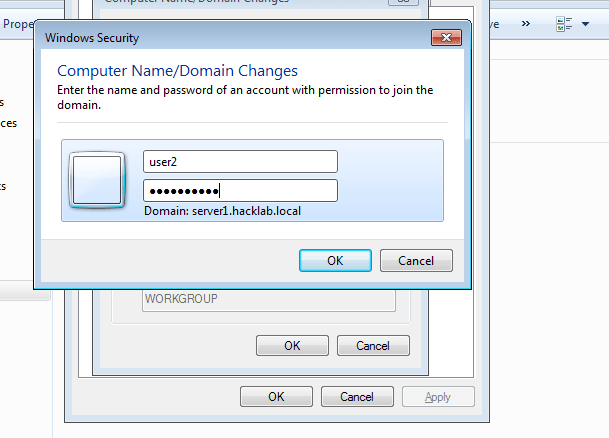
Cybersecurity has been a dynamic world ever since, and ethical hacking has always played an important role in securing digital worlds. Since cyber threats are now surging in a fast manner all over the world, mastering the right tools for the right task will enable an ethical hacker to stay afloat in his field. Therefore, the article makes the case for must-know ethical hacking tools in 2025, along with the well-covered associated services like Ethical Hacking Services in Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah, and certifications such as ISO 27001, which is a hallmark in Saudi Arabia.
1. Metasploit Framework
The Metasploit Foundation is one of the primary tools that penetration testers use even today. This open-source platform was conceived for security professionals to discover, exploit, and test systems for vulnerabilities. In fact, for businesses in Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah, Metasploit is a valuable instrument that is used by Ethical Hacking Services and penetration testing services in conducting a very thorough assessment of network security.
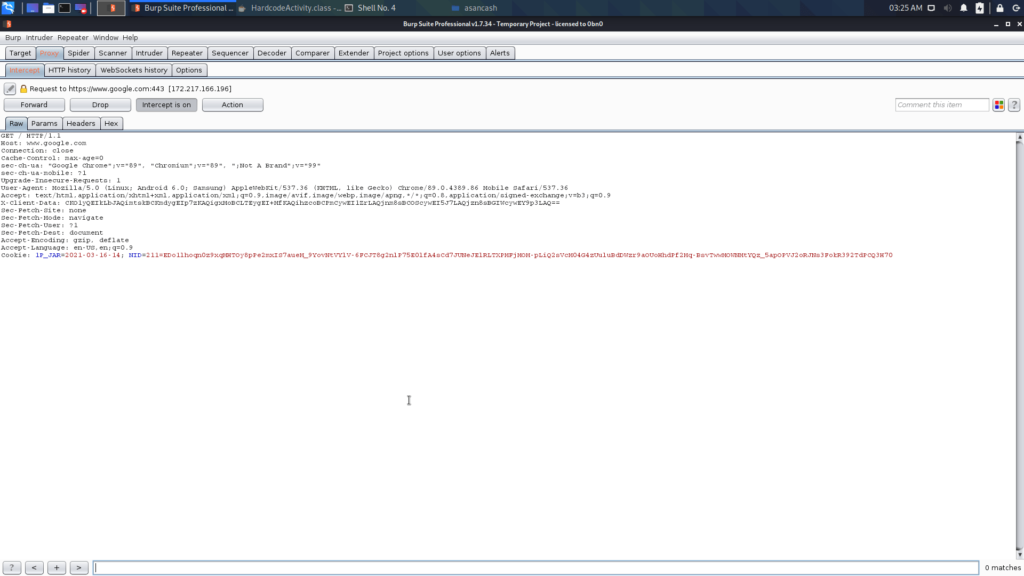
2. Burp Suite
Burp Suite has become an indispensable network application tool for performing the security over the application. Among ethical hackers and IT security professionals, Burp is in fact one of the most sought-after tools in the field of hacking because it scans and exploits the vulnerabilities found within Web applications. Web applications’ services offered in Jeddah, KSA, commonly depend on Burp Suite for the provision of strong defenses of web platforms.
3. Wireshark
Wireshark is a tremendous and high-performance network protocol analyzer used for dicing through network traffic with immense insights. Ethical hacking services in Ras Al Khaimah and Fujairah often make use of the Wireshark during an IT security audit to detect possible anomalies and expose unauthorized access.
4. Nmap (Network Mapper)
Nmap is a highly effective instrument for discovering networks and auditing their security. Identifying open ports, services, and vulnerabilities is the use of this tool. Nmap is generally used to understand the attack surface and buildings that need to be defended by penetration testing services in Ras Al Khaimah and Fujairah.
5. Nessus
Nessus is great when it comes to vulnerability assessment because it scans entirely. Most VAPT Services in Saudi Arabia and Jeddah utilize Nessus for potential threat identification and compliance with security standards like ISO 27001 Certification.
6. John the Ripper
Password security is still an important aspect of cybersecurity. John the Ripper is an open source tool which ethical hackers use in checking password strength. IT security services in Fujairah and IT security services in, are most likely to employ this tool to identify weak password practices and recommend improvements.
7. SQLmap
SQLmap can automatically detect and exploit SQL injection vulnerabilities. Ethical hacking services in Ras Al Khaimah make use of SQLmap to prevent unauthorized data extraction from databases.
8. Hydra
Hydra is a speedy and flexible login cracker for testing login security. Penetration testing services in Fujairah often use Hydra to test authentication mechanisms and develop security protocols.
9. Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a suite that amalgamates numerous tools into an all-encompassing hacking environment. Saudi Arabian courses about VAPT training incorporate Kali Linux within the scope of learning for those practicing, with emphasis on experience through actual working scenarios.
10. OWASP ZAP
OWASP ZAP is widely appreciated across all application security services across Saudi Arabia as their most favorite open-source tool for online application security, paying attention to strengthening the security posture of their clients by finding out vulnerabilities.
Regional Insights and Services
Those businesses are Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah more recently demanding Ethical Hacking Services, Penetration Testing Services, or IT Security Services to safeguard their digital assets. Provider also offer source code review services in Ras Al Khaimah to ensure that the codes of an application are free from vulnerabilities.
In Saudi Arabia, with an increasing call for VAPT Services in jeddah ksa | Application Security Services, and other regions, organizations require only practicing experts who are certified under ISO 27001 and VAPT to ensure compliance and upgrade the security infrastructure as well. A notable VAPT Services in Saudi Arabia (KSA) – Security Pact provider in Saudi Arabia, revealing the dedication to application and network security.
The Future: Keep Ahead with Effectual Ethical Hacking Tools in 2025
These tools, if mastered by ethical hackers, are a must-have in offering the best services through VAPT certification in Saudi Arabia and penetration testing in Fujairah and Ras Al Khaimah. This ensures robust security measures for businesses in regions worldwide.
The investments in such tools and ISO 27001 Certification in Saudi Arabia will strengthen ethical hackers’ positions in facing cyber challenges in the future, starting with 2025. It will either make an individual strong in cybersecurity or ensure that any business finds services from the right partners in a safe digital environment.