic analysis can uncover evidence of the attack.
Tools and Techniques for EDR Bypassing
Overview of EDR Bypass tools
Tools commonly used in EDR bypassing can include Metasploit, Cobalt Strike, Mimikatz, and various other open-source tools.
Importance of choosing the right tool for the right job
Choosing the right tool for the right job is essential for successful EDR bypassing.
Techniques for improving the effectiveness of EDR Bypassing
Techniques for improving the effectiveness of EDR Bypassing can include using code obfuscation, evading detection, and using anti-hooking measures.
Best Practices for EDR Bypassing
Importance of following best practices
Following best practices can help ensure that EDR bypassing is done in a safe and effective way.
Frequently used best practices for EDR Bypass
Frequently used best practices include using a testing environment, minimizing the system’s exposure, and implementing anti-hooking measures.
Importance of continuous improvement
Continuously improving EDR bypassing techniques is essential as new vulnerabilities are discovered, and new detection mechanisms are developed.
Common Misconceptions about EDR Bypassing
Debunking Myths about EDR Bypassing
EDR bypassing can be shrouded in misconceptions, which can lead to ineffective techniques and unsuccessful attacks.
Common misconceptions about EDR Bypassing
Common misconceptions about EDR bypassing include that it is easy to do and that there are no consequences for unethical practices.
Explanation of the truth behind the myths
The truth is that EDR bypassing can be challenging, and there can be severe consequences if done unethically.
Ethical Considerations
Importance of Ethical considerations
Ethical considerations are critical for ensuring that EDR bypassing is done in a responsible and legal manner.
Ethics related to EDR Bypassing
Ethical considerations related to EDR bypassing include avoiding affecting innocent parties, maintaining confidentiality, and avoiding causing harm to the system.
Consequences of unethical practices
Unethical EDR bypassing practices can lead to legal consequences, loss of reputation, and damage to the security industry.

Legal Considerations
Importance of Legal Aspects
Legal considerations are important for ensuring that EDR bypassing is done within the legal framework.
Legal considerations for EDR Bypassing
Legal considerations for EDR bypassing include understanding the legal limitations, ensuring that all legal requirements are met, and avoiding causing harm to the system or others.
Consequences of violating legal framework
Violating the legal framework for EDR bypassing can lead to severe consequences, including fines, imprisonment, and damage to the security industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, EDR bypassing is a critical technique for security researchers and hackers. Successful EDR bypassing requires an understanding of hooking and unhooking, anti-hooking measures, evasion techniques, and the legal and ethical considerations of the activity. By following best practices and continuously improving techniques, security researchers and hackers can bypass EDR with confidence, at the same time, ensuring they avoid harming innocent parties or violating the law.
Honeypot in Cybersecurity
What Is a Honeypot in Cybersecurity?
Honeypots, a highly advantageous technique, empower IT teams to effectively counter and outsmart potential of Hackers. A honeypot involves simulating an IT system or software application, designed as enticing bait to lure the focus of attackers. Despite presenting itself as a genuine target, the honeypot is, in reality, counterfeit, meticulously supervised by the IT security team. Derived from the notion that this ruse acts as a “sweet” trap for attackers, the term “honeypot” harks back to the age-old adage “You catch more flies with honey than with vinegar.”
Purpose of a Honeypot in Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, honeypots serve multiple purposes:
- Distraction: Honeypots act as a strategic diversion for attackers, consuming their time and efforts that could otherwise be directed at actual targets. The attention drawn to honeypots reduces the resources attackers allocate to real attacks.
- Threat Intelligence: By duping malicious actors into engaging with honeypots, organizations gain insights into their attack techniques and tools. Monitoring attacker behavior within honeypots enhances IT teams’ comprehension of these attacks, aiding in effective defense strategies.
- Research and Training: Honeypots provide a controlled environment for IT professionals and students to conduct research and training activities. Serving as a secure arena, honeypots facilitate observation and analysis of diverse cyberattack types.
What Are the Different Types of Honeypots?
Honeypots come in various forms and sizes, tailored to the specific attack types of interest to IT teams. Here are a few essential honeypot types to familiarize yourself with:
- Email Traps: An email trap serves as a honeypot aimed at gathering spam and malicious emails. IT teams establish a fictitious, publicly accessible email address that exposes cybercriminals. Messages directed to this address can be promptly marked as potential spam or harmful content.
- Decoy Databases: Decoy databases function as honeypots that present counterfeit data to attackers, enticing and confusing them during an attack. While the contents of such a database may resemble genuine information, they are essentially useless or potentially damaging to the intruder. This diversion keeps attackers from uncovering genuine, valuable data.
- Malware Honeypots: A malware honeypot is a specialized decoy designed to ensnare malicious software by simulating a vulnerable system or network, like a web server. This honeypot intentionally incorporates security vulnerabilities that attract malware attacks. The collected malware can be analyzed by IT teams to comprehend its actions and trace its source.
- Spider Honeypots: Spider honeypots are devised for software that explores the web, often referred to as “spiders.” IT professionals create fabricated websites or pages susceptible to internet-based assaults like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). These vulnerabilities attract malevolent automated programs that scour websites for weaknesses, searching for potential targets.
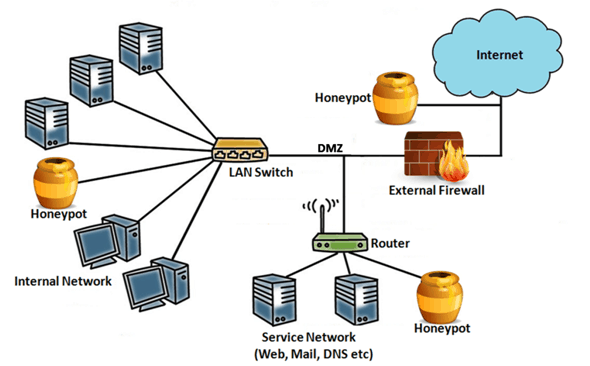
Security Interaction of Honeypots
- High-Interaction Honeypots: These honeypots replicate fully operational systems, faithfully imitating authentic IT devices or applications. As the name suggests, they allow attackers to engage with them as if they were genuine entities, affording complete privileges and access. While high-interaction honeypots yield extensive insights into attackers’ methods, they necessitate intricate setup and ongoing maintenance due to their complexity.
- Low-Interaction Honeypots: Conversely, low-interaction honeypots emulate specific segments of IT environments, implementing only select applications or services. These honeypots grant attackers a restricted array of interactions. Consequently, low-interaction honeypots are simpler to create, demand fewer resources, yet offer a reduced level of realism and information.
Physical vs. Virtual Honeypots
- Physical Honeypots: As the name implies, physical honeypots are tangible IT devices or systems linked to a network, each possessing its distinct IP address. While they offer enhanced realism, their usage is less prevalent due to the associated expenses.
- Virtual Honeypots: Conversely, virtual honeypots emulate operating systems or applications within virtual machines. This approach facilitates rapid deployment and creation of new honeypots. However, it lacks the ability to capture attacks targeting physical vulnerabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Honeypots
Advantages:
- Early Detection of Attacks: Honeypots offer the advantage of promptly identifying novel or previously undiscovered cyberattacks, enabling rapid and efficient responses from IT security teams.
- Wasted Time and Effort: Honeypots can divert attackers’ attention towards an imitation target, causing them to expend their time and efforts on a nonproductive pursuit, thereby mitigating real threats.
Disadvantages:
- Attracting Excessive Attention: The revelation that attackers have been ensnared by a honeypot might lead them to retaliate by intensifying their assaults on the organization’s legitimate systems, potentially escalating the overall risk.
- Resource-Intensive: Honeypots demand substantial resources and specialized knowledge for proper setup and maintenance, which could result in a relatively low return on investment compared to other cybersecurity measures.
Best Practices for Implementing Honeypots
Here are some best practices for implementing honeypots in cybersecurity:
- Proper Configuration and Maintenance: Ensure honeypots are configured accurately and undergo consistent maintenance to retain their allure as targets for attackers.
- Integration with Other Security Systems: Honeypots yield optimal results when seamlessly integrated into the broader spectrum of IT security tools and protocols.
- Regular Monitoring: Maintain vigilant oversight of honeypots to promptly detect any ongoing attacks, enabling timely responses from the IT security team.
Applications of Honeypots in the Real-World
Below are several real-world scenarios showcasing the application of honeypots in cybersecurity:
Government and Military: Honeypots play a pivotal role in governmental and military contexts by diverting assailants away from high-value targets. These deceptive systems safeguard critical infrastructure like power grids and communication networks.
Financial Industry: Given their prominence as prime targets, financial institutions leverage honeypots effectively. These institutions utilize honeypots to uncover fraudulent financial activities and thwart endeavors to pilfer customer data.
Intellectual Property Protection: Enterprises seeking to safeguard their intellectual property (IP) employ honeypots to confound and confine potential attackers, thereby safeguarding valuable IP assets.
Don’t forget to check out our latest Blog – Sim Box Fraud
A Brief History Of Cybercrime
A Brief History of Cybercrime: From Telegraph Hacks to Ransomware- as-a-Service
Introduction:
Over the once decade, cybercrime has evolved into a thriving industry, generating stunning gains and adopting sophisticated tactics. Still, the roots of cybercrime can be traced back not just decades, but centuries. In this blog, we embark on a fascinating trip through time to explore the history of cybercrime, from its humble onsets in the 19th century to the present day.
The Birth of Cybercrime:
The first recorded cyber attack took place in France in 1834, long before the internet was indeed conceived. Attackers sneaked the French telegraph system to steal fiscal market information, marking the dawn of cybercrime. From there, cybercriminals have continually improved their tactics to exploit technological advancements for vicious gain.
The Mid-20th Century: Cybercriminals Embrace Technology:
It was not until the mid-20th century, with the arrival of the digital revolution, that cybercrime gained traction. Beforehand adopters of technology, cybercriminals utilized their head start and intelligence to mastermind innovative methods of extracting data and money from individualities and organizations. Notable attackers emerged, capturing the attention of civil investigators and fellow hackers likewise.
1962: Allen Scherr's MIT Cyber Attack:
In 1962, Allen Scherr executed a cyber attack on the MIT computer networks, stealing passwords from their punch card database. This incident marked a significant milestone in the evolution of cybercrime, signifying the beginning of its ultramodern history.
1971: The Creeper Virus:
Bob Thomas created the first computer virus, known as the Creeper Virus, as a research trial. This self- replicating program spread through the ARPANET network, furnishing a glimpse into the implicit damage that unborn viruses could cause.
1981: Ian Murphy's AT&T Hack:
Ian Murphy became the first person condemned of cybercrime after hacking into AT&T’s internal systems and causing chaos by changing the computers’ clocks. This event highlighted the disruptive power of cyber attacks.
1988: The Morris Worm:
Robert Morris unleashed the Morris Worm, the first major cyber attack on the internet. It infected computer systems at prestigious institutions, demonstrating the vulnerability of interconnected networks.
The 1990s: New Technology Brings New Crime:
As the internet connected people worldwide, cybercrime grew in strength during the 1990s. The lack of original trust and safety controls paved the way for hackers to exploit arising technologies. This decade witnessed escalating rates of cybercrime, with attackers finding fresh openings to manipulate data and gain unauthorized access.
Notable Cyber Crimes of the 1990s:
- Data stream Cowboy and Kuji’s attacks on the Air Force’s Rome Laboratory.
- Vladimir Levin’s attempted bank robbery by hacking into Citibank’s network.
- Kevin Mitnick’s infiltration of large networks by manipulating people and insiders.
- Max Butler’s hacking of U.S. government websites and posterior lengthy sentences.
- The Melissa Virus caused wide damages of around$ 80 million.
The New Millennium: Cybercrime Ramps Up:
The first decade of the new millennium brought indeed more sophisticated cyber attacks, with advanced patient threat actors patronized by nation- states. Cybersecurity became a pressing concern, particularly for government agencies and large corporations.
Notable Cyber Crimes of the 2000s:
- ” Mafiaboy’s” distributed denial of service( DDoS) attacks on major marketable websites.
- Security breach compromising 1.4 million HSBC Bank MasterCard users.
- Heartland Payment Systems breach compromising data of 134 million users.
An Explosion of Cyber Attacks in the 2010s:
The once decade witnessed an unknown explosion of cybercrime, transforming it into a profitable industry. Trillions of dollars were lost as bushwhackers developed increasingly sophisticated programs and employed ransomware- as-a-service models, targeting organizations of all sizes.
Notable Cyber Crimes of the 2010s:
- Operation Aurora targeting technology companies and intellectual property theft.
- Sony PlayStation Network breach compromising particular information of 77 million users.
- WannaCry and NotPetya ransomware attacks causing wide disruption.
- Equifax data breach compromising particular information of 147 million people.

The Current Landscape: Challenges and the unborn:
As we enter the 2020s, cybercrime continues to evolve. bushwhackers exploit vulnerabilities in interconnected systems, compromising critical infrastructure and extorting organizations through ransomware attacks. Major incidents similar to the SolarWinds breach and the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack emphasize the ongoing threat posed by cybercriminals.
The future of cybercrime remains uncertain, but one thing is clear:
Cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement agencies must stay watchful and acclimatize to the ever- changing threat geography. Technological advancements, including machine learning and AI, are being employed by both defenders and bushwhackers, shaping the future of cyber warfare.
Conclusion:
The history of cybercrime is a confirmation to human imagination and the nonstop evolution of criminal tactics in the digital age. From early telegraph hacks to the current era of ransomware- as-a-service, cybercriminals have shown remarkable adaptability and resilience. As we move forward, it’s crucial for individualities, organizations, and governments to prioritize cybersecurity, collaborate, and develop robust defense mechanisms to safeguard against the ever-present threat of cybercrime.
Don’t forget to check out our latest Blog – Sim Box Fraud
Account Takeover Flaw In Azure AD Fixed By Microsoft
Account takeover flaw in Azure AD fixed by Microsoft
Microsoft has addressed an authentication flaw in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) that could allow threat actors to escalate privileges and potentially fully take over the target’s account. The flaw, named nOAuth by the Descope security team, involved a misconfiguration that could be abused in account and privilege escalation attacks against Azure AD OAuth applications.
The attack method relied on the vulnerable applications using the email claim from access tokens for authorization. The attacker would modify the email on their Azure AD admin account to match the victim’s email address. Then, by using the “Log in with Microsoft” feature, they could gain authorization on the targeted app or website.
The impact of this vulnerability was significant. If the targeted resources allowed the use of email addresses as unique identifiers during the authorization process, the attacker could take complete control over the victim’s account. It was even possible to exploit this flaw when the victim did not have a Microsoft account.
This flaw was possible because Azure AD did not require validation for email changes. However, Microsoft has now fixed the issue to prevent further account takeovers and protect users from this form of privilege escalation.
Descope, the security team, has highlighted that if an app merges user accounts without validation, the attacker gains full control over the victim’s account, regardless of whether the victim has a Microsoft account.
After successfully logging in, the attacker has various options depending on the app or site they have taken over. They can establish persistence, exfiltrate data, explore possibilities for lateral movement, and more.
Descope linked several large organizations, including a design app with millions of frequent users, a publicly traded client experience establishment, and a leading multi-cloud consulting provider, that were set up to be vulnerable to this attack.
Descope has also shared a video detailing the exploitation of this Azure Active Directory (AAD) authentication misconfiguration, showcasing how it can result in a complete account takeover. The video also provides information on preventive measures to mitigate this vulnerability.
On April 11, 2023, Descope reported an initial finding to Microsoft regarding the nOAuth configuration. Today, Microsoft has issued mitigations to address the issue.
Redmond confirmed that several multi-tenant applications had users utilizing email addresses with unverified domain owners. However, if developers did not receive a notification, it indicated that their application did not consume email claims with unverified domain owners.
To safeguard customers and applications vulnerable to privilege escalation, Microsoft has implemented mitigations. These mitigations involve excluding token claims from unverified domain owners for most applications.
Microsoft strongly advised developers to conduct a comprehensive assessment of their app’s authorization business logic and adhere to the provided guidelines to prevent unauthorized access.
Furthermore, developers were encouraged to adopt the recommended best practices for token validation when utilizing the Microsoft identity platform.
Disclosure Timestamps
- April 11, 2023 – Descope reported the nOAuth configuration issue to Microsoft, initiating the disclosure process.
- April 12, 2023 – Microsoft promptly opened a ticket in response to the reported issue.
- April 17-21, 2023 – Descope informed the vulnerable associations about the identified vulnerability.
- April 18, 2023 – Microsoft acknowledged the issue and committed to providing guidance to affected customers while actively working on a fix. They also updated their documentation concerning OAuth claims.
- May 2, 2023 – Descope reached out to authentication providers that were merging accounts without proper validation, alerting them to the issue.
- May 4, 2023 – Both authentication providers acknowledged the problem and verified its existence.
- May 6, 2023 – The authentication providers promptly resolved the vulnerability by implementing necessary fixes.
- June 20, 2023 – Microsoft released the fixed version, addressing the nOAuth configuration flaw. Microsoft and Descope jointly carried out a public disclosure to raise awareness about the issue and its resolution.
Don’t forget to check out our latest Blog – Sim Box Fraud
Danger of MOVEit Vulnerability Explained
Is Your Data Safe? The Danger of MOVEit Vulnerability Explained
Data security is a crucial element in today’s digital age, particularly regarding sensitive information. When it comes to secure file transfer, businesses rely on Moveit to transfer their files safely and securely. However, Moveit’s vulnerability could pose serious risks to the security of sensitive data. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of Moveit, discussing what it is, how it works, and most importantly, the vulnerability it possesses. We’ll also provide insight into identifying and assessing who is at risk of being affected by Moveit, the consequences of a potential data breach, and preventing or mitigating any damage that might ensue.
What is MOVEit and How Does it Work?
Moveit is a managed file transfer (MFT) solution used to transfer files securely from one place to another. The software is a product of Ipswitch, Inc, and its primary objective is to transfer files securely while implementing various data security measures. Moveit employs industry-standard encryption protocols to prevent unauthorized access and preserve the confidentiality of sensitive data.
The software also includes different features that make file transfer effortless. For instance, users can automate transfers, schedule transfers in advance, embed secure links, and choose between on-premises, cloud or hybrid deployment options.
The MOVEit Vulnerability
Recently, researchers discovered that Moveit was vulnerable to attacks, whereby an attacker could execute malicious code remotely. The vulnerability was first spotted by Digital Defense, a cybersecurity company. Their analysis revealed that hackers could exploit Moveit’s vulnerability to compromise an organization’s entire network.
Moveit’s vulnerability arises from a flaw in the software’s access control mechanism, which, if exploited, could enable unauthorized access to the Moveit service. The attackers could execute any malicious code of their choice and compromise the entire network.
Who is Impacted?
Impacted entities include any business or industry that utilizes Moveit to transfer their data. This includes, but is not limited to, healthcare facilities, financial institutions, government entities, and law firms. These organizations usually transfer sensitive data across networks, which makes them more vulnerable to security breaches.
The types of information transferred also play an essential role in determining the degree of impact a potential breach could cause. Sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII), proprietary intellectual property, and confidential health records, are of the utmost concern.
Impact of a Breach
In the event of a breach, the consequences could be detrimental to an organization’s bottom line or reputation. The costs of security breaches can be incredibly high, not only financially but also in terms of reputational risks.
Organizations may face regulatory penalties, costs incurred from hiring cybersecurity professionals to investigate and remediate the breach, legal fees, and potential lawsuits from affected individuals. Additionally, a data breach could result in brand damage and loss of customer trust.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Preventative Measures
The first line of defense against Moveit vulnerabilities is to implement preventative measures. Here are some best practices to implement:
Regularly patch software and update all systems: Always keep-up-to-date with the latest software patches to prevent vulnerabilities. Regular software updates ensure that all systems are operating at the highest security level possible.
Use strong passwords: Strong passwords are crucial to enhancing security. Always ensure that passwords are complex, are at least eight characters long, and have alphanumeric combinations.
Utilize two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an additional layer of security. It requires the user to provide two forms of identity verification before granting access to the service.
Implement proper access controls: Limit access to users who need it and who have passed the necessary security clearances. All access to Moveit should be kept on a “need-to-know” basis.
Detection Measures
An essential aspect of protecting data from Moveit vulnerabilities is detecting breaches. Here are some tips on how to detect a Moveit vulnerability breach:
Monitor system alerts: Be vigilant in monitoring system alerts that indicate unusual activity. This will allow you to detect a potential breach and employ remedial measures quickly.
Analyze log files: Analyze log files to identify any unusual activity within the system or network. Regular log reviews can help detect security threats before they become serious.
Investigate anomalous network traffic patterns: Increase vigilance and investigate any anomalous network traffic that might indicate an attack or a security threat.
Mitigation Strategies
In the unfortunate instance of a Moveit vulnerability breach, implementing mitigation strategies will help minimize potential impact. Here are some strategies to consider:
Immediately disconnect from the network: If possible, immediately disconnect the system or network from the internet to prevent further infection by attackers.
Implement emergency access controls: Implement emergency access controls to identify and reset all potentially malicious user passwords.
Notify cybersecurity authorities: Report the event to authorized cybersecurity authorities, such as CISA, to obtain guidance and support on remediation measures.
Recovery of affected files: Backup all data and recover all affected files from the last clean backup. It is essential to remove all traces of the attacker’s control from the system or network.
Conclusion
Moveit is a critical tool for secure file transfer, but its vulnerability can cause severe damage to an organization. By being vigilant and implementing preventative, detection, and mitigation measures, businesses and other entities can reduce the impact of any security breach. Always ensure that software is up-to-date, implement strong passwords, and provide proper access controls. Be diligent in monitoring system activity and anomalous network activity patterns. And in the case of a breach, disconnect immediately from the network, employ emergency access controls and notify the proper authorities. With these best practices in place, your organization can be better prepared to face potential security threats.
Sharp Increase In Cyberattacks In Q1 2023
Report India witnesses sharp increase in cyberattacks in Q1 2023

According to the State of Application Security Report by Indusface, India has witnessed a significant swell in the number of cyberattacks during the first quarter of 2023. Out of a billion attacks recorded overall, over 500 million cyberattacks were successfully blocked during Q1 2023.
During the first quarter of 2023, cybersecurity establishment CheckPoint Research observed a significant rise in cyberattacks in India. The data indicated that daily attacks in the country increased by 18, surpassing the global average increase of 7. On average, India encountered around 1,248 attacks per week. With a notable 16% increase, the Asia Pacific region endured the loftiest time- on- time swell in cyberattacks, comprising around 1,835 attacks per week. This statistic highlights the growing trouble geography in the region and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to cover associations from evolving cyber pitfalls. These findings punctuate the growing need for robust cybersecurity measures to combat the raising trouble geography in the region.
Indusface’s exploration revealed that the BFSI sector in India, particularly insurance, was the primary target of cyberattacks. Among Indian insurance websites, roughly 11 educated attacks, significantly advanced than the global normal of 4. Interestingly, the nature of these attacks differed from traditional distributed denial of service( DDoS) attacks or ransomware. rather, 99 of the attacks were vulnerability- grounded, with inquiry attacks exercising botnets being the most current. This emphasizes the need for enhanced security measures to alleviate the pitfalls posed by similar targeted vulnerability attacks in the BFSI sector.
A concerning fact surfaced during the period despite uncovering over 24,000 critical, medium, and high vulnerabilities, a significant 31 of these vulnerabilities had been left unaddressed for over 6 months.
According to Ashish Tandon, CEO of Indusface, it’s apparent that bushwhackers have a lesser focus on carrying tête-à-tête Identifiable Information( PII) from sectors similar to BFSI. Still, diligence like SaaS and manufacturing are primarily targeted by DDoS attacks, conceivably due to the challenge of icing operation vacuity. Tandon also emphasized that the affordability of cipher power makes launching DDoS attacks significantly easier.
According to the CheckPoint report, cybercriminals are decreasingly employing advanced tactics in their juggernauts, including the weaponization of licit tools. One notable illustration is the application of ChatGPT, an AI model, to induce vicious law for launching cyberattacks. This trend highlights the evolving nature of cyber pitfalls and the need for robust security measures to combat them.
Encyclopedically, the education and exploration sector endured the loftiest number of attacks, with over 2,500 incidents per week. Following nearly were the government and military sectors, which encountered over 1,700 attacks. Among specific diligence, retail witnessed the most significant swell in attacks, recording a 40 increase, while healthcare observed a 22 rise. These findings emphasize the different range of sectors targeted by cybercriminals and emphasize the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures across diligence.
Data perceptivity from Indusface report
- In the first three months of 2023, over 500 million attacks were successfully blocked.
- The banking and healthcare diligence endured the loftiest number of bot attacks.
- Further than 50 of the attacks targeting the banking assiduity were baffled using custom rules.
- The insurance assiduity was the primary target, facing 12 times further attacks compared to all other diligence.
- On average, the insurance assiduity encountered 995,455 attacks per point, while the normal for all diligence was 83,264 attacks per point.
Global attack trends from CheckPoint Research report
- In Q1 2023, global diurnal attacks witnessed a 7% increase compared to the same quarter last time, performing in a normal of 1,248 attacks per week for each association.
- This rise in cyberattacks highlights the growing need for robust cybersecurity measures to guard businesses from evolving pitfalls.
- In comparison to the matching period in 2022, during the first quarter of 2023, India witnessed an 18 increase in average daily attacks. Each association faced a normal of 2108 daily attacks per association, emphasizing the raising cyber trouble geography and the imperative for associations to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses.
- APAC region endured the topmost YoY swell in diurnal attacks, with an normal of 1,835 attacks per association, marking a 16 increase
- 1 out of every 31 associations worldwide endured a ransomware attack every week
Sim Box Fraud
Sim Boxing

A sim box, also known as a SIM bank or GSM gateway, is a device that can be used to bypass traditional phone networks and make cheap international calls using VoIP technology. However, sim boxing is illegal in many countries, and can result in significant financial penalties and legal consequences for those caught using them. In this blog post, we will explore sim box technology and the risks associated with it.
How does a sim box work?
Sim box works by taking advantage of the difference in cost between international calls made through traditional phone networks and VoIP technology.
A sim box has multiple SIM cards from different mobile network operators inserted into it. When a user makes an international call, the sim box selects the SIM card with the lowest international call rate and uses it to route the call through the internet to the intended destination.
To the recipient, the call appears to be coming from a local number, even though it is being routed through the sim box and the internet. This allows the sim box operator to avoid paying the high international call rates charged by traditional phone networks and instead pay the cheaper local rates for the country where the sim card is located.
In essence, a sim box acts as a bridge between traditional phone networks and VoIP technology, allowing users to make cheaper international calls. However, sim boxing is illegal in many countries because it can be used for fraudulent and criminal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and drug trafficking.
Why is sim boxing illegal?
Sim boxing is illegal in many countries because it can be used for fraudulent and criminal activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and drug trafficking. Additionally, sim boxes can cause significant revenue losses for telecommunication companies by bypassing traditional phone networks and avoiding international call rates.
What are the risks of using a sim box?
The risks of using a sim box include legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational damage. Some of the potential risks are:
Legal Consequences: Sim boxing is illegal in many countries, and those caught using a sim box can face severe legal consequences such as imprisonment, fines, and other legal sanctions. In some cases, the use of a sim box can be considered a criminal offense, and violators can be subject to criminal prosecution.
Financial Penalties: Sim boxing can result in significant financial penalties for individuals and companies caught using them. In addition to the fines imposed by regulators, violators may be required to pay compensation for the losses caused to telecom operators and other affected parties.
Reputational Damage: Companies found to be using sim boxes can suffer reputational damage and loss of business. The use of sim boxes can undermine the trust of customers, investors, and other stakeholders, leading to a loss of confidence in the company’s business practices.
Network Disruption: Sim boxes can cause network disruptions and reduce the quality of service offered by telecom operators. They can congest the network, leading to call drops, poor call quality, and other network-related issues.
Security Risks: Sim boxing can be used for criminal and fraudulent activities such as money laundering and terrorist financing. These activities can pose a security risk to individuals, companies, and national security.
How can sim boxing be detected?
Telecommunication companies use advanced technologies such as traffic analysis, call tracing, and radio frequency detection to identify sim boxing activity. They also collaborate with law enforcement agencies to monitor and investigate suspicious activity related to sim boxing.
How can companies protect themselves from sim boxing?
Companies can protect themselves from sim boxing by implementing strict internal policies and procedures, such as prohibiting the use of sim boxes and conducting regular audits to detect any unauthorized activity. They can also work with telecommunication companies to identify and report any suspicious activity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sim boxing is a risky and illegal practice that can have significant consequences for individuals and companies. It is important to understand the risks associated with sim boxes and take necessary steps to protect yourself and your business from potential legal and financial consequences.
Disposed of, not devastated:Old Network Devices Uncover Corporate Secrets
Scrapping a dead router and skimming on a shiny new update is a daily occurrence in many business networking environments. However, the fate of the waste must be as important as the replacement and use of new materials on the shelf. Unfortunately, this is not usually the case.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cyber Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cyber Security
In today’s connected world, cybersecurity has become an increasingly complex issue. As technology advances the capabilities of hackers and cybercriminals, it becomes more important than ever to protect sensitive data and systems. One of the ways businesses are tackling this challenge is to use artificial intelligence (AI) to improve their cybersecurity measures.
Artificial intelligence is used in many ways to improve cybersecurity.
Threat Detection:
One of the most promising areas of Artificial intelligence is threat detection.
Traditional cybersecurity solutions rely on predefined rules and signatures to identify threats, but these methods are becoming less effective as hackers become more sophisticated. Using machine learning algorithms, artificial intelligence can detect anomalies in network connections or user behaviour that could indicate a threat. This can help organizations detect and respond to threats faster before they cause significant damage.
Incident Response:
Another area where AI is used to improve cybersecurity is incident response. Artificial intelligence helps organizations automate incident response processes in the event of a cyberattack, allowing them to respond faster and better.
AI tools can analyze the data collected during an attack, identify the source of the attack and determine the appropriate response. This can help organizations mitigate the impact of an attack and shorten recovery time.

Access Control:
AI is also used to improve cybersecurity in the field of access. By analyzing user behaviour and patterns, AI can detect possible intrusion attempts and block them in real-time. This can help organizations prevent data breaches and protect valuable information.
However, it is important to be mindful of AI-driven cybersecurity solutions and to address the issues and concerns that come with the use of this technology. By doing this, organizations can better protect themselves and their customers against cyber threats in an ever-changing world.
The Anatomy of a Ransomware Attack
Ransomware attacks are a serious threat to data security, and can cause significant damage to organizations. They are a type of cyber attack in which an attacker gains access to a victim’s computer or network, encrypts the victim’s files or data, and then demands payment, usually in the form of cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key.
Cyber attackers that breach IT networks and databases of organisations often use ransomware, a sort of virus assault, to demand payment in exchange for access to the data they have stolen. These attacks, which first appeared as lone cyberthreat actors in the early days of the digital transformation era, have since developed into a widespread and indiscriminate Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model that may target businesses in a variety of industries.
Attacks on facilities that store vital personal data, such as hospitals and healthcare facilities, frequently involve this cyberthreat. By taking advantage of access security flaws, cybercriminals aim to make as much money as possible from their cybercrime. They do this by capitalising on the assumption that a ransomware assault may steal vast amounts of data from these firms.
The information in Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report is effective in illuminating the considerable lengths that ransomware criminals have recently gone to. The report claims that there have been 13% more ransomware assaults this year than there were last. This rise is nearly equal to the sum of the previous five years. Additionally, ransomware assaults account for around 70% of malware-related data breaches.
Ransomware Attack Stages

1. Campaign
It describes how a cyberattacker launches a ransomware campaign. These techniques include remote web server attacks, website weaponization, and malicious emails. One of the most popular techniques is the use of fraudulent emails, which has evolved into a systematic social engineering campaign. With this technique, the attacker coerces victims into unintentionally downloading dangerous software.
2. Infection
At this point, the targeted IT network begins to experience the spread of the malicious code or code block that the cyber attacker has prepared. The malware propagates throughout the IT network, but if it is discovered and the required steps are quickly followed, there may be a chance to recover the credentials.
3. Staging
By making modest adjustments to the established cyber attack vector, the attacker tries to integrate the ransomware into the system he is breaking into during the staging step. In contrast to the infection stage, the ransomware and C2 server communicate during the staging phase, protecting the encryption key.
4. Scanning
As the ransomware begins searching the IT network for files to encrypt, it starts to encrypt those files. It is crucial for the cyber attacker to succeed at this point. Because the path an attacker can travel after scanning is determined by the permission levels and allowed access definitions in your system.
5. Encryption
The process of encryption is started after the scanning is finished. Within seconds, local data on your IT network are encrypted by ransomware, which subsequently spreads to shared network files and the cloud. The network copies and encrypts data. In order to replace the original files on the network, the duplicated and encrypted data is then once more uploaded.
6. Remuneration
Once the hacker has obtained crucial data, he sends ransom notes to the accounts of network users outlining the terms of the payment. Attackers will occasionally set a timer, and the ransom will rise over time. For their victims to debate the payment arrangements, hackers would occasionally even provide a customer service number. Even if you use the payment mechanism to pay the ransom, there is no assurance that the data will be recovered.
Approach for Ransomware Attack
- Disconnect from the network: To stop ransomware from infecting more devices, disconnect from the network as soon as you think that your computer or network has been compromised.
- Determine the attack’s scope: Make an effort to ascertain the extent of the ransomware attack. What systems or files have been impacted? Is it limited to one area or widespread? This will assist you in planning your answer and comprehending the scope of the issue.
- Identify the type of ransomware: Determine the sort of ransomware you are dealing with. By doing this, you can better comprehend its possible effects and decide what course of action to take. Some ransomware can be cracked, but not all of it.
- Do not pay the ransom: Paying the ransom is not advised because there is no assurance that you will be able to access your files or that the attackers won’t demand additional payments.
- Inform Law Enforcement Agency: Make a call to your neighborhood police department to report the attack. They might be able to offer suggestions on how to handle the circumstance.
- Restore from backup: After eradicating the ransomware, if you have a backup of your data, you should restore your files from that backup.
- Seek professional help: Consider hiring a security company that specialises in ransomware recovery to help with the cleanup and recovery process if you need professional assistance.
- Educate yourself and take preventative measures: Take proactive steps to establish security measures including frequent software upgrades, strong passwords, and security software. Train yourself and your staff on how to recognise and avoid ransomware attacks in the future.
Defensive Measures Against Ransomware Attacks
1. Restrict privileged access
Based on the zero trust principle, create the privileged access mechanism. Reduce the number of members in the domain administrator group and regulate their IT network usage.
2. Protect privileged accounts
Privileged accounts are the most critical component of your protection against ransomware assaults. You can guarantee a high level of protection for privileged account credentials by utilising privileged access management (PAM) solutions with sophisticated password protection and auditing components.
3. Secure Active Directory
Delete domains with suspect security, even if companies deem them to be such. To guarantee that necessary domain actions are carried out in compliance with cyber security rules, establish a sophisticated auditing framework.
4. Eliminate lateral movement paths
By segmenting the SMB, RPC, and RDP networks, lateral movement channels can be removed.
5. Prevent phishing threats
Create a system that can identify and stop phishing emails before they reach users. Your work will be made easier if you use sophisticated email security software that can identify such emails.
6. Use patch management
Implement a patch management solution to prioritise the patches that are vulnerable to assaults on your IT network.